ZZEN9313
Webinar 1
Data, Big and Small

ZZEN9313 20H4
Author: Hayden Smith
As we move to more structured data, it becomes easier to manipulate and work with, but often comes with a larger overhead of maintenance.
For example, JSON creates a structured standard of data storage that allows it to be used somewhat universally, however, this comes at the expense of it being very restrictive in data types being able to be used.

Unstructured
Semi-Structured
Structured
ZZEN9313 20H4
Author: Hayden Smith
Data volume
Understanding data volume helps you understand the relative size of stored data.
Data can either be:
- bits (b): Individual pieces of binary that reflect the actual underlying electronics
- bytes (B): a grouping of 8 bits that usually forms the smallest amount of addressable memory
From these we can have kilo, mega, giga, tera, peta, or even more bits or bytes.
Example: Be careful when internet companies say 10mb connections! That's only (10/8)mB!

ZZEN9313 20H4
Author: Hayden Smith
Using big data

ZZEN9313 20H4
Author: Hayden Smith
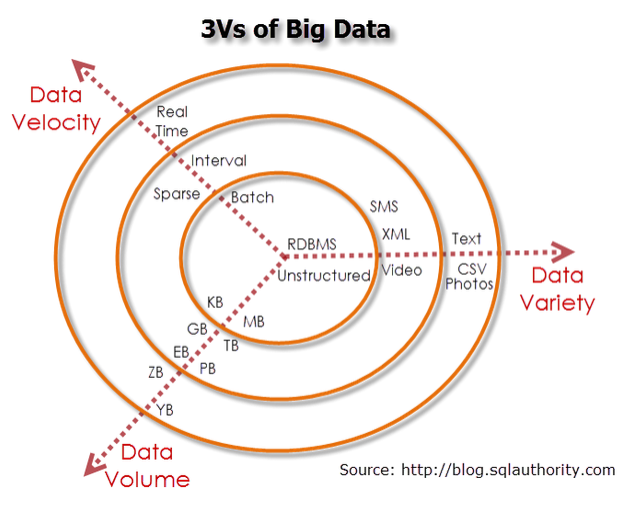
It's important we get on the same page around terminology to use with different types of data. There are 3 common dimensions of data that we can look at:
- Volume: How much space it requires
- Variety: How diverse it is
- Velocity: How quickly it accumulates or changes
Databases
Ed has some good detail around databases. In this course we explore a couple of key types of databases:
- Relational Databases
- Non-relational databases
We use relational databases for highly structured data. Operational relational databases tend to be even more structured (reducing redundant data), whereas data warehouses that use relational databases tend to be more "flat" and used for offline analytics

ZZEN9313 20H4
Author: Hayden Smith
Assessment 1
- Watch the PBS "The Human Face of Big Data" documentary
- Answer each of the 3 questions, writing between 200-1000 words
No further reading is required beyond the watching of the documentary to answer the question. If you want to include further material, you are welcome to and will not be penalised, but you are not required to.

ZZEN9313 20H4
Author: Hayden Smith