Journal Club
9/19/18
Franklin Danger, MD
Introduction
Over utilization of Health Care Resources for Breast Pain
What drove me to review this article?
What was my clinical research question?
STORY TIME!

Introduction
What drove me to review this article?
What was my clinical research question?
Clinical question
Does breast pain, in the absence of other symptoms, merit diagnostic evaluation?
BUT
Before delving into this question, it's probably a good idea to see whether or not it's something worth investigating - marrying WHAT WE KNOW with WHAT WE DON'T.
WHAT WE KNOW
What is the prevalence of women with breast pain in the general population?
- 15%
- 25%
- 35%
- 50%
- 70%
WHAT WE KNOW
What is the prevalence of women with breast pain in the general population?
- 15%
- 25%
- 35%
- 50%
- 70%
WHAT WE KNOW
Of those 50%, how much report a decreased quality of life?
- 20%
- 40%
- 50%
- 60%
- 80%
WHAT WE KNOW
Of those 50%, how much report a decreased quality of life?
- 20%
- 40%
- 50%
- 60%
- 80%
WHAT WE KNOW
Females younger than 35 yo are at increased risk of undergoing a mammogram, but by how much?
- 2x
- 3x
- 4x
- 5x
- 10x
WHAT WE KNOW
Females younger than 35 yo are at increased risk of undergoing a mammogram, but by how much?
- 2x
- 3x
- 4x
- 5x
- 10x
WHAT WE KNOW
What is the median age for breast pain?
- 30
- 36
- 44
- 48
- 54
WHAT WE KNOW
What is the median age for breast pain?
- 30
- 36, with the pain lasting, on average, for 5 years
- 44
- 48
- 54
WHAT WE KNOW
What is the most common primary indication for breast related visits in a large HMO - as listed in the study?
- Palpable lump
- Annual screening mammogram
- Pain
WHAT WE KNOW
What is the most common primary indication for breast related visits in a large HMO - as listed in the study?
- Palpable lump
- Annual screening mammogram
- Pain - 47%
WHAT WE KNOW
- 50% of women have breast pain.
- 40% of women have breast pain that affects quality of life.
- The median age for breast pain is 36, and lasts approximately 5 years (on average).
- Breast pain is the primary indication for almost 50% of patients that presented at a large HMO.
WHAT WE DON'T
Is isolated breast pain a true sign of breast cancer?
If not, what kind of unneeded cost does this create?
WHAT WE DON'T
Is isolated breast pain a true sign of breast cancer?
If not, what kind of unneeded cost does this create?
Today's article aims to answer this.

What was the purpose of the study? /
What was their research question?
Was it well constructed? /
Did it observe the four basic components of a good, evidence based, research question?

What was the purpose of the study? /
What was their research question?
What was the purpose of the study? /
What was their research question?
Analyze the imaging findings, outcomes, and workup costs for women with breast pain - with the intent of determining whether or not it is reasonable to do so.
What was the purpose of the study? /
What was their research question?
Was it well constructed? /
Did it observe the four basic components of a good research question?
What was the purpose of the study? /
What was their research question?
Was it well constructed? /
Did it observe the four basic components of a good research question?
We can answer this by using PICO
PICO
P - ?
I - ?
C - ?
O - ?

PICO
P - Population: who was studied?
I - ?
C - ?
O - ?
PICO
P - Population
I - Intervention: what was the intervention tested?
C - ?
O - ?
PICO
P - Population
I - Intervention
C - Control: what was the alternative that the intervention was compared to?
O - ?
PICO
P - Population
I - Intervention
C - Control
O - ?
PICO
P - Population
I - Intervention
C - Control
O - Outcome: Outcome we aim to measure or achieve
PICO
P - Population
I - Intervention / Indicator
C - Control / Comparison
O - Outcome
PICO
P - Population: Female patients at 3 community imaging centers in 2014 with breast pain.
I - Intervention: Diagnostic imaging - Breast pain
C - Comparison: Screening mammograms
O - Outcome: Early detection of breast cancer
Methods
3. What study design was used for the study? What limitations are inherent in this type of study design?
Methods
3. What study design was used for the study? What limitations are inherent in this type of study design?
"We performed an institutional review board–approved, HIPAA-compliant retrospective review of the billing databases at the three largest breast imaging centers in a metropolitan, community-based, nonprofit hospital network."
Methods
3. What study design was used for the study? What limitations are inherent in this type of study design?
Methods
3. What study design was used for the study? What limitations are inherent in this type of study design?
More prone to bias, as it is not randomized.
Randomization ensures the internal validity of a study by minimizing the impact of selection and informational biases.
Methods
3. What study design was used for the study? What limitations are inherent in this type of study design?
More prone to bias, as it is not randomized.
Randomization ensures the internal validity of a study by minimizing the impact of selection and informational biases.
Methods
4. What were the inclusion criteria for the study? What were the exclusion criteria?
Methods
4. What were the inclusion criteria for the study? What were the exclusion criteria?
INCLUSION: ?
EXCLUSION: ?
Methods
4. What were the inclusion criteria for the study? What were the exclusion criteria?
INCLUSION: Female patients with breast pain.
EXCLUSION: ?
Methods
4. What were the inclusion criteria for the study? What were the exclusion criteria?
INCLUSION: Female patients with breast pain.
EXCLUSION: Patients who were male, pregnant, lactating, had a history of breast cancer, or presented with palpable nipple or skin findings were excluded.
Methods
5. What were the limitations of this study? Were these limitations adequately acknowledged and discussed?
Methods
5. What were the limitations of this study? Were these limitations adequately acknowledged and discussed?
- Same Institution.
- Limited follow-up.
- No tumor registry.
- Included all kinds of breast pain.
- All US of the breast was whole-breast.
Methods
Mammography, Ultrasound, and MRI studies were read. What kind of radiologists read them - and what was their experience?
Methods
Mammography, Ultrasound, and MRI studies were read. What kind of radiologists read them - and what was their experience?
All imaging interpretations were performed by either fellowship-trained or dedicated breast radiologists with 6–23 years of experience.
Methods
5. What was included in their retrospective chart review?
Methods
5. What was included in their retrospective chart review?
- Patient age
- Menopausal status
- Family history of breast or ovarian cancer
- Laterality, type, frequency, location of pain.
- Types of studies performed
Methods
What was used to evaluate cost?
$
Methods
What was used to evaluate cost?
Standard CPT billing codes and Centers for
Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) charge master reimbursements for Medicare were used for
the cost calculations.
Patient demographic
Total: 799
Patient Demographic
Total: 799
Age range: 13–92
Patient Demographic
Patient Demographic
Total: 799
Age range: 13–92
37% were menopausal
56% were premenopausal
7% unknown menopause status
18% of menopausal women were taking hormone replacements.
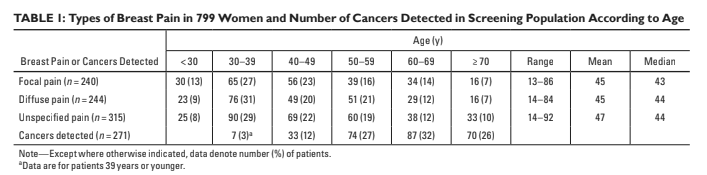
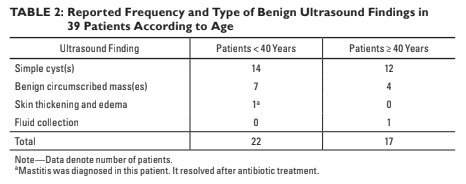
Imaging findings
85,841 total imaging examinations
13,982 diagnostic evaluation
1196 of these for breast pain (1.4%).
Breast pain leading to diagnostic evaluation
centers was 5.7% (790 of 13,892 patients).
Imaging findings
Mammograms for breast pain in 78% of patients.
94% of which were diagnostic mammograms
A mammographic finding in the area of breast pain was seen in four of 625 mammograms.
Stereotactic biopsy was performed for two pa-
tients because of incidental findings; for both
patients, the findings were benign.
Imaging findings
Imaging findings

Imaging findings

Imaging findings
Imaging findings
Imaging findings
Imaging findings

Imaging findings
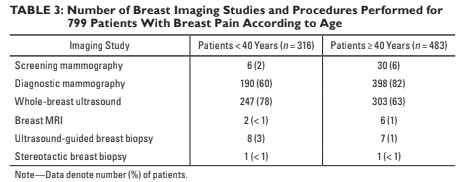
Imaging findings

Results
What is the recommended imaging follow-up for women with breast pain under 40?
Results
What is the recommended imaging follow-up for women with breast pain under 40?
Trick question! There is none.
Results
No patient younger than
40 years was found to have breast cancer at the time of the study or at follow-up.
Results
Patients > 40 years old.
80% had follow-up of 12 months or
longer, with a maximum follow-up of 43.7
months.
5.5% of patients BI-RADS category 3
Results
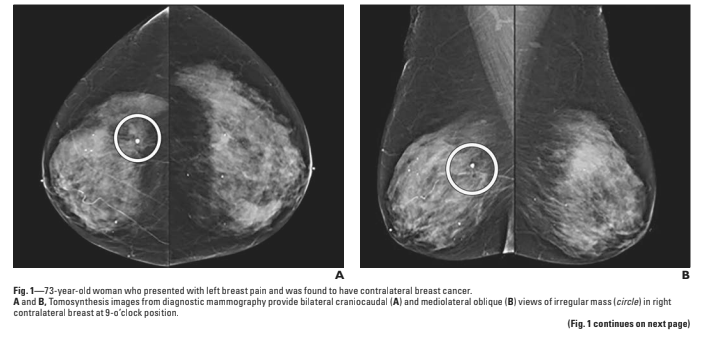
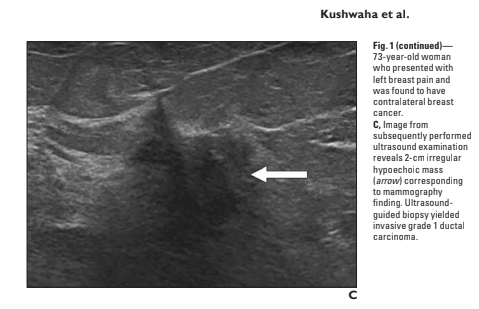
4 patients were described with breast cancer.
What did they find, and was it associated with breast pain?
Results
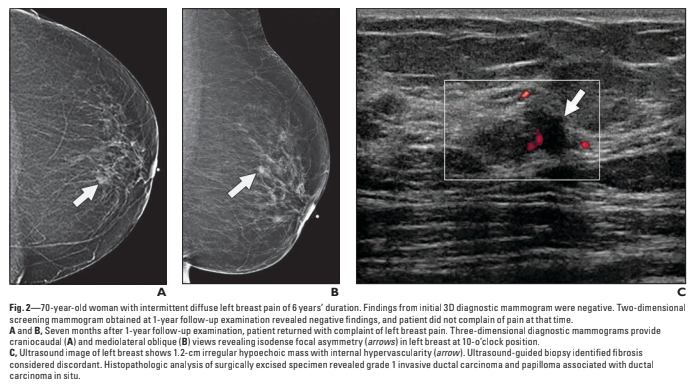
Results
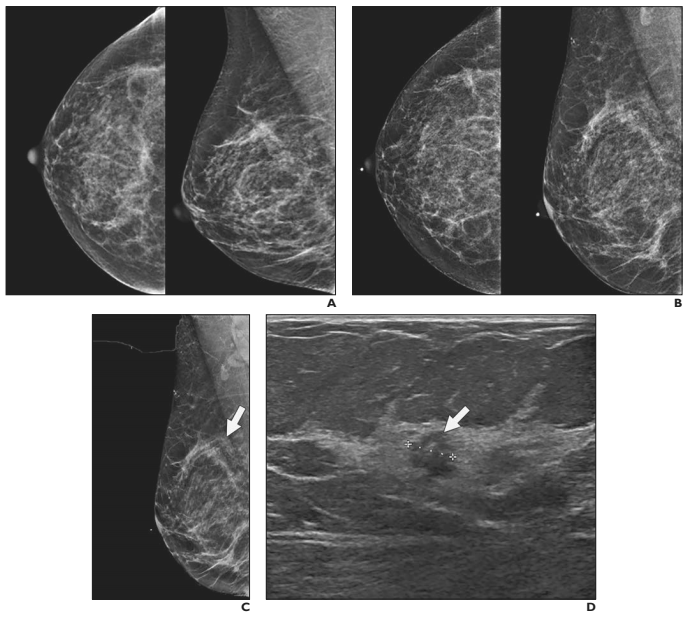
Cost estimates
< 40 years: total estimated cost of $87,322 in 1 year.
No cancers in these 316 patients.
54 additional studies led to an added cost
of $15,800.
Cost estimates
> 40 years: total estimated cost of $152,732 in 1 year.
No cancers in these 483 patients at their area of pain.
15 patients had an additional 15
ultrasound examinations, 10 diagnostic mammography studies, and one ultrasound-guided biopsy, for an additional cost of $5962.
The total estimated cost was $261,816.
Mean cost per patient workup was $328.
Results
6. Was the research question answered? Are the results internally and externally valid? If not, what affected validity?
Conclusion
7. How would you improve this study / what were potential shortcomings / how would you improve it?
Conclusion
7. How would you improve this study / what were potential shortcomings / how would you improve it?
Include more institutions.
Improve their method of follow-up.
Include tumor registry, if possible.
Only focal pain should be assessed.
Targeted ultrasound.