Day 1 - Intro
About us
About your professor...
- Working for USJ part-time during the last 7 years
- Works for Telefónica R&D
- Previously Head of Engineering for FirefoxOS
- Currently CTO of the Data Transparency Lab (http://datatransparencylab.org/)
- Love Software Development, in particular anything related to how different aspects affect Software Quality
- Web Technologies are key to me: JavaScript, HTML, CSS...
- Privacy and Transparency advocate, especially because I believe Data is the next big thing
- On a personal part... 3 kids, love chess and music
About you?
- Programming Languages?
- Methodologies
- Tools: Trello, Bugzilla, Redmina, SVN, Git, etc...
- Anything else?
and...
WHY DO YOU THINK SOFTWARE QUALITY IS IMPORTANT TO SPEND THE NEXT 4 MONTHS TALKING ABOUT IT?
Content
Unit 1
Introduction to Software Quality
Unit 2
Software Quality Metrics
Unit 3
Software Configuration Managment
Unit 4
Testing
Unit 5
QA Activities beyond Testing
"METODOLOGÍA"
Discusiones Abiertas
PREFIERO HABLAR SOBRE LO QUE OS PREOCUPA A VOSOTROS QUE SOBRE LO QUE ME PREOCUPA A MI
Tan práctico como sea posible
PERO
TENIENDO EN CUENTA QUE ESTA ASIGNATURA TIENE ASPECTOS TEÓRICOS Y CASI FILOSÓFICOS EN ALGUNOS CASOS
ES ESENCIAL EL TRABAJO EN CASA
NO PARA MEMORIZAR SINO PARA APRENDER
(SOLO TENEMOS 4 SESIONES PRESENCIALES!)
SESIÓN 1
(4-FEB)
INTRODUCCIÓN, UNIDAD 1, TAREAS DE LA UNIDAD 1
2 SEMANAS HASTA LA SIGUIENTE SESIÓN
SESIÓN 2
(18-FEB)
DUDAS DE LO ESTUDIADO EN LA UNIDAD 1, TAREAS, ETC.
PRESENTACIÓN UNIDAD 2, UNIDAD 3 Y SUS TAREAS CORRESPONDIENTES
6 SEMANAS HASTA LA SIGUIENTE SESIÓN (EVALUACIÓN)
SESIÓN 3
(1-ABRIL)
PRUEBA DE EVALUACIÓN
SESIÓN 4
(29-ABRIL)
UNIDAD 4 - RESOLUCIÓN DE DUDAS (HABRÉIS DEBIDO TRABAJAR INDEPENDIENTEMENTE DESDE EL EXAMEN)
EJERCICIOS PRÁCTICOS
3 SEMANAS HASTA LA SIGUIENTE SESIÓN
SESIÓN 5
(27-MAYO)
UNIDAD 5
REPASO DE TODA LA MATERÍA
EJERCICIOS
2 SEMANAS HASTA LA SIGUIENTE SESIÓN (EVALUACIÓN)
SESIÓN 6
(10-JUNIO)
PRUEBA FINAL
EVALUACIÓN

Intro
AT&T Bug
"The Jan. 1990 incident showed how bugs in self-healing software can bring down healthy systems, and the difficulty of detecting obscure load- and time-dependent defects in software."
1990: A mis-placed "break" clause in the code caused 50% of the AT&T calls fail during 9 hours ($60 million)
Software Crisis
The demand of highly skilled software developers have surpassed the offer of good development resources
Complexity of problems to be solved via software have outpaced the improvements in software development
... and having good disclaimers or lawyers is not a remedy
What is Software Quality?
What is Quality?
Easy to identify intuitively but difficult to explain, define or measure
... and highly influenced by the environment

Quality of an essay?
Usually you know which one you like the most but it's difficult to explain why
Situation determines quality?
Think about having the same meal in a nice place, with nice silvers, fantastic service or having in an awful place with plastic fork, lame service...
Would you perceive the same meal quality?
Software Quality: View1
Formal Definition
Conformance to explicitly stated functional and performance requirements, explicitly documented development standards and implicit characteristics that are expected from all professionally developed software"
- Software Requirements
- Specified Development Standards
- Implicit Requirements
Can you think about examples of any of these 3 types of requirements/standards ?
- + ?
+ - ?
complexity to check conformance?
Software Quality: View2
Human point of view
Product Quality is...
Implicit requirements... there is something more beyond what is explicitly required

USERS AND THEIR EXPECTATIONS
How much it changes the world for better
or
... the value to some person
The degree it meets:
- Specified Requirements
- User needs or expectations
INFORMALLY
FORMALLY (IEEE)
Are all of you going to perceive exactly the same quality in the same product?
As engineers you should not only care about requirements.
What else you should be thinking about?
Software Quality: View3
Internal vs External Quality
Does the software do what is supposed to?
Conformance
Reliability
Accuracy
Robustness
Usability
Is the software implemented in the way it was supposed to be?
Conformance
Standards
Best Practices
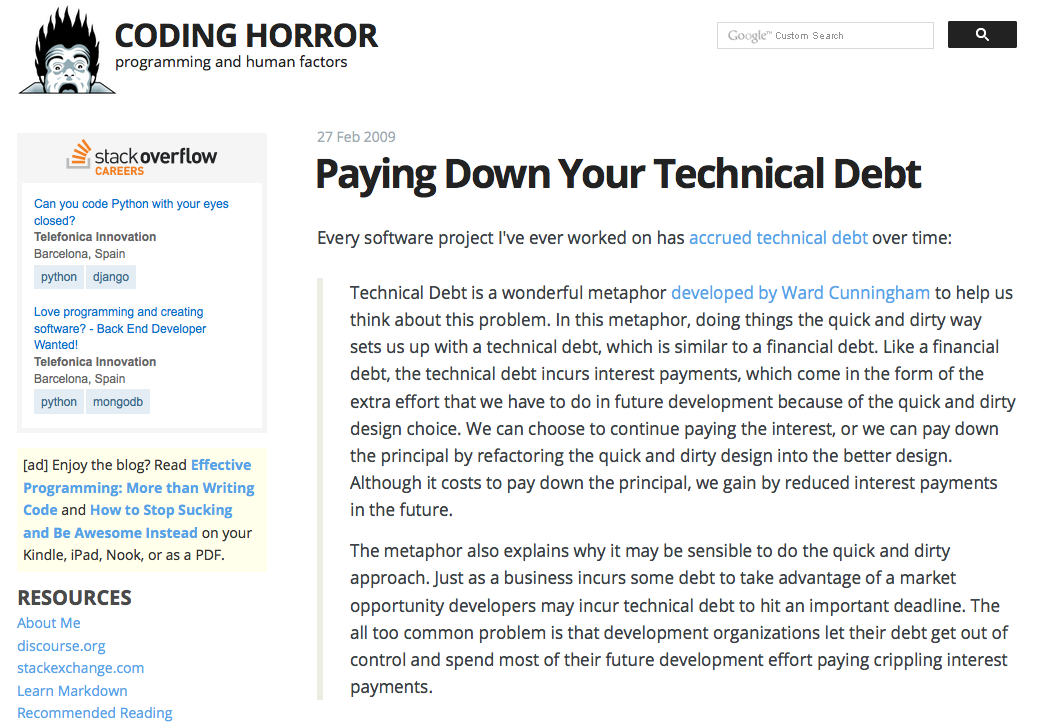
But if our target is making software for end-users, should we care about internal quality?
http://blog.codinghorror.com/paying-down-your-technical-debt/
Some properties that are linked to internal quality are:
- Concision: the code just does what is supposed to be doing
- Cohesion: each module devoted to one purpose
- Low Coupling: reduce dependencies reduce error propagation
- Simplicity: Always as simple as possible so it's less error-prone
- Generality: use general solutions vs. specific ones ease maintenance
- Clarity: so it's easy to be understood and maintained
Sometimes external problems are symptoms of internal problems. This is specially true when the software is evolving and the need to change it is affected by the poor internal quality.

Software Quality: View4
ISO 9126
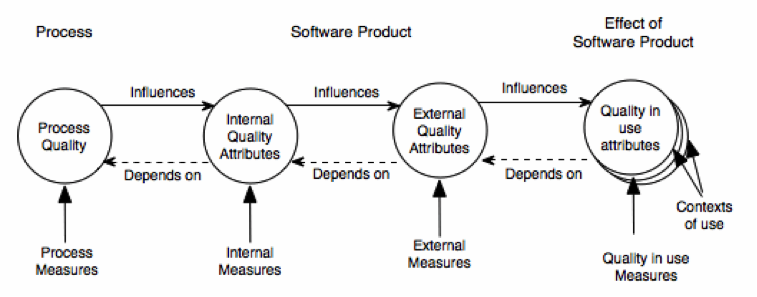
The Quality is determined by the Development Process, the Product itself and the usage of the Product
Software Quality: View4
ISO 9126

Does it work with the required performance for a period of time?
Does it work as expected?
Is it easy to use?
Does it just use the required amount of resources but no more?
Is it easy to make modifications to the software?
Can it be re-used to other environments?
Are these all characteristics equally important for any product?
Summary:
Not a single definition of quality!
Quality of a product is extremely subjective and affected by the process for implementing it.
External quality is essential, but internal quality might be even more important as it affects software in the long-term and it's more difficult to be measured
Different products have different purposes, and hence, the key aspects for determining their quality should be different
KEY DEFINITIONS
KEY CONCEPTS
- Fault / Bug / Defect: Mistake in the software. I.e. something the developer did wrong.
- Error Situation / Fault: System state in which the system was not expected to be. I.e. it occurs when a buggy code is executed.
- Failure: Any deviation of the observed behaviour from the specified behaviour. I.e. something that the end-user notices.
Peter is driving his car towards Oxford. While he is driving, the road diverts into two different directions:
1. Left road to Oxford
2. Right road to Cambridge
By mistake, Peter takes the road to Cambridge. That is a fault that is committed by Peter.
Suddenly, Peter is in an error situation or state: Peter is heading
Cambridge and not Oxford.
If Peter goes on and arrives to Cambridge, that would be a failure:
Peter was planning to get to Oxford but he has arrived to Cambridge instead.
If Peter realizes of the error situation while he is driving Cambridge, returns to the junction and takes the right road to Oxford no failure would happen as Peter recovers from the error condition.
A REAL WORLD EXAMPLE
public static int numZero (int[] x) {
// effects: if x == null throw NullPointerException
// else return the number of occurrences of 0 in x
int count = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < x.length; i ++) {
if (x[i] == 0) {
count ++;
}
}
return count;
}
A SOFTWARE EXAMPLE
Is there any bug?
In which circumstances will there be a failure?
Bugs
Faults
Failures
Source Code
Internal Exec Status
External Exec Status
The developer committed a mistake
... that led to a wrong situation
... which impacted the end-users
CAUSE - EFFECT
Some Examples
Therac-25
Therac-25 was a linear accelerator used in hospitals during the 80s to treat cancers. The machine had two possible configurations:
-
Mode A: Radiate high energy on cells with cáncer without damaging the cells sourrounding them. There was no need to protect the patient in this mode. -
Mode B: Radiate X-rays with megavolts power that required filters and special protection to the patients.
People who operated the machine acquired great experience managing the machine and entering the command sequence to start the treatment, which they did very fast.
However, due to a programming bug, if during the process they made a sequence of operations in less than 8 seconds, the machine could use the wrong mode due to a race-condition. Because of this bug 5 people died and tens of them suffered the consequences of being exposed to a high radiation because treatment B was applied instead of mode A.
-
Think about the concepts of Bug, Error Situation and Failure in this example. -
Think about some measurements that allow containing the bug in a way that the bug did not lead to a failure or at least the failure consequences were minimized.
Zune Player
SOFTWARE QUALITY ASSURANCE
SQA TARGET
Improve Software Quality
What? Reducing two things:
#1 - Number of defects
#2 - defects' impact to users
How?
It depends! an answer typical from Spotify :-) way of working
Bugs
Faults
Failures
HOW?
Devs
What can we do to reduce #defects and their impact?
Prevent
Remove
Contain
Prevent
Actions intended to minimize the number of defects that are injected in the software by developers
Can you think about ways to prevent defects?
Remove
Actions intended to remove defects once they have been injected
Can you think about ways to remove defects?
Contain
Actions intended to avoid or minimise any impact defects have on end-users
Can you think about ways to contain defects?
Bugs
Faults
Failures
Devs
Defect Prevention
Fault Tolerance
Defect Removal
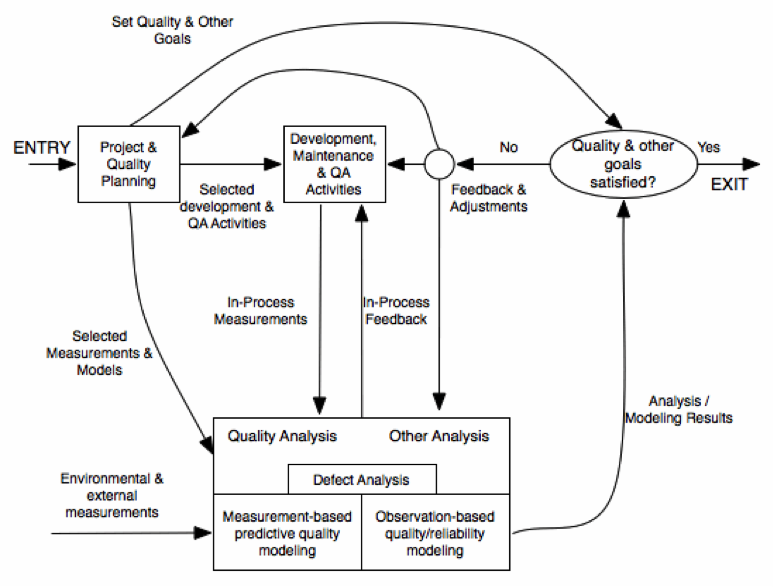
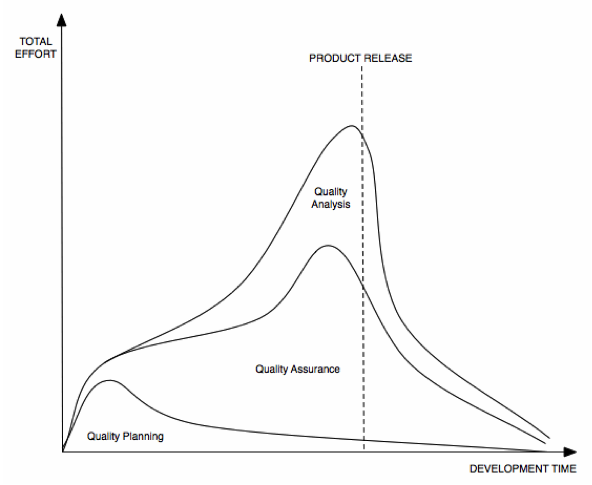
SOFTWARE QUALITY ENGINEERING
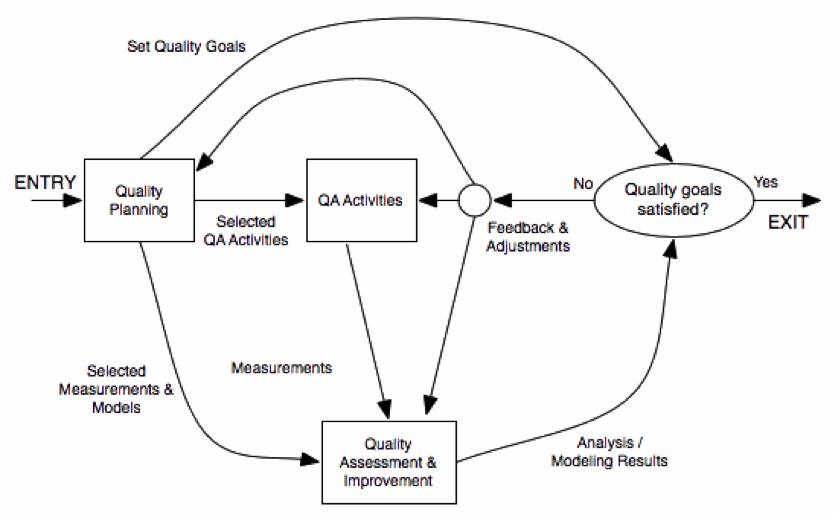
QUALITY IMPROVEMENT PROCESS
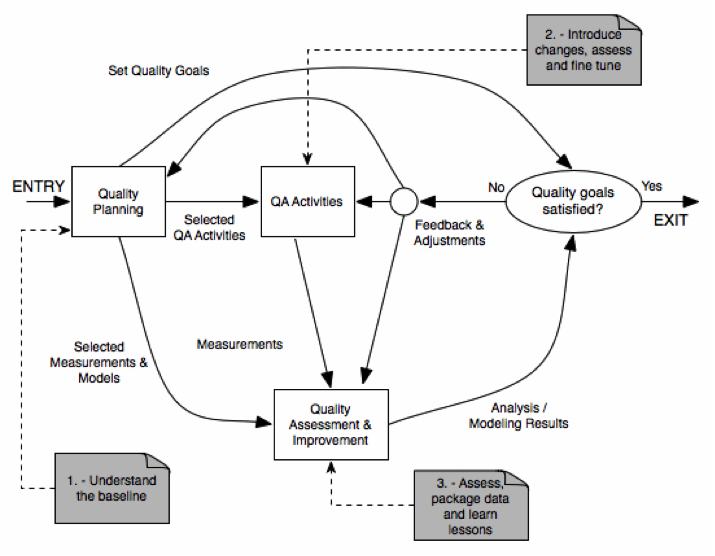
SOFTWARE QUALITY AND SOFTWARE ENGINEERING