Fletcher & Adler Checksum
Group.6
Fletcher's checksum
Fletcher's checksum(introduction)
- The Fletcher checksum was devised to weight each data item according to its position
- Fletcher has many algorithms: 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit and 64-bit
-
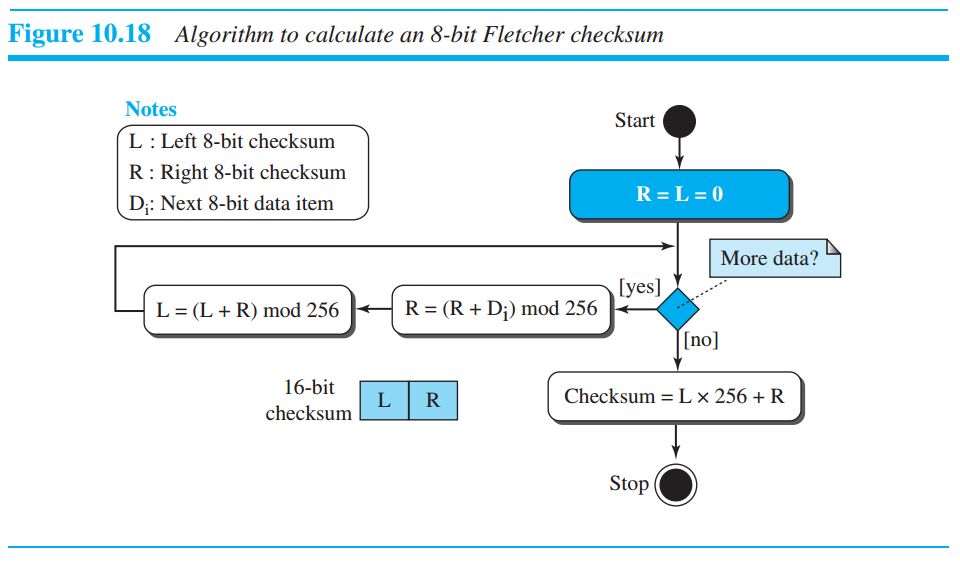
8-bit Fletcher will creates a 16-bit checksum
Fletcher's checksum( 16 bit checksum )
A = ['1','2']
L = 0
R = 0
def Fletcher(A,n):
global L,R
for i in range(n):
R = (R+int(A[i])) % 255
L = (L+R) % 255
print hex((L << 8) | R) #'<<' mean binary left shift and '|' mean binary OR
def CheckBytes(L,R):
tempR = 255 - ((R+L) % 255)
tempL = 255 - ((R+tempR) % 255)
print hex(tempR),hex(tempL)
#Checksum
Fletcher(A,len(A))
#Checkbytes
CheckBytes(L,R)
#check sum
print (L*65536)+R
Implement in python
Example calculation of the Fletcher-16 checksum :

Weaknesses
The Fletcher checksum cannot distinguish between blocks of all 0 bits and blocks of all 1 bits
For example:
0x0000 (0) have checksum as 0xff (255)
0xFFFF (65535) also have checksum as 0xff (255)
Adler's checksum
Adler's checksum(introduction)
- The Adler checksum is a 32-bit checksum
- It is similar to the 16-bit Fletcher
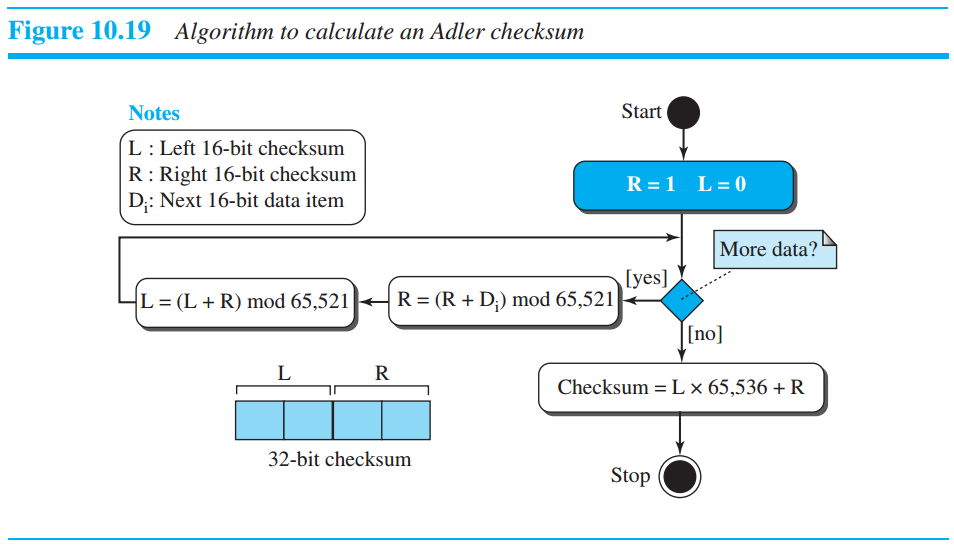
Adler's checksum( 32 bit checksum )
A = 'abcd123456' #data
L = 0
R = 1 #
def Adler(A,n):
global L,R
for i in range(n):
R = (R+ord(A[i])) % 65521 #2^16 = 65536 and 65521 is prime number that close to 2^16
L = (L+R) % 65521
Adler(A,len(A))
#check sum
print (L*65536)+R
Implement in python
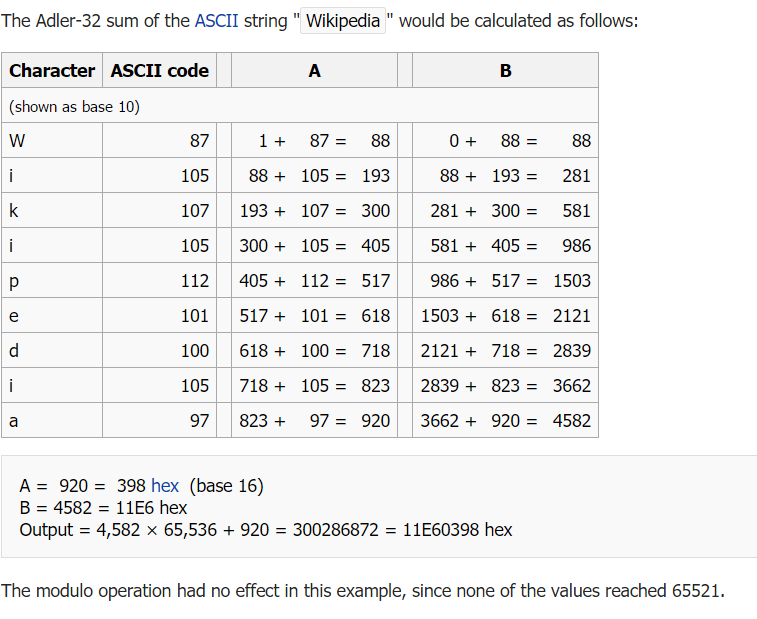
Example calculation of the Adler-32 checksum :
Weaknesses
- Adler-32 is weak for short messages because the checksums for these messages have a poor coverage of the 32 available bits
- The maximum sum of a 128-byte message is 32640, which is below the value 65521 used by the modulo operation, meaning that roughly half of the output space is unused