Zero to DevOps in
Under an Hour with
http://slides.com/dalealleshouse/k8/live


Agenda
-
What is Kubernetes?
-
Kubernetes Goals
-
Kubernetes Basic Architecture
-
Awesome Kubernetes Demo!
-
What Now?
What is Kubernetes?
- AKA K8S (K-8 letters-S)
- Greek for Ship's Captain (κυβερνήτης)
- Google's Open Source Container Management System
- https://github.com/kubernetes
- Lessons Learned from Borg/Omega
- K8S is speculated to replace Borg
- Released June 2014
- 1.0 Release July, 2015
- Currently in Version 1.19
- Highest Market Share
- Bundled with Docker
K8S Goals
- Container vs. VM Focus
- Portable (Run everywhere)
- General Purpose
- Any workload - Stateless, Stateful, batch, etc...
- Flexible (consume wholesale or a la carte)
- Extensible
- Automatable
- Advance the state of the art
- cloud-native and DevOps Focused
- mechanisms for slow monolith/legacy migrations
K8S Architecture

More Architecture Info
- Omega: flexible, scalable schedulers for large compute clusters
- https://research.google.com/pubs/pub41684.html
- Large-scale cluster management at Google with Borg
- https://research.google.com/pubs/pub43438.html
- Borg, Omega, and Kubernetes
- https://research.google.com/pubs/pub44843.html
- https://github.com/kubernetes/community
Demo System
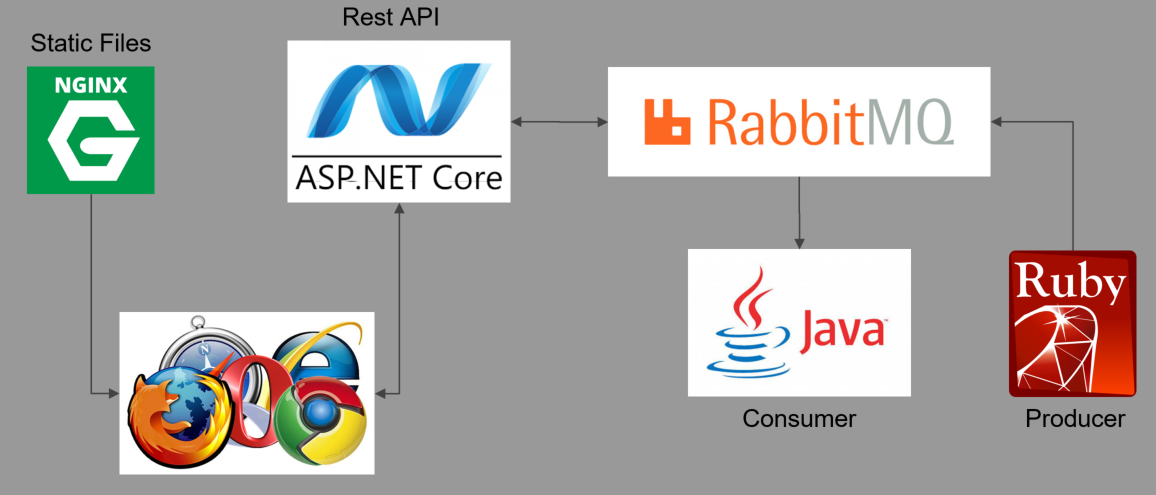
https://github.com/dalealleshouse/zero-to-devops
Setup
- Full setup instructions available in repo
- Cluster
- Docker Desktop
- DNS - Hosts File
- 127.0.0.1 demo.com
- 127.0.0.1 status.demo.com
- Docker Hub
- Images downloaded and built locally before demo
Deployments
- Deployments consist of pods and replica sets
- Pod - One or more containers in a logical group
- Replica set - controls number of pod replicas
kubectl run html-frontend --image=html-frontend:1.0 --port=80 --env STATUS_HOST=status.demo.com
kubectl run java-consumer --image=java-consumer:1.0
kubectl run ruby-producer --image=ruby-producer:1.0
kubectl run status-api --image=status-api:1.0 port=5000
kubectl run queue --image=rabbitmq:3.6.6-management# View the pods created by the deployments
kubectl get pods
# Run docker type commands on the containers
kubectl exec -it *POD_NAME* -- bash
kubectl logs *POD_NAME*# Create a deployment for each container in the demo systemServices
Services provide a durable end point
kubectl expose pod queue --port=15672,5672 --name=queueThe above only creates an internal endpoint, below creates an externally accessible endpoint
kubectl expose pod html-frontend --port=80 --name=html-frontend --type=NodePort
kubectl expose pod status-api --port=80 --target-port=5000 \
--name=status-api --type=NodePortThe website is now externally accessible at the cluster endpoint
kubectl logs java-consumerkubectl logs java-consumer -f# Notice the java-consumer cannot connect to the queue# The following command makes the queue discoverable via the name queue# Running the command again shows that it is connected now# Create an endpoint for the HTML page as the REST API ServiceInfrastructure as Code
The preferred alternative to using shell commands is storing configuration in yaml files. See the kube directory
kubectl delete -f kube/
kubectl delete pods --allkubectl create -f kube/# Delete all objects made previously
# Each object has a matching file in the kube directory# Recreate everythingDefault Monitoring
K8S has a default dashboard
kubectl proxyhttp://localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/kubernetes-dashboard/services/https:kubernetes-dashboard:/proxy/
kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard describe secret \
$(kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard get secret \
| grep admin-user | awk '{print $1}')# Get the authentication token# configuration specific - most cloud providers have something similar
# create a tunnel from the cluster to the local machineScaling
K8S will automatically load balance requests to a service between all replicas. Making subsequent requests to the html page reveals different pod names.
kubectl scale deployment html-frontend --replicas=3K8S can create replicas easy and quickly
# Scale the NGINX deployment to 3 replicasAuto-Scaling
K8S can scale based on load.
kubectl autoscale deployment java-consumer --min=1 --max=5 --cpu-percent=50# Run this repeatedly to see # of replicas created
# Also, the "In Process" number on the web page will reflect the number of replicas# Maintain between 1 and 5 replicas based on CPU usagekubectl get deploymentsSelf Healing
K8S will automatically restart any pods that die.
docker ps -f label=io.kubernetes.container.name=html-frontend# View the html-frontend pods# Containers are regenerated immediately# Forcibly shut down container to simulate a node\pod failuredocker rm -f *CONTAINER*docker ps -f label=io.kubernetes.container.name=html-frontendHealth Checks
If the endpoint check fails, K8S automatically kills the container and starts a new one
kubectl get pods...
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /healthz.html
port: 80
initialDelaySeconds: 3
periodSeconds: 2
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /healthz.html
port: 80
initialDelaySeconds: 3
periodSeconds: 2Specify health and readiness checks in yaml
# Find frontend pod# Simulate a failure by manually deleting the health check file# See the restart in the event logskubectl exec *POD_NAME* -- rm /usr/share/nginx/html/healthz.htmlkubectl get events | grep *POD_NAME*Rolling Deployment
K8S will update one pod at a time so there is no downtime for updates
kubectl set image deployment/html-frontend html-frontend=dalealleshouse/html-frontend:2.0Viewing the html page shows an error. K8S makes it easy to roll back deployments
kubectl rollout undo deployment html-frontend# Roll back the deployment to the old image# Run repeadly to see the number of available replicas# Update the deployment imagekubectl get deploymentsMore Cool Stuff
The demo covers a subset of the most notable K8S features. Some more to investigate on your own:
Helm
Secrets
Volumes
Stateful Sets
Daemon Sets
Jobs
Cron Jobs
So Much More...
What Now?
- K8S Docs
- https://kubernetes.io/docs/home/
- Free Online Course from Google
- https://www.udacity.com/course/scalable-microservices-with-kubernetes--ud615