Franklin Danger, M.D.

Introduction to Nuclear Medicine
- General concept
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Common studies
- Cases describing various different imaging modalities - offering some things to take with you to look good on your interviews

3 Main differences
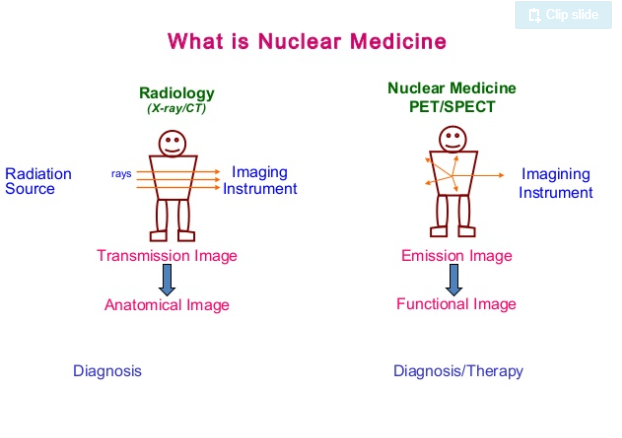
Take home point
- Radio-pharmaceutical
- Patient
- Gamma Camera
- Images
Common radionucleotides
- Tc-99m **
- I-131
- Tl-201
- Ga-67
- In-111

What you're looking for
- Available
- Low cost
- Pure gamma emitter
- Optimal gamma energy (100-200 keV) *140
- Optimal physical half life *6 hr
- Safe
- Chemically active
- Various radiopharmaceuticals
Skeletal system eg. Bone scan
Endocrinology: Thyroid scan, Parathyroid scan
Cardiovascular system: Myocardial perfusion scan, Radionuclide venography
Genitourinary system: Renogram, Testicular scan, Radionuclide cystography
Pulmonary system: Perfusion/ Ventilation lung scan
Gastrointestinal system: Liver scan, Hepatobiliary scan, GE reflux study
Tumor imaging: Ga-67 scan for Lymphoma, I-131 scan for pheochromocytoma, Tc-99m MIBI for parathyroid adenoma
SCOPE OF STUDIES
Functional
Sensitive
Quantitative
Very safe
Minimally invasive
Low radiation exposure
Screening
Follow-up
Advantages

Not widely available
Radiation (less than you'd expect)
Generally non-specific
Require NM instrument & radiopharmaceuticals
Higher cost than routine X-ray or U/S
Disadvantages

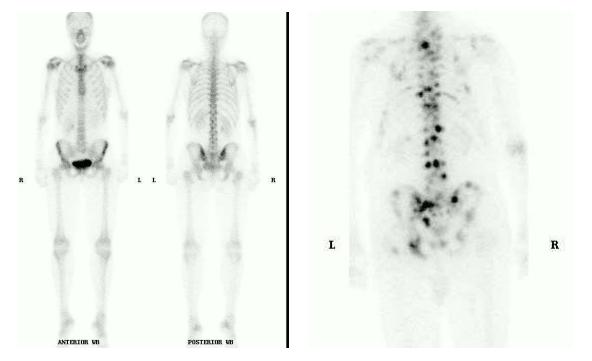
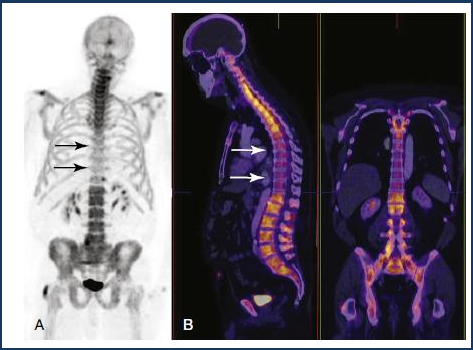
Bone scan
Principles, Indications, and Examples
Principles and indications
Detection, staging and follow-up of bone metastasis
Differentiating between osteomyelitis and cellulitis
Determination of bone viability
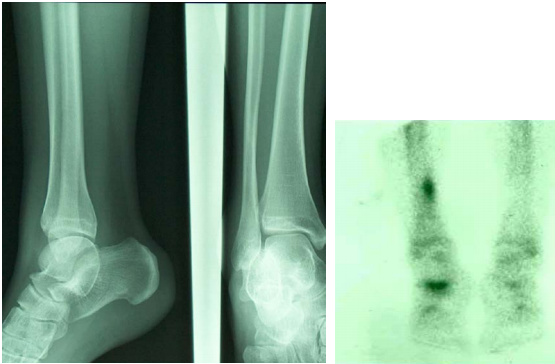
Evaluation of difficult fracture (stress fracture, fracture in battered child)
Evaluation of prosthetic joint problems (loosening, infected prosthesis)
Evaluation of bone pain in patient with normal plain radiograph (unexplained bone pain) Radiotracer: 99mTc-MDP (methylene diphosphonate)
Pathophysiology
Chemisorption to the hydroxyapatite crystal
Increased uptake
Increased blood flow
Increased osteoid formation
Increased mineralization of osteoid
Interrupted sympathetic nerve supply

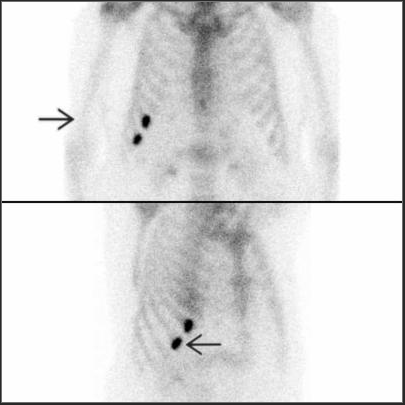



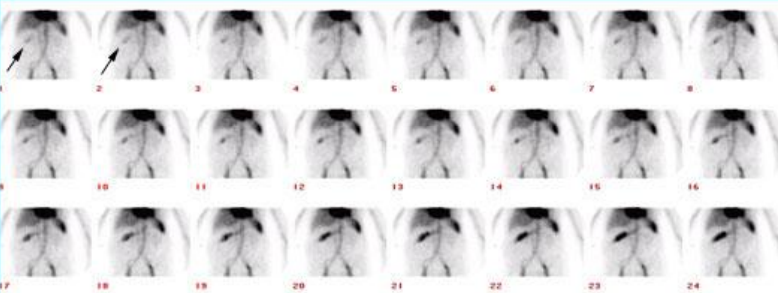
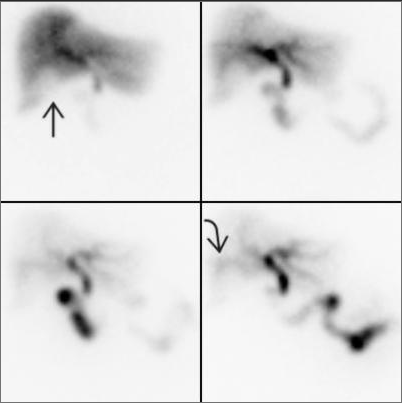
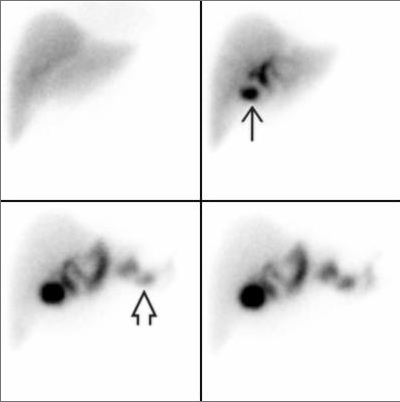
GI Bleeding Scintigraphy (Red blood cell scan)
Principles, Indication, and Examples
- Indications : To detect and localize lower GI bleeding (sensitivity 93% & specificity 95%, Laing CJ 2007)
- Radiotracer : Tc-99m labelled RBC
- Interpretation : Positive = extravasation of the radiotracer into bowel lumen
- Criteria for diagnosis of GI bleeding - Focal activity appears & conforms to bowel anatomy - Activity increases overtime - Activity movement along the bowel loop - Movement may be anterograde or retrograde

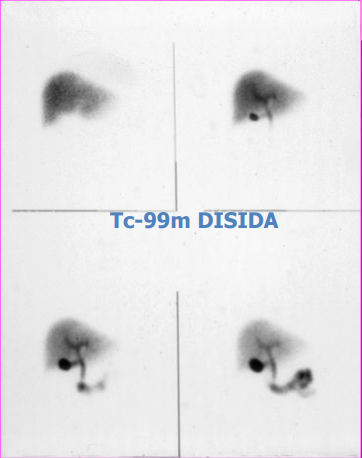
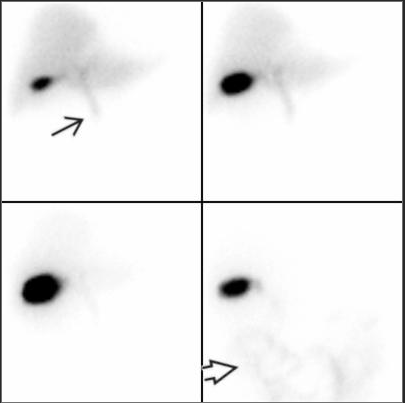
HIDA Scan
Principles, Indication, and Examples
HIDA SCAN
- Indications :
- Biliary tract obstruction
- Biliary atresia (BA)*
- Acute cholecystitis
- Choledochal cyst
- Bile leak
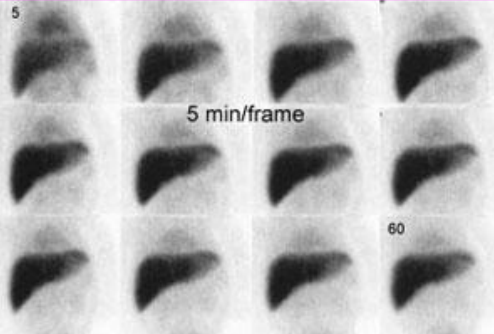
4 things we want to see in one hour
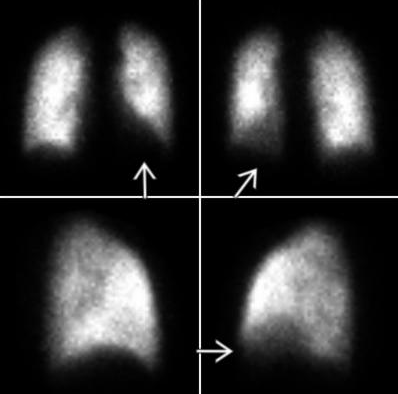
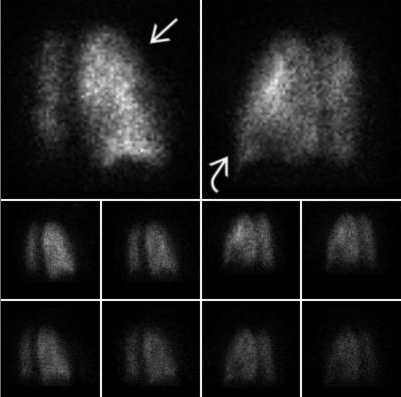
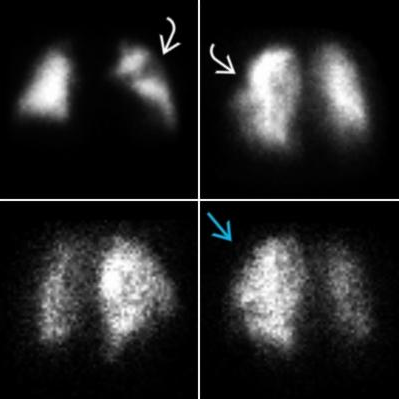
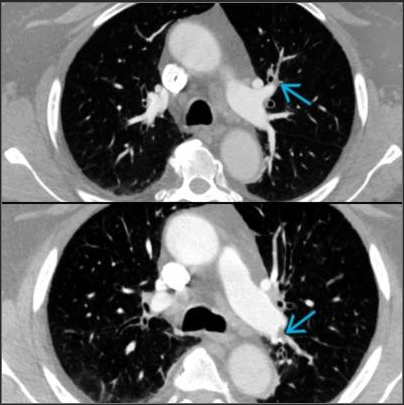
VQ Scan
Principles, Indication, and Examples
Evaluation of PE
- Ventilation: Xenon gas / DTPA
- Perfusion: 9mTc labelled microspheres or MAA
- Look for mismatched defects