Confidence
agenda
Competency & Confidence
Dunning-Kruger
Imposter Syndrome
Objectives
Understand the relationship between competency and confidence
Be aware of Dunning-Kruger and Imposter Syndrome
Confidence & Competency
Perceived competency & projected confidence
- People that exude confidence are perceived to be competent
- People that exude no confidence are perceived to be incompetent
- This is because judging confidence is easy while judging competency is very difficult
- So we often don't judge competency and make assumptions about competency based on confidence
Is this fair? Why? Discuss with your neighbor.
COnfidence
Write down from 0-5 how confident you feel about performing these tasks:
Perceived Proxy of Competence.
- Create an array with the elements 1, 2, and 3 in it
- Write a VP8 video encoding/decoding program
- Count how many bricks are in the walls in the classroom
- Acquire the tender to pay bus fare today
- Push changes in a git repo to GitHub
- Use jQuery to create a button that dances on the screen when clicked
COmpetency
Discuss with your neighbor what you need to do to prove you can perform the action:
Ability to do Something Successfully.
- Create an array with the elements 1, 2, and 3 in it
- Write a VP8 video encoding/decoding program
- Count how many bricks are in the walls in the classroom
- Acquire the tender to pay bus fare today
- Push changes in a git repo to GitHub
- Use jQuery to create a button that dances on the screen when clicked
- Was it easier to say how confident you were or how to prove competency?
- If someone is confident they can do something, does that mean they can do it?
- If someone is not confident they can do something, does that mean they can not do it?
- Is Mastery Tracking a measure of confidence or competence?
DUNNING-KRUGER
A cognitive bias in which low-competency individuals suffer from illusory superiority
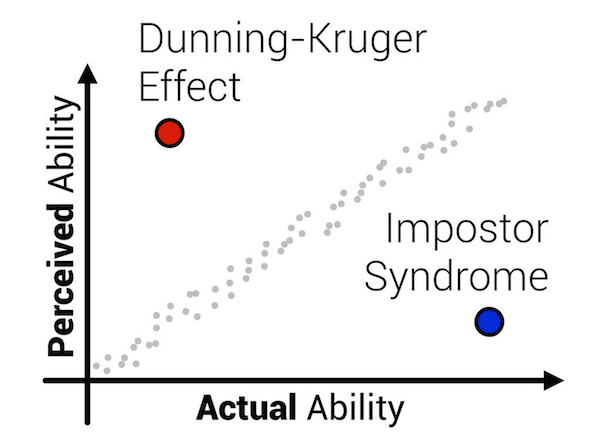
Those with poor Competency have a tendency to compensate with more confidence
We compensate because we all try to tell ourselves we are normal and normal people can do this
Q1 Confidence
Student with Dunning-Kruger Q1
- Thinks they don't have to work hard or learn
- Don't even try because that would break their illusion of competence
- Exudes confidence despite not being able to perform tasks
- Struggles during Q2 because they developed poor learning habits during Q1
What are some actions a student could do to recognize they are suffering Dunning-Kruger?
Imposter Syndrome

Those with high competency have a tendency to compensate with lower confidence
Q1 Confidence
Student with Imposter Syndrome Q1
- Will do a task and tell themselves they still don't understand it after proving competency
- Will feel like a fraud that doesn't belong
- Exudes no confidence despite being able to perform tasks
- Struggles with interviews
What are some actions a student could do to recognize they are suffering Imposter Syndrome?
In Software Development
More people identify with Imposter Syndrome than Dunning-Kruger
Going forward:
-
stop associating confidence with competence
-
THIS IS A SPECTRUM, not a boolean
*This is a problem almost exclusive to the USA
Europe has less of a negative correlation between confidence and competence
Asia has direct correlation between confidence and competence