Intro to Graph Databases
and Neo4j
About Me
@dabernathy89
What's a graph?
Nodes
And relationships between nodes
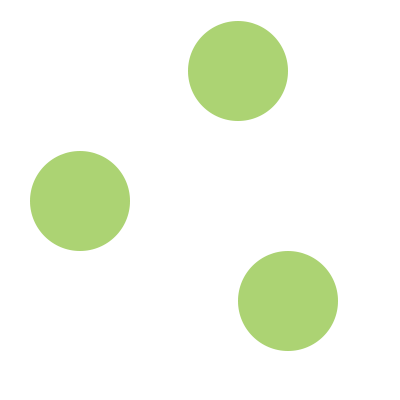
Property Graph Model
Animal
"name" : "Banana",
"color" : "orange"
Furnishing
"type" : "carpet"
Scratched
"timestamp" : 1417126199
Barfed On
"timestamp" : 1417136235
- Nodes and relationships have properties
- Relationships have names and a direction
- Any number of relationships between nodes
Querying with Cypher
Parentheses = nodes
(user)
Arrows and square brackets = relationships
-[:has]->
Together
(user)-[:has]->(role)
Querying with Cypher
Identifiers
(foo:User)-[bar:has]->()
- Used for referring to later in the query
Labels
- let you differentiate between nodes
- multiple are allowed
(creature:Dog)
Relationship types
- required, only one allowed
[:purchased]
Querying with Cypher
Properties
(user {name:"Daniel"}) -[:purchased {timestamp: 1417631772}]->
NoSQL
Graph databases are part of the NoSQL family
... but they're pretty different.
NoSQL
Aggregate-Oriented
- Key/Value
- Column Family
- Document Store
2 main categories of NoSQL databases:
Graph Databases
When people talk about NoSQL, they're usually referring to the aggregate oriented databases.
Graph vs Relational Databases
Let's build a to-do list app
- Users
- Tasks
- Users can be friends
- Users can create a task
- Users can assign tasks to friends or themselves
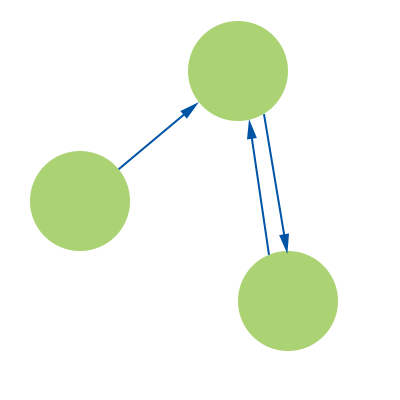
To-do List: Relational
Relationships
- Relationships between tables use joins, may require pivot table
- example - get the tasks owned by Daniel, and the users assigned to those tasks:
SELECT tasks.id, tasks.description, users.name owner, users2.name assignee
FROM tasks
JOIN users ON users.id = tasks.creator_id
JOIN users users2 ON users2.id = tasks.assignee_id
WHERE users.name = "Daniel";- “join-intensive query performance deteriorates as the dataset gets bigger” 1
1 - "Graph Databases" e-book, O'Reilly, pg 8
To-do List: Graph
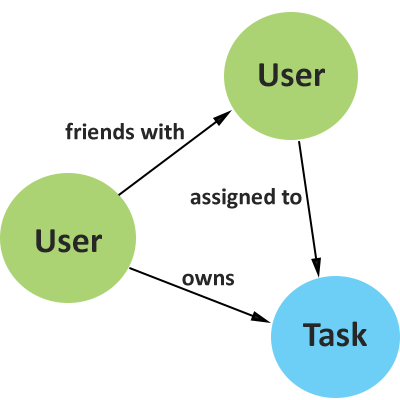
Stored the same way you might describe your data naturally
Reflects your application's domain
Relationships
- Relationships between nodes are "first class citizens"
- just as important as nodes
- Allows for "index free adjacency"
- nodes point directly to connected nodes
- Same query as before - find user's owned tasks:
MATCH (User {name:"Daniel"})-[:OWNS]->(task),
(task)<-[:IS_ASSIGNED_TO]-(assignee)
RETURN task, assigneeEven with many 'joins', query performance is only limited by the portion of the graph that is searched.
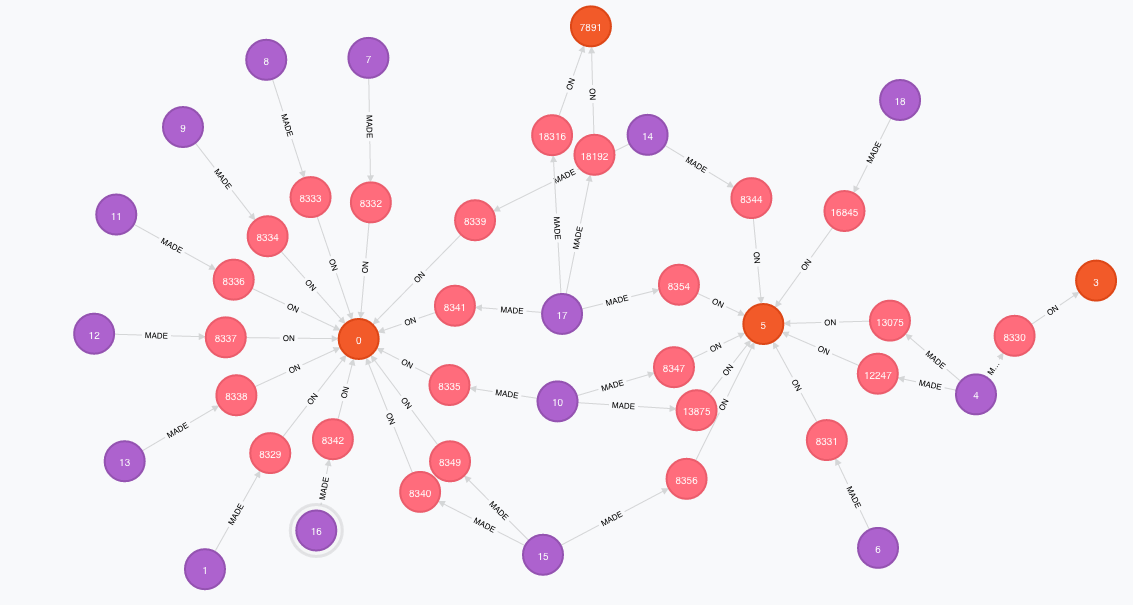
Performance
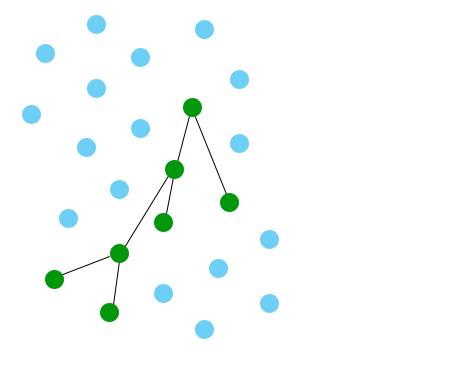
This graph search...
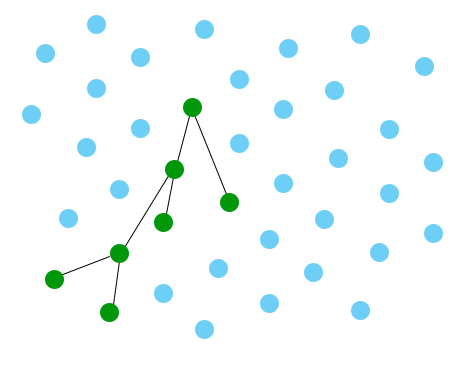
... has the same performance as this one
Graph advantages summarized:
- Graph databases are a natural representation of your data.
- Graph query languages like Cypher are extremely readable.
- Graphs make complex questions simpler to ask.
- When dealing with many relationships, performance can be improved significantly over both relational and aggregate-oriented NoSQL databases.
- They're fun, especially with visualizations.
So let's switch all our apps to graph databases!
Hold your horses.
Considerations
- Don't just use because you think it'll get you better performance
- Have you really optimized your current system?
- Getting peak performance in graph databases can also require work, such as:
- modeling your data so queries are limited in scope
- optimizing queries
- using Java-based extensions to Neo4j
- configuration for load balancing
- queue or batch writes
- Take time to investigate the use cases that graph databases excel at
PHP
- REST API wrappers
- ORM
- More at Neo4j
Resources
Videos
References / Training
Books
- "Graph Databases" - O'Reilly
- "Learning Neo4J" - Packt
PHP/Neo4j People
- Michelle Sanver
- Christophe Willemsen
- Ed Finkler