Clustering Analysis in Soccer teams by playing style
Daniel Diaz
Alejandro Suarez
Introduction
Clustering is the task of arrangement a set of objects so that objects in the identical group are more related to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). The clustering is unsupervised learning.

Problem Statement
- How to apply cluster techniques and data normalization in a real dataset. (The ultimate Soccer database)
- it's possible group the data in by playing style.
- Find a good technique to reduce the dimensionality of a data set.
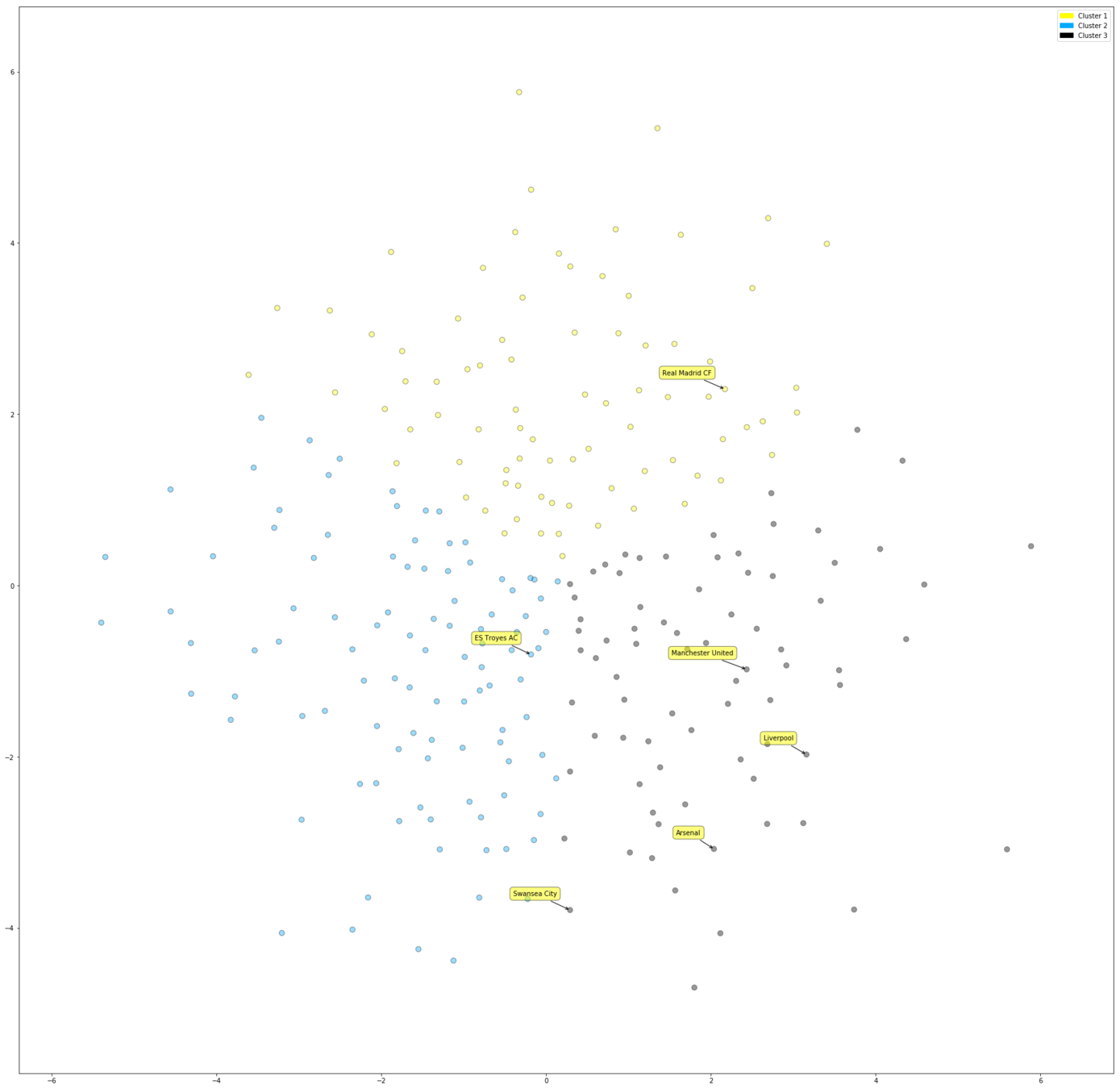
Objectives
- Sort soccer teams by their style of play (Cluster representation).
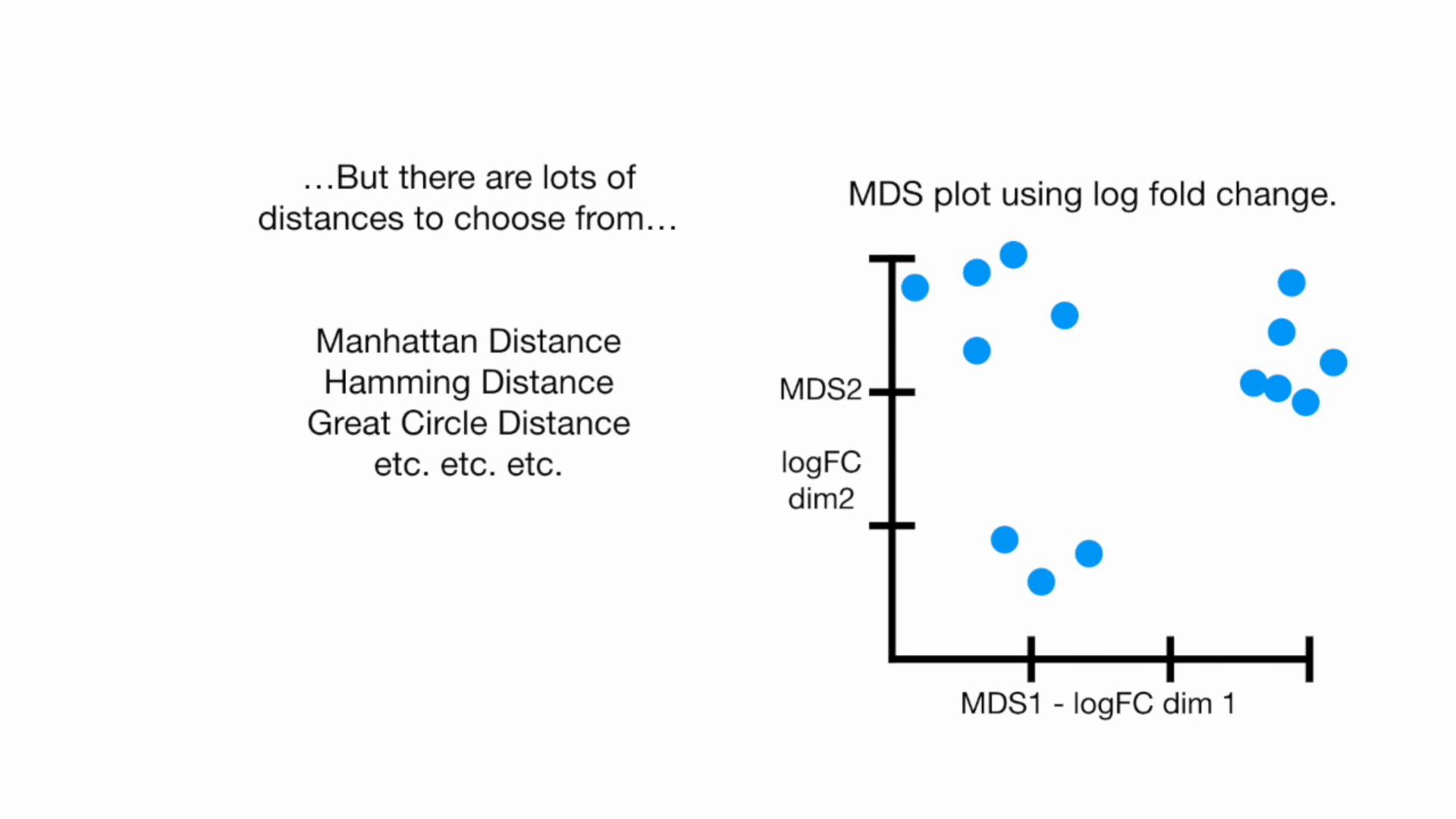
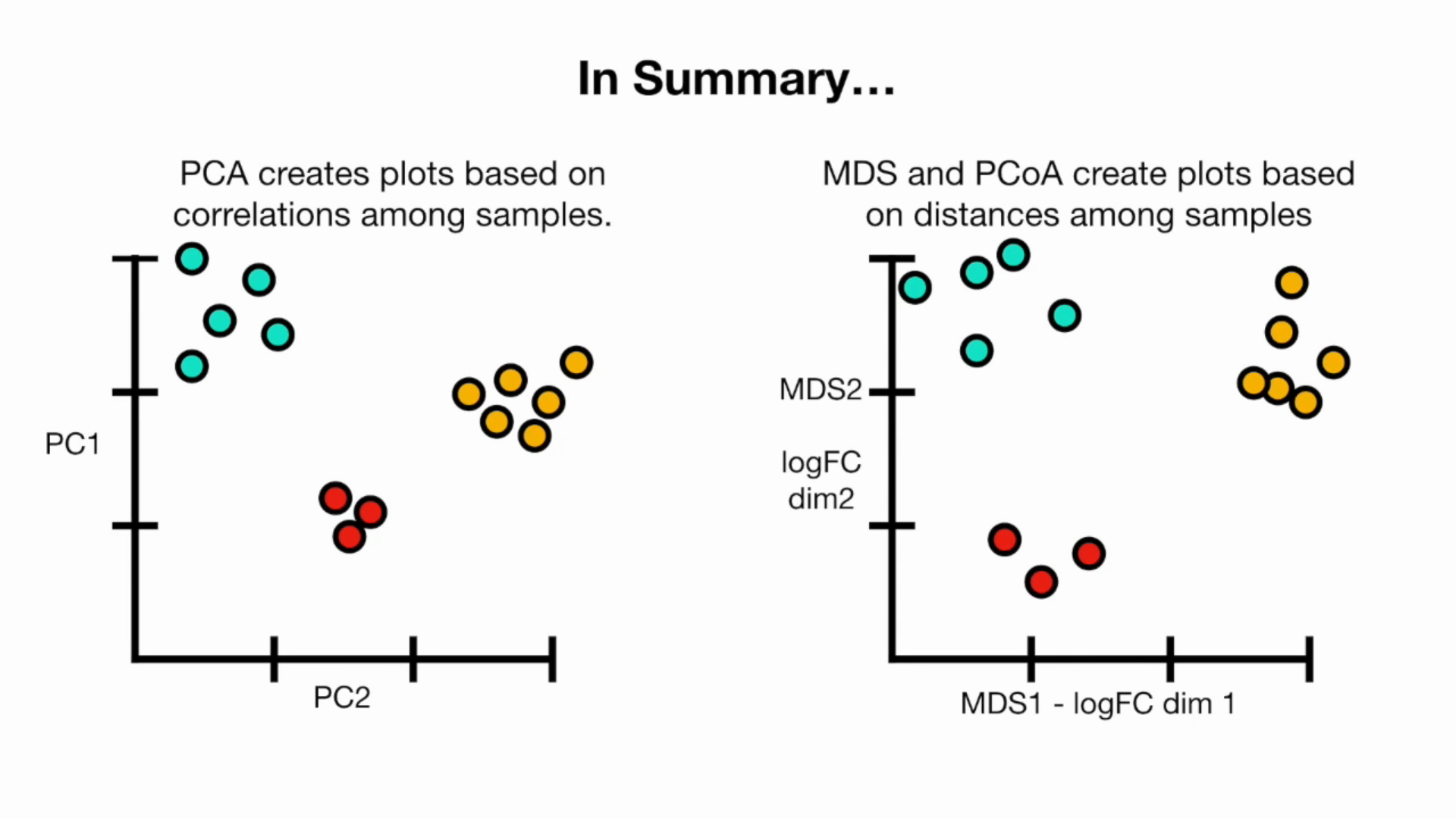
- PCA. Vs Multi Dimensional Scaling (MDS).
- K Means algorithm.
- Spectral Clustering.
Describe in a computational model:
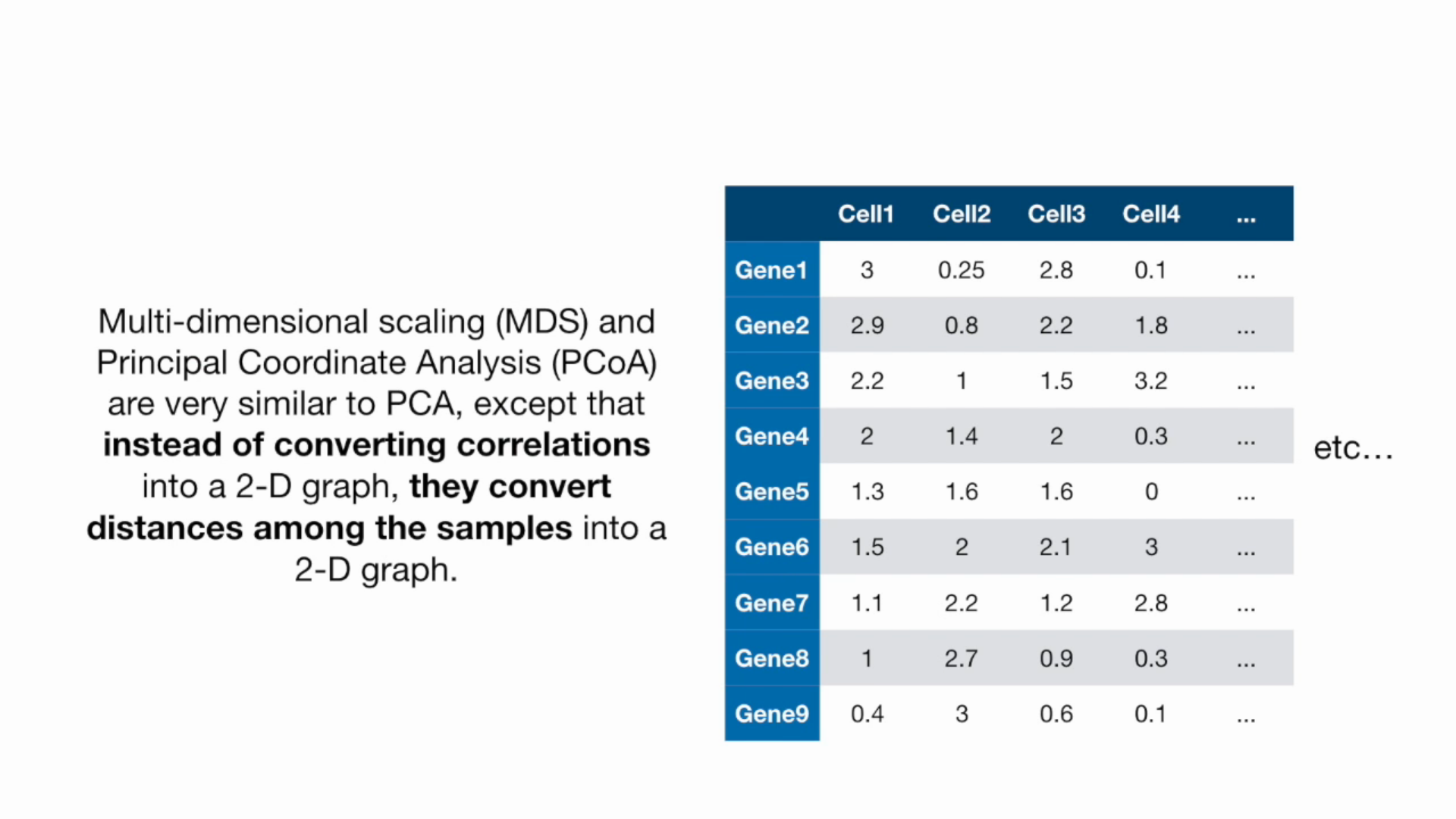
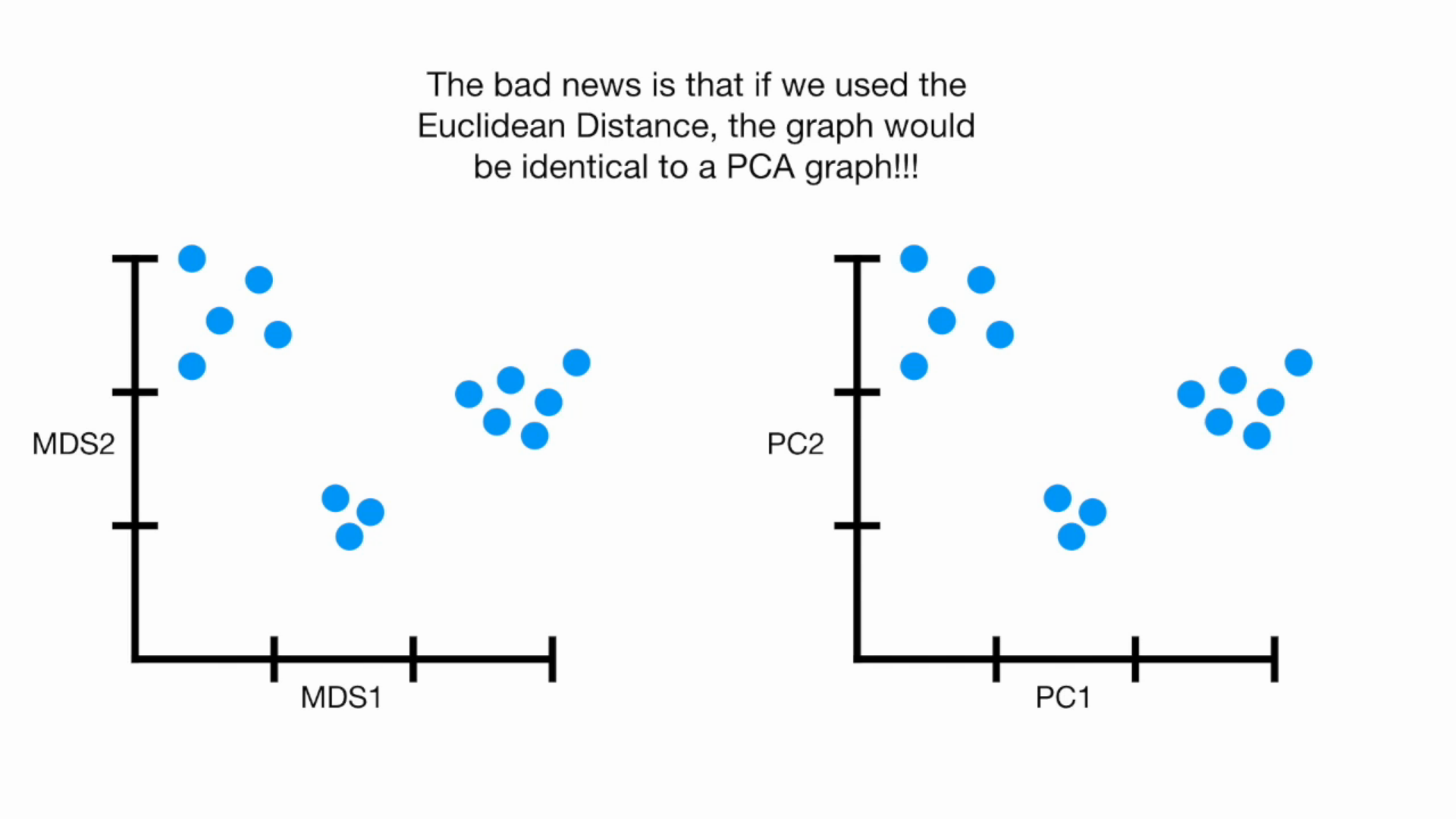
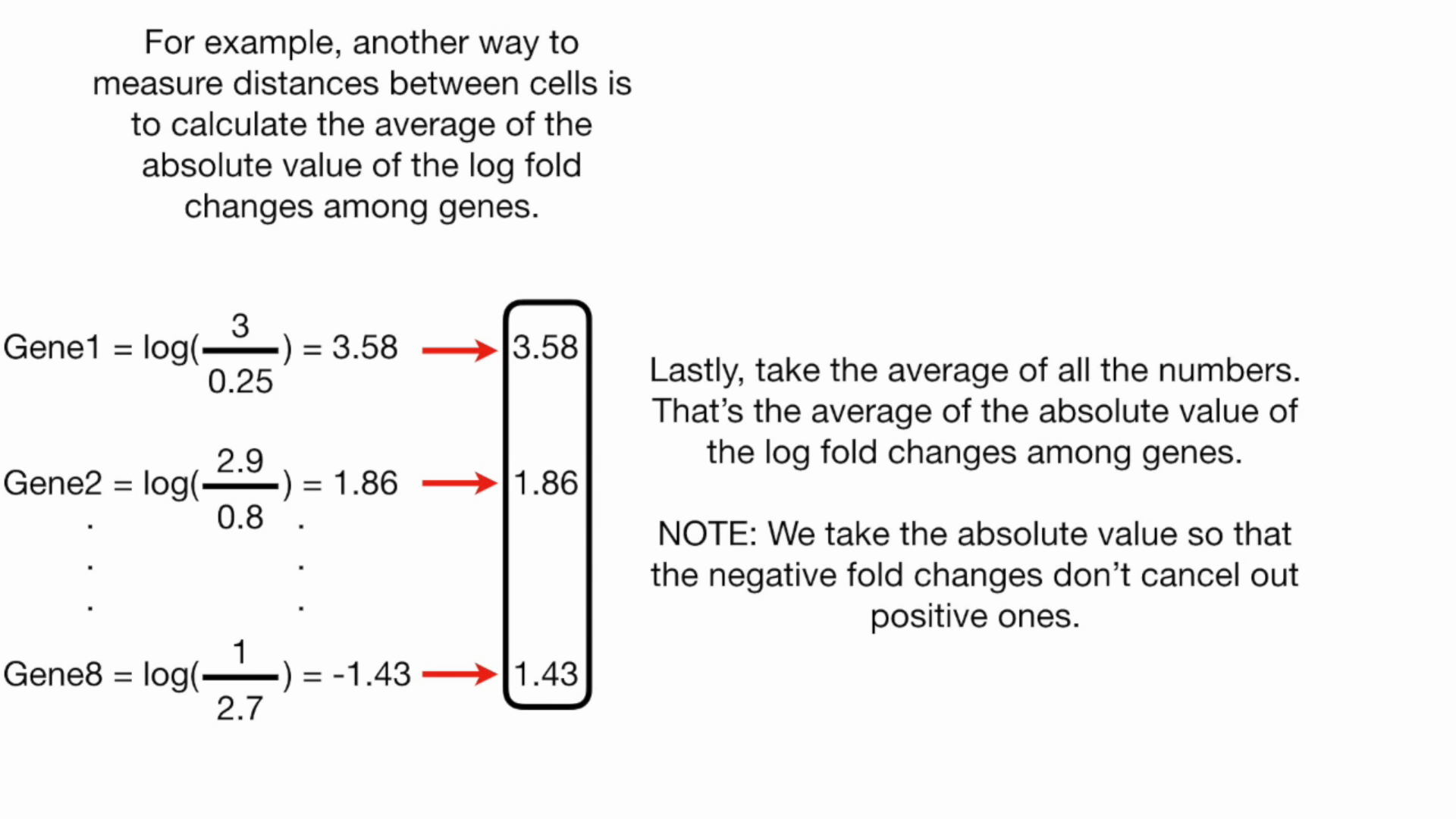
MDS

Kmeans
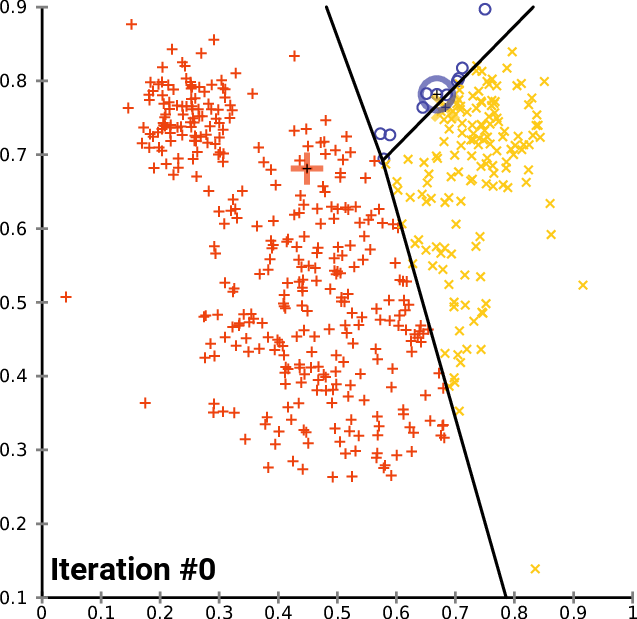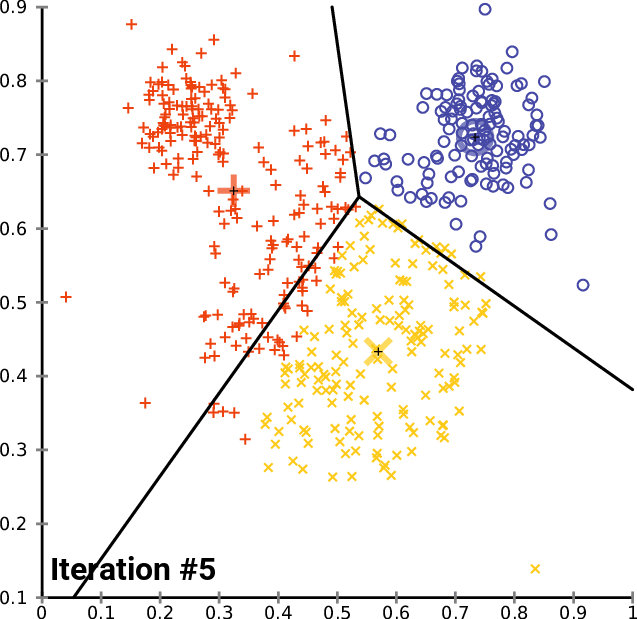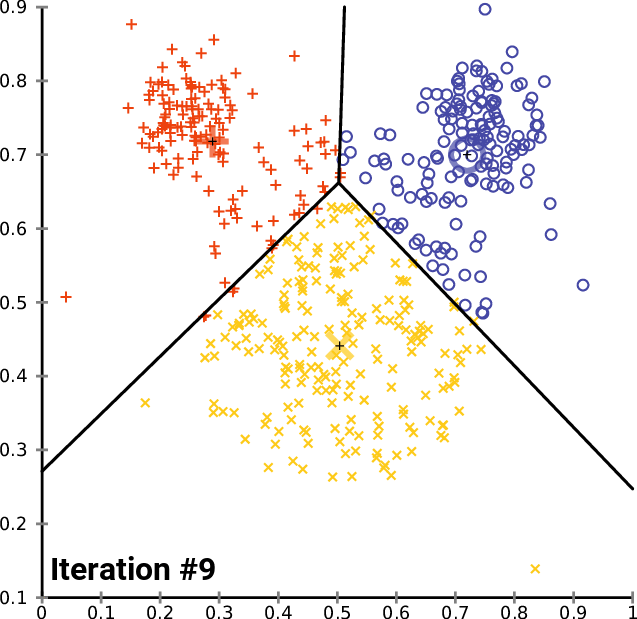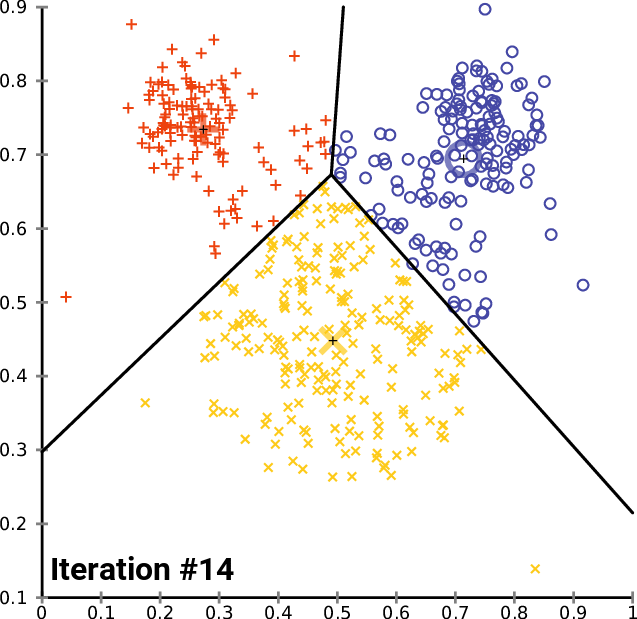
k-means clustering aims to partition n observations into k clusters in which each observation belongs to the cluster with the nearest mean, serving as a prototype of the cluster.
The Κ-means clustering algorithm uses iterative refinement to produce a final result.
The algorithms starts with initial estimates for the Κ centroids, which can either be randomly generated or randomly selected from the data set.
Each centroid defines one of the clusters. Each data point is assigned to its nearest centroid, based on the squared Euclidean distance.
The centroids are recomputed. This is done by taking the mean of all data points assigned to that centroid's cluster.
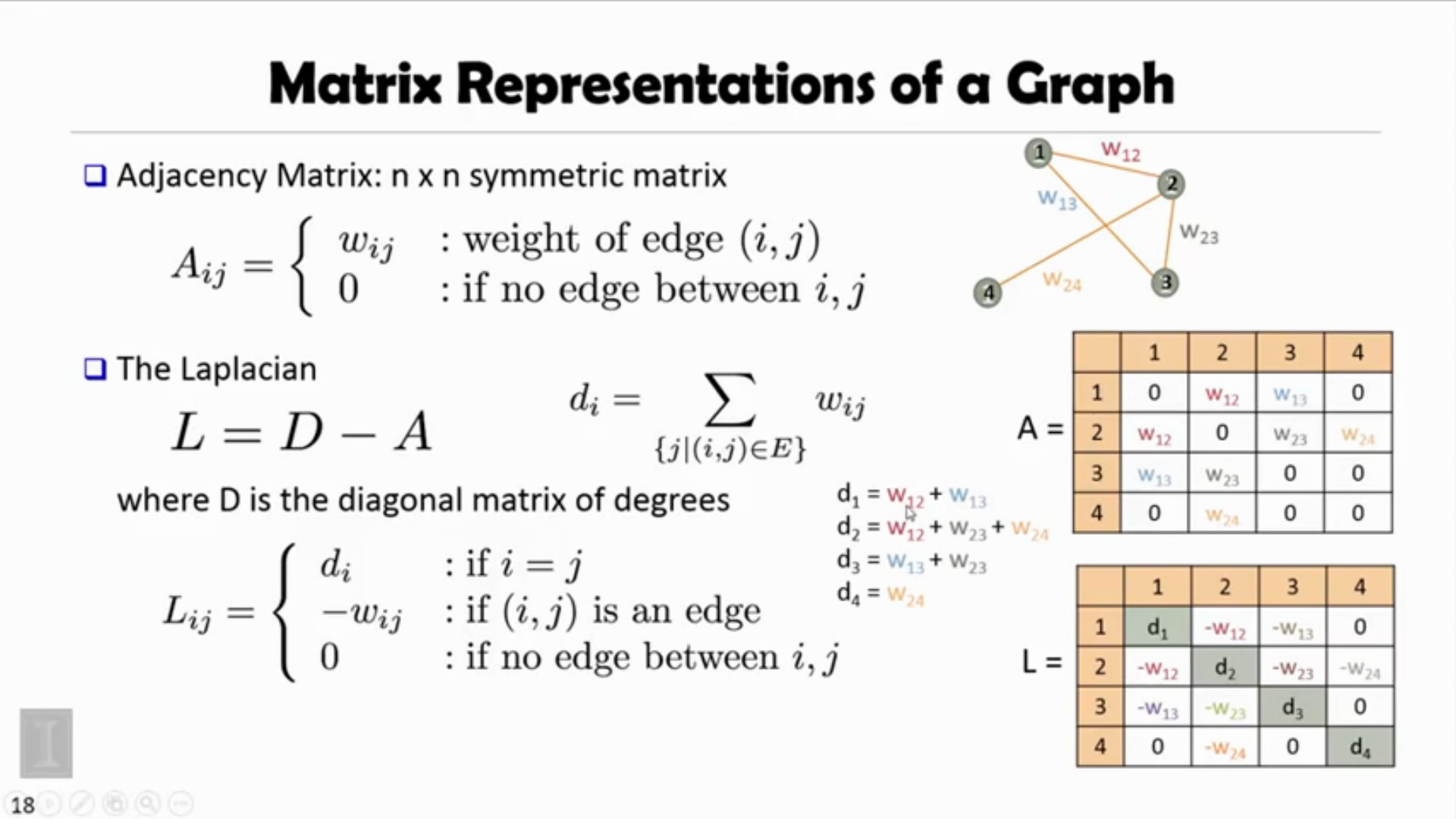
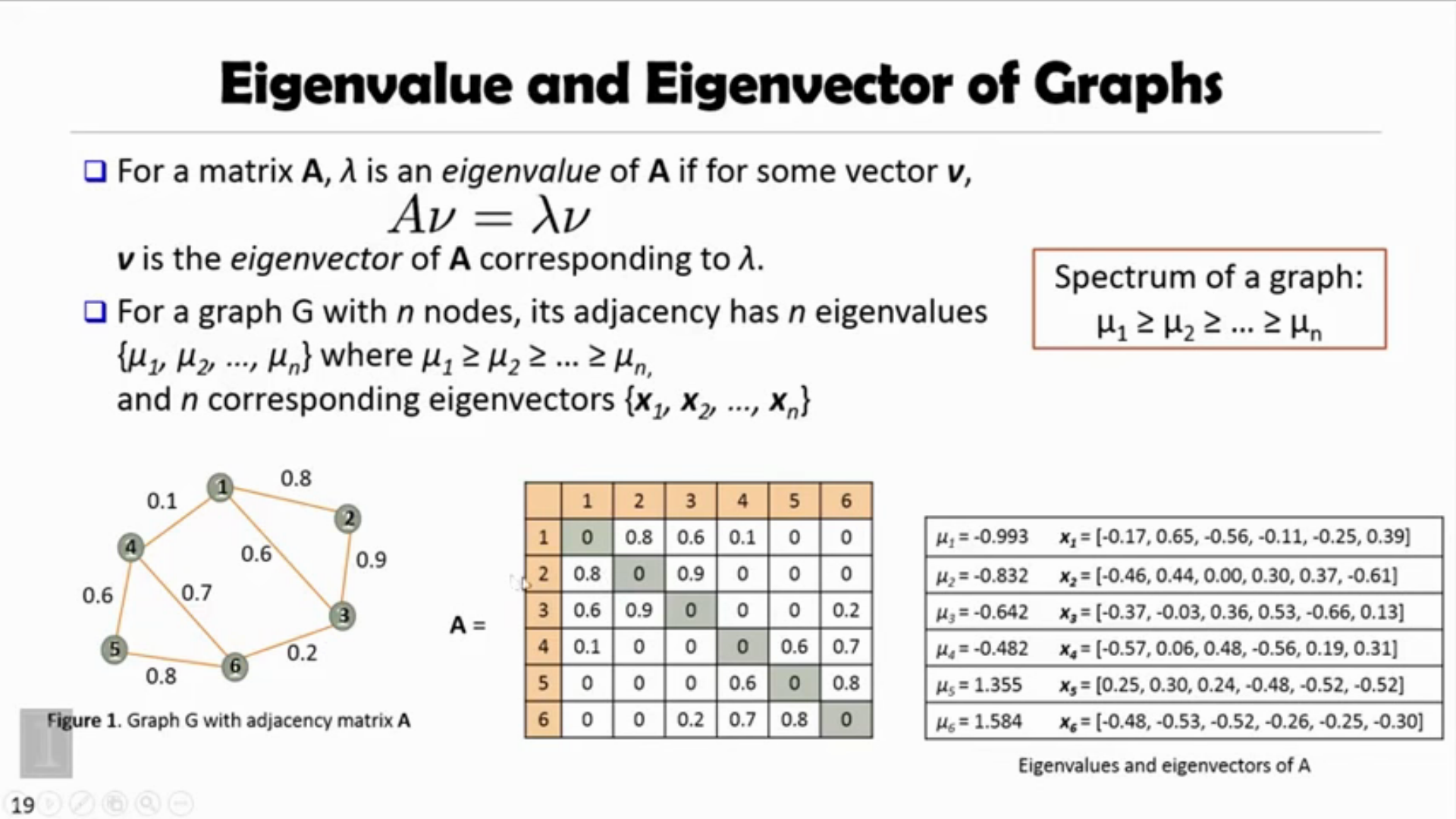
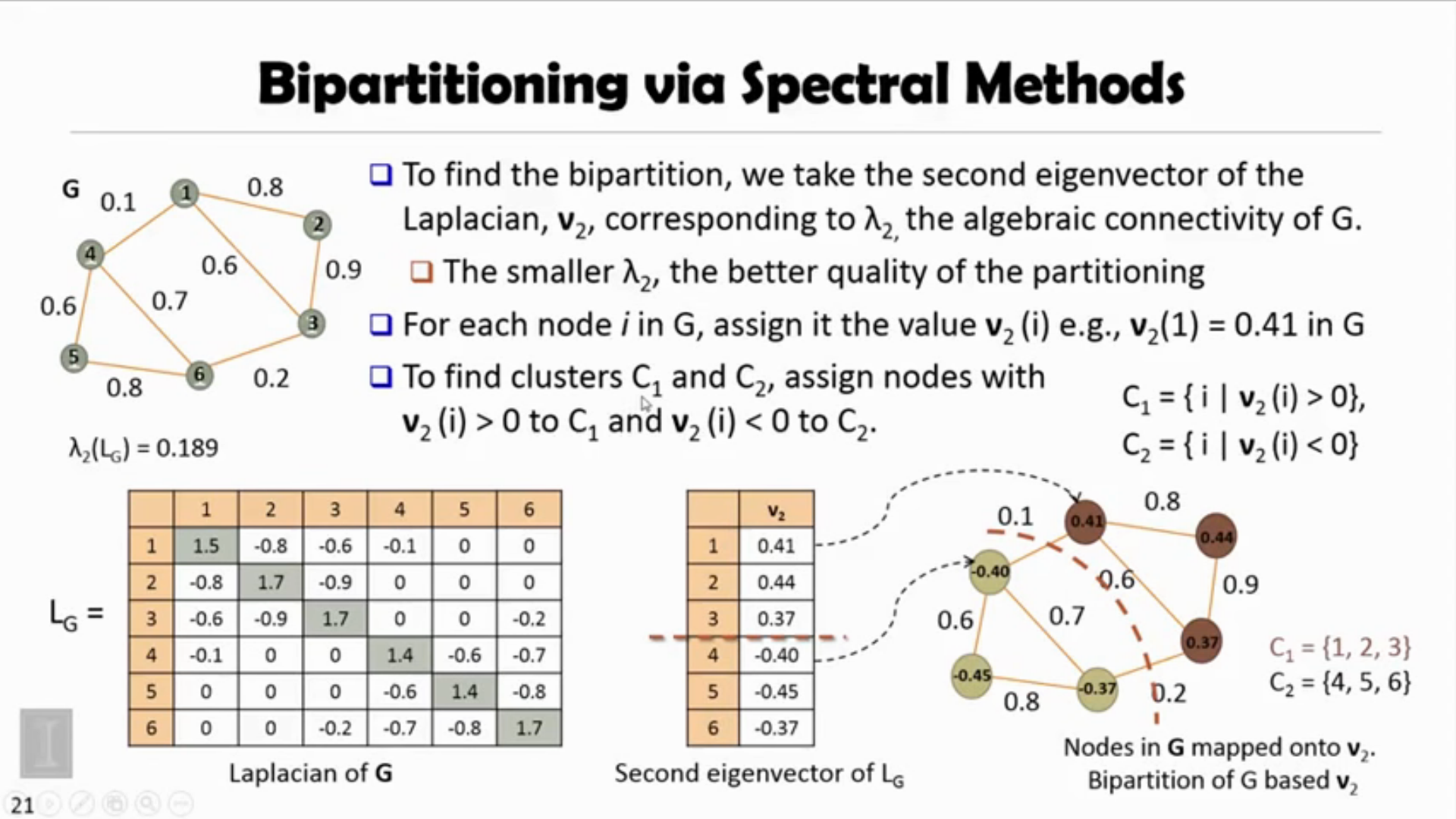
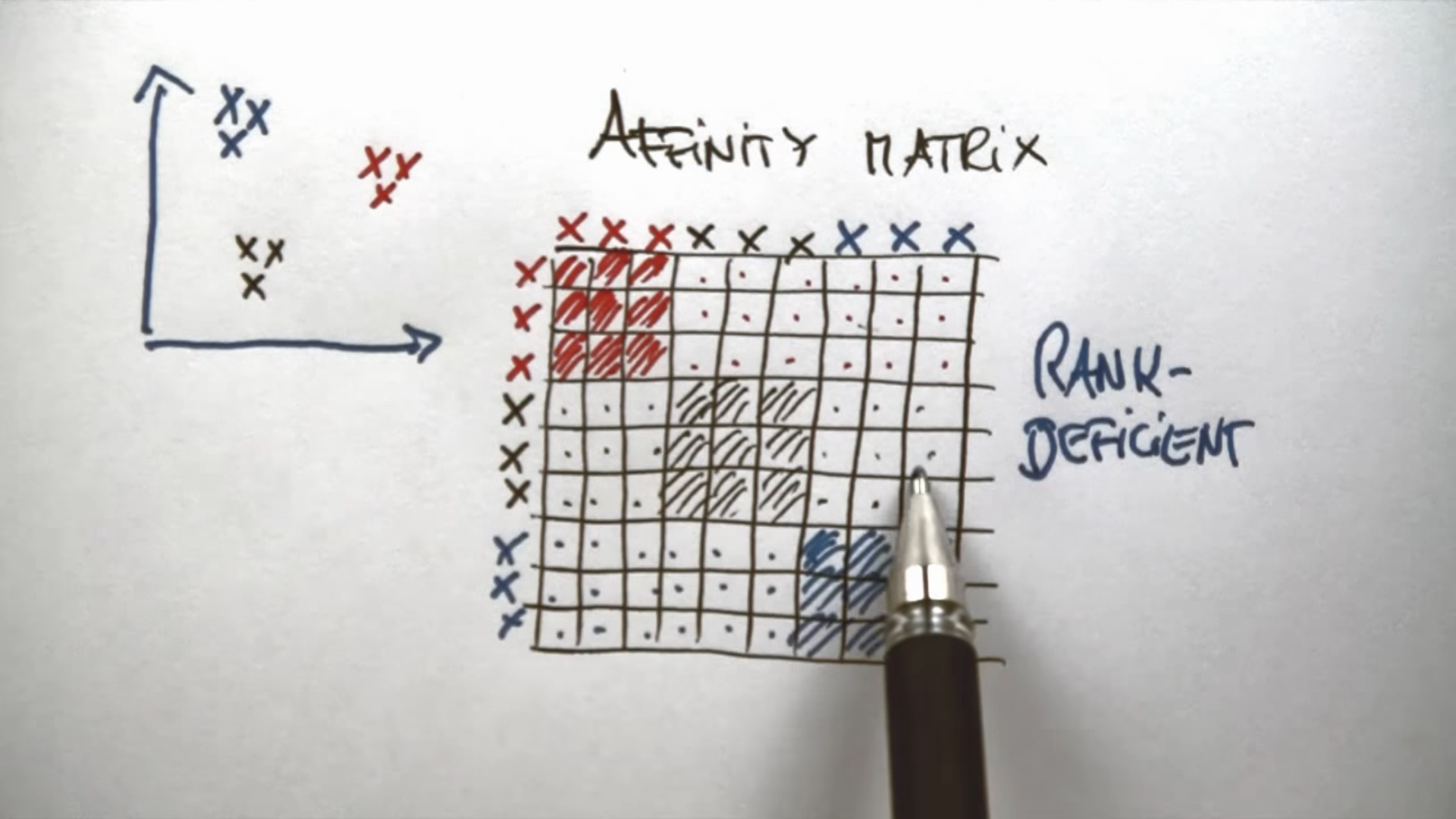
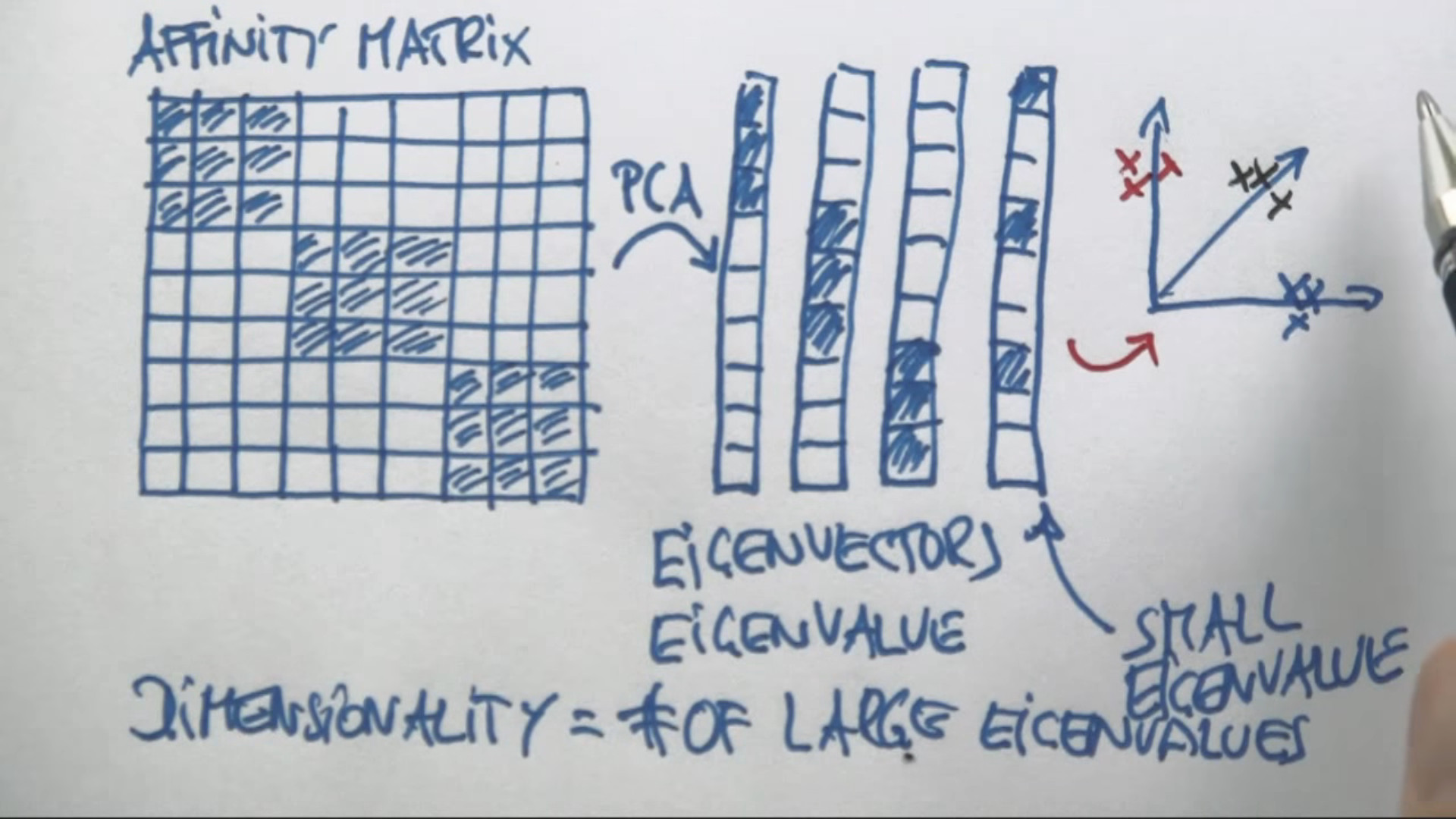
Spectral Clustering
Strength of SC
Makes no assumptions on the shapes of clusters, can handle intertwined spirals, etc.
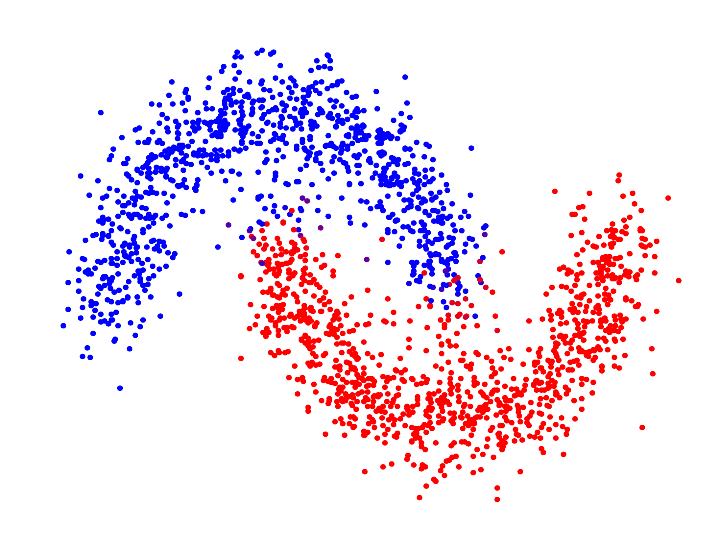
Process of S.C
- Construct a similary graph (e.g. KNN) for all the data points.
- Embed data points in a low-dimentsional space, in which the clusters are more obvious, with the use of the eigenvectors of the graph.
- A classical clustering algorithm (e.g k-means) is applied to partition the embedding
Conclusions
- Understand your dataset.
- Reduce dimensionality.
- Learn to differentiate between cluster algorithms
References
- MDS and PCoA:
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GEn-_dAyYME
- SC:
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zkgm0i77jQ8
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P-LEH-AFovE
- Kernel:
- https://www.kaggle.com/teamaker/clustering-teams-based-on-style-of-play