COMP6771 Week 5.2
Exceptions
Let's start with an example
- What does this produce?
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main() {
std::cout << "Enter -1 to quit\n";
std::vector<int> items{97, 84, 72, 65};
std::cout << "Enter an index: ";
for (int print_index; std::cin >> print_index; ) {
if (print_index == -1) break;
std::cout << items.at(print_index) << '\n';
std::cout << "Enter an index: ";
}
}Let's start with an example
- What does this produce?
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main() {
std::cout << "Enter -1 to quit\n";
std::vector<int> items{97, 84, 72, 65};
std::cout << "Enter an index: ";
for (int print_index; std::cin >> print_index; ) {
if (print_index == -1) break;
try {
std::cout << items.at(print_index) << '\n';
items.resize(items.size() + 10);
} catch (const std::out_of_range& e) {
std::cout << "Index out of bounds\n";
} catch (...) {
std::cout << "Something else happened";
}
std::cout << "Enter an index: ";
}
}Exceptions: What & Why?
-
What:
-
Exceptions: Are for exceptional circumstances
- Happen during run-time anomalies (things not going to plan A!)
-
Exception handling:
- Run-time mechanism
- C++ detects a run-time error and raises an appropriate exception
- Another unrelated part of code catches the exception, handles it, and potentially rethrows it
-
Exceptions: Are for exceptional circumstances
-
Why:
- Allows us to gracefully and programmatically deal with anomalies, as opposed to our program crashing.
What are "Exception Objects"?
- Any type we derive from std::exception
- throw std::out_of_range("Exception!");
- throw std::bad_alloc("Exception!");
- Why std::exception? Why classes?
Standard Exceptions
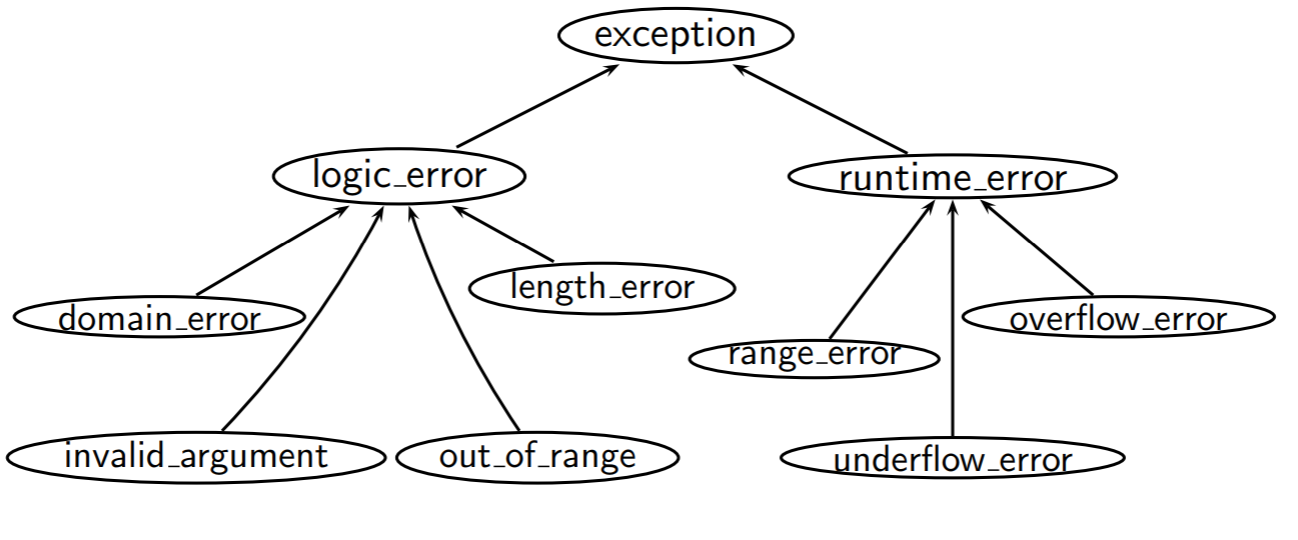
- #include <stdexcept>
- Your class can inherit from these types
Conceptual Structure
- Exceptions are treated like lvalues
- Limited type conversions exist (pay attention to them):
- nonconst to const
- other conversions we will not cover in the course
try {
// Code that may throw an exception
} catch (/* exception type */) {
// Do something with the exception
} catch (...) { // any exception
// Do something with the exception
}Multiple catch options
- This does not mean multiple catches will happen, but rather that multiple options are possible for a single catch
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main() {
std::vector<int> items;
try {
items.resize(items.max_size() + 1);
} catch (std::bad_alloc& e) {
std::cout << "Out of bounds.\n";
} catch (std::exception&) {
std::cout << "General exception.\n";
}
}Catching the right way
- Throw by value, catch by const reference
- Ways to catch exceptions:
- By value (no!)
- By pointer (no!)
- By reference (yes)
- References are preferred because:
- more efficient, less copying (exploring today)
- no slicing problem (related to polymorphism, exploring later)
(Extra reading for those interested)
- https://blog.knatten.org/2010/04/02/always-catch-exceptions-by-reference/
Catch by value is inefficient
#include <iostream>
class Giraffe {
public:
Giraffe() { std::cout << "Giraffe constructed" << '\n'; }
Giraffe(const Giraffe &g) { std::cout << "Giraffe copy-constructed" << '\n'; }
~Giraffe() { std::cout << "Giraffe destructed" << '\n'; }
};
void zebra() {
throw Giraffe{};
}
void llama() {
try {
zebra();
} catch (Giraffe g) {
std::cout << "caught in llama; rethrow" << '\n';
throw;
}
}
int main() {
try {
llama();
} catch (Giraffe g) {
std::cout << "caught in main" << '\n';
}
}Catch by value inefficiency
#include <iostream>
class Giraffe {
public:
Giraffe() { std::cout << "Giraffe constructed" << '\n'; }
Giraffe(const Giraffe &g) { std::cout << "Giraffe copy-constructed" << '\n'; }
~Giraffe() { std::cout << "Giraffe destructed" << '\n'; }
};
void zebra() {
throw Giraffe{};
}
void llama() {
try {
zebra();
} catch (const Giraffe& g) {
std::cout << "caught in llama; rethrow" << '\n';
throw;
}
}
int main() {
try {
llama();
} catch (const Giraffe& g) {
std::cout << "caught in main" << '\n';
}
}Rethrow
- When an exception is caught, by default the catch will be the only part of the code to use/action the exception
- What if other catches (lower in the precedence order) want to do something with the thrown exception?
try {
try {
try {
throw T{};
} catch (T& e1) {
std::cout << "Caught\n";
throw;
}
} catch (T& e2) {
std::cout << "Caught too!\n";
throw;
}
} catch (...) {
std::cout << "Caught too!!\n";
}(Not-advisable) Rethrow, catch by value
#include <iostream>
class Cake {
public:
Cake() : pieces_{8} {}
int getPieces() { return pieces_; }
Cake& operator--() { --pieces_; }
private:
int pieces_;
};
int main() {
try {
try {
try {
throw Cake{};
} catch (Cake& e1) {
--e1;
std::cout << "e1 Pieces: " << e1.getPieces() << " addr: " << &e1 << "\n";
throw;
}
} catch (Cake e2) {
--e2;
std::cout << "e2 Pieces: " << e2.getPieces() << " addr: " << &e2 << "\n";
throw;
}
} catch (Cake& e3) {
--e3;
std::cout << "e3 Pieces: " << e3.getPieces() << " addr: " << &e3 << "\n";
}
}Stack unwinding
- Stack unwinding is the process of exiting the stack frames until we find an exception handler for the function
- This calls any destructors on the way out
- Any resources not managed by destructors won't get freed up
- If an exception is thrown during stack unwinding, std::terminate is called
void g() {
throw std::runtime_error{""};
}
int main() {
auto ptr = new int{5};
g();
// Never executed.
delete ptr;
}void g() {
throw std::runtime_error{""};
}
int main() {
auto ptr = std::make_unique<int>(5);
g();
}Not safe
Safe
Exceptions & Destructors
- During stack unwinding, std::terminate() will be called if an exception leaves a destructor
- The resources may not be released properly if an exception leaves a destructor
- All exceptions that occur inside a destructor should be handled inside the destructor
- Destructors usually don't throw, and need to explicitly opt in to throwing
- STL types don't do that
RAII
-
Resource acquisition is initialisation
-
A concept where we encapsulate resources inside objects
- Acquire the resource in the constructor
- Release the resource in the destructor
-
eg. Memory, locks, files
-
Every resource should be owned by either:
-
Another resource (eg. smart pointer, data member)
-
The stack
-
A nameless temporary variable
-
Partial construction
- What happens if an exception is thrown halfway through a constructor?
- The C++ standard: "An object that is partially constructed or partially destroyed will have destructors executed for all of its fully constructed subobjects"
- A destructor is not called for an object that was partially constructed
- Except for an exception thrown in a constructor that delegates (why?)
#include <exception>
class MyInt {
public:
MyInt(int i) : i_{i} {
if (i == 2) throw std::exception();
}
private:
int i_;
};
class UnsafeClass {
public:
UnsafeClass(int a, int b):
a_{new MyInt{a}}, b_{new MyInt{b}} {}
~UnsafeClass() {
delete a_;
delete b_;
}
private:
MyInt* a_;
MyInt* b_;
};
int main() {
UnsafeClass a{1, 2};
}Spot the bug
Partial construction: Solution
- Option 1: Try / catch in the constructor
- Very messy, but works (if you get it right...)
- Doesn't work with initialiser lists (needs to be in the body)
- Option 2:
- An object managing a resource should initialise the resource last
- The resource is only initialised when the whole object is
- Consequence: An object can only manage one resource
- If you want to manage multiple resources, instead manage several wrappers , which each manage one resource
- An object managing a resource should initialise the resource last
#include <exception>
#include <memory>
class MyInt {
public:
MyInt(int i) : i_{i} {
if (i == 2) throw std::exception();
}
private:
int i_;
};
class UnsafeClass {
public:
UnsafeClass(int a, int b):
a_{std::make_unique<MyInt>(a)},
b_{std::make_unique<MyInt>(b)} {}
private:
std::unique_ptr<MyInt> a_;
std::unique_ptr<MyInt> b_;
};
int main() {
UnsafeClass a{1, 2};
}Exception safety levels
- This part is not specific to C++
- Operations performed have various levels of safety
- No-throw (failure transparency)
- Strong exception safety (commit-or-rollback)
- Weak exception safety (no-leak)
- No exception safety
No-throw guarantee
- Also known as failure transparency
- Operations are guaranteed to succeed, even in exceptional circumstances
- Exceptions may occur, but are handled internally
- No exceptions are visible to the client
- This is the same, for all intents and purposes, as noexcept in C++
- Examples:
- Closing a file
- Freeing memory
- Anything done in constructors or moves (usually)
- Creating a trivial object on the stack (made up of only ints)
Strong exception safety
- Also known as "commit or rollback" semantics
- Operations can fail, but failed operations are guaranteed to have no visible effects
- Probably the most common level of exception safety for types in C++
- All your copy-constructors should generally follow these semantics
- Similar for copy-assignment
- Copy-and-swap idiom (usually) follows these semantics (why?)
- Can be difficult when manually writing copy-assignment
Strong exception safety
- To achieve strong exception safety, you need to:
- First perform any operations that may throw, but don't do anything irreversible
- Then perform any operations that are irreversible, but don't throw
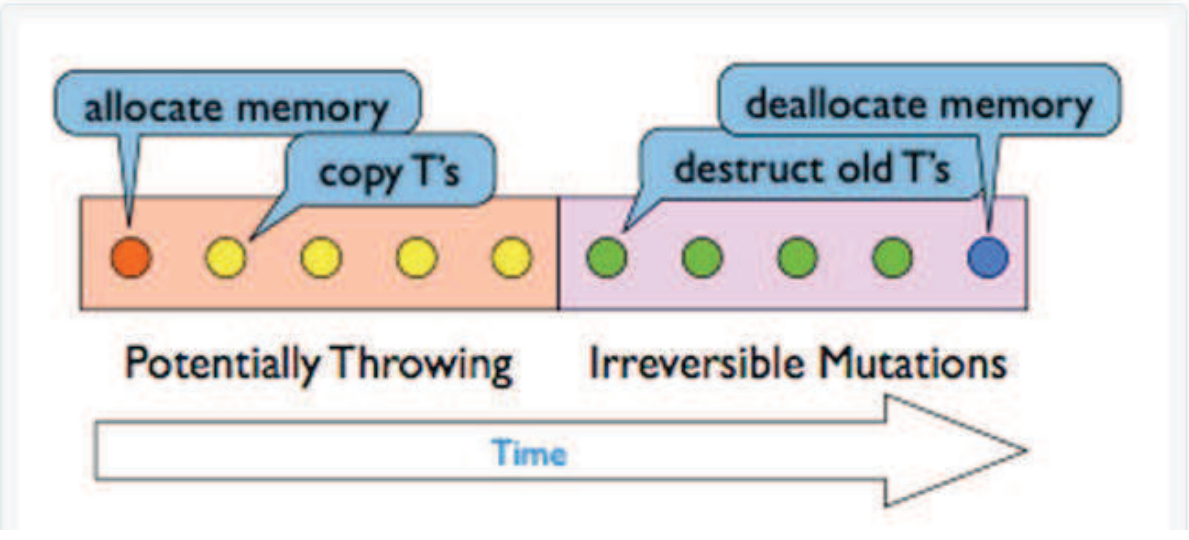
Basic exception safety
- This is known as the no-leak guarantee
- Partial execution of failed operations can cause side effects, but:
- All invariants must be preserved
- No resources are leaked
- Any stored data will contain valid values, even if it was different now from before the exception
- Does this sound familiar? A "valid, but unspecified state"
- Move constructors that are not noexcept follow these semantics
No exception safety
- No guarantees
- Don't write C++ with no exception safety
- Very hard to debug when things go wrong
- Very easy to fix - wrap your resources and attach lifetimes
- This gives you basic exception safety for free
Exception safety: example
- Consider meallocating for a std::vector<MyClass> (required upon push_back)
- Assume copy constructor for MyClass has a strong guarantee
- We can assume this because a copy-constructor takes a const ref
- Can't perform any irreversible mutations, because const
-
Let's discuss how we can provide a strong exception safety guarantee as MyClass changes
- Move constructor: no-throw or weak guarantee
noexcept specifier
- Specifies whether a function could potentially throw
- https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/language/noexcept_spec
- STL functions can operate more efficiently on noexcept functions
class S {
public:
int foo() const; // may throw
}
class S {
public:
int foo() const noexcept; // does not throw
}