Life Narratives
Special examples of Life-span development
Social media across the lifespan
Pre-natal and Newborn
- De Choudhury, M., Counts, S., & Horvitz, E. (2013, April). Predicting postpartum changes in emotion and behavior via social media. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on human factors in computing systems (pp. 3267-3276). ACM.
-
De Choudhury, M., Counts, S., & Horvitz, E. (2013, February). Major life changes and behavioral markers in social media: case of childbirth. In Proceedings of the 2013 conference on Computer supported cooperative work (pp. 1431-1442). ACM.
-
Rodger, D., Skuse, A., Wilmore, M., Humphreys, S., Dalton, J., Flabouris, M., & Clifton, V. L. (2013). Pregnant women’s use of information and communications technologies to access pregnancy-related health information in South Australia. Australian journal of primary health, 19(4), 308-312.
- High use of social media can predict post-partum depression (1)
- Post-partum alters social media use-- less private engagement (2)
- “puppeteering mother"
- Information Resource (3)

Infancy
- Screen Time
- American Academy of Pediatrics: None <2yo, Less than an hour 2-5yo
- Baby Einstein
- video deficit effect (present both for TV and Apps)
- Social media as a driving force for parenting
- anti-vaccination movement
- Parent mediation through online services
- intimate surveillance concerns
- Rights of the child?


Early Childhood
Concerns for "Technologisation" of childhoods
Media literacy initiatives in response to and driving the digital divide
- Sociocultural
- solitary, stunts social development
- virtual experiences don't represent lessons for reality
- Tech companies preying on vulnerable children
- Parents preying on children (e.g. Youtube)

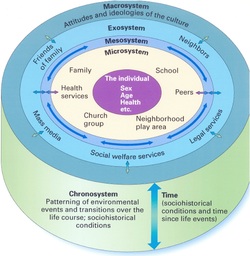
Early Childhood
- Cognitive
- Tech consumes cognitive resources better used elsewhere
- Inhibition of imagination, increase in passivity
- Linguistic development inhibited
- Wellbeing
- Indoors instead of outdoors (sedentary instead of active)
- Technology is addictive
- Unsuitable content
- Predators online
- Reduce meaningful interactions, thus less attachment and emotional development

Middle-Late Childhood
- 56% children have a SM account before age 12 (set up by parent)
- Personal usage at around age 12.6 on average (80%)
- Recommended early use to be monitored
- children are still in concrete operational phase
- still addressing Industry v. Inferiority
- Under age 13, some protection on data allowed to be collected without parental consent.
- Lying about age is legal and common

Adolescence

- "Digital natives" and trendsetters
- Counter-surveillance and parent/child conflict over SM
- Negative impacts of social media"
- cyberbullying
- imposter syndrome and relative well being
- Low self-esteem
- sexting🍑
- correlated with anxiety/depression
- Esp Facebook
- correlated with suicide attempts
- Lack of privacy protections
- permanence of digital footprint
- Corporate manipulations
Adolescence
- Benefits from Social Media
- More socialization and supportive resources
- May supplement social needs missing IRL
- Greater perspective of community/political issues
- Creative outlet
- More learning opportunities (e.g. learning communities)
- Access to taboo or embarrassing information (e.g. Puberty info)
-
Group identity v. Alienation
-
tension of "Broadcasting" and parent privacy
Emerging-Early Adulthood
- Correlated with staying in touch with family
- Face to face preferred with friends
- College transition
- Intimacy v isolation
- Social media seen as important part of dating
- Dating apps generally after college
- Privacy becomes more of a concern, esp employers
- Network expansion

Middle Adulthood
- 56% on social media
- More vocational focus
- Focus on network maintenance
- Less support-seeking
- Prefer more segmented social media presence
- eg. Facebook for family, Twitter for fun, etc
- Less enjoyment and time on social media
- Parents interested in surveillance

Late Adulthood
- Use for reflection and tracking family
- Growing adoption, but least time spent online
- Often set up by family members
- Tension between young and old
- late adults want to track and support family
- youth want to hide information from older family members

End of Life
- Digital Mourning
- Data ownership after death
- control of legacy
- The Poking Dead-- deceased will outnumber living n facebook
