Database Design
Contents
- What is Database?
- Relational DB
- Tables
- Relationships
- SQL
- Joins
- ACID
- Normalization
- Database Design
Database
- A database is an organized collection of data
- collection of information that is organized so that it can be easily accessed, managed and updated.
- We must organize the data to model aspects of reality in a way that supports processes requiring information
- e.g modelling the availability of rooms in hotels in a way that supports finding a hotel with vacancies.
- A database-management system (DBMS) is a computer-software application that interacts with end-users, other applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze data.
- Types: relational, distributed, graph, NoSQL etc.
Relational Database
- A relational database is a collection of data items organized as a set of formally-described tables from which data can be accessed or reassembled in many different ways without having to reorganize the database tables.
- Organized in such a way that there are clear relations defined between different sets of data.
- Database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970
- Almost all relational database systems use SQL (Structured Query Language) for querying and maintaining the database
Table
- A table is a collection of related data held in a structured format within a database.
- A table is a set of data elements (values) using a model of vertical columns (identifiable by name) and horizontal rows, the cell being the unit where a row and column intersect
- A table has a specified number of columns, but can have any number of rows.
- A specific choice of columns which uniquely identify rows is called the primary key.
KEY
* A KEY is a value used to identify a record in a table uniquely. A KEY could be a single column or combination of multiple columns.
* A primary is a single column value used to identify a database record uniquely.
* A composite key is a primary key composed of multiple columns used to identify a record uniquely.
- A primary key cannot be NULL
- A primary key value must be unique
- The primary key values cannot be changed
- The primary key must be given a value when a new record is inserted.
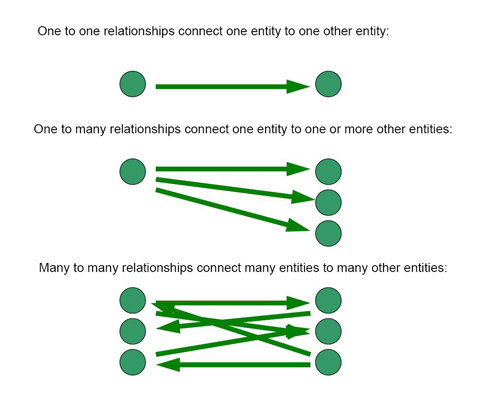
Relationships
SQL
- Structured Query Language
- The standard means of manipulating and querying data in relational databases
- These SQL commands are mainly categorized into four categories
- DDL(Data Definition Language)
- DML(Data Manipulation Language)
- DCL(Data Control Language)
- TCL(Transaction Control Language)
DDL
Create and modify the structure of database objects in database
- CREATE – is used to create the database or its objects (like table, index, function, views, store procedure and triggers).
- DROP – is used to delete objects from the database.
- ALTER-is used to alter the structure of the database.
- TRUNCATE–is used to remove all records from a table, including all spaces allocated for the records are removed.
- COMMENT –is used to add comments to the data dictionary.
- RENAME –is used to rename an object existing in the database.
DML
SQL commands that deals with the manipulation of data present in database belong to DML
- SELECT – is used to retrieve data from the a database.
- INSERT – is used to insert data into a table.
- UPDATE – is used to update existing data within a table.
- DELETE – is used to delete records from a database table.
DCL
Commands which deals with the rights, permissions and other controls of the database system.
- GRANT-gives user’s access privileges to a database
- REVOKE-withdraw user’s access privileges given by using the GRANT command.
DTL
Commands which deals with the transaction within the database.
- COMMIT– commits a Transaction.
- ROLLBACK– rollbacks a transaction in case of any error occurs.
- SAVEPOINT–sets a savepoint within a transaction.
- SET TRANSACTION–specify characteristics for the transaction.
ACID
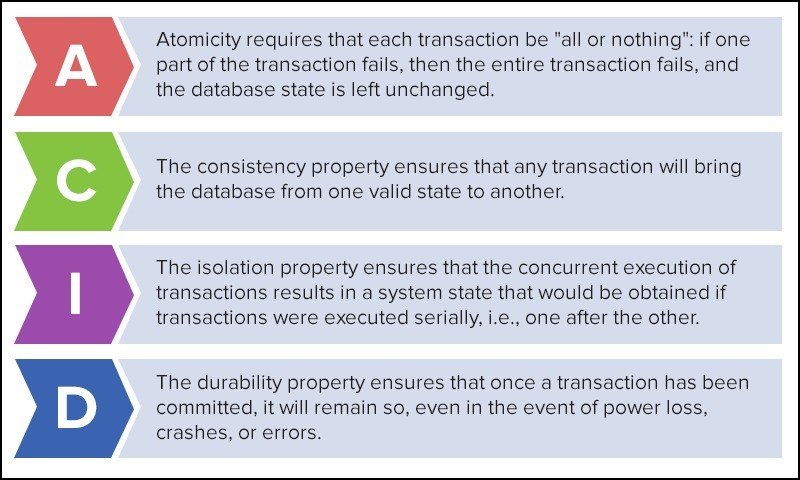
unit of work performed within a database management system (or similar system) against a database
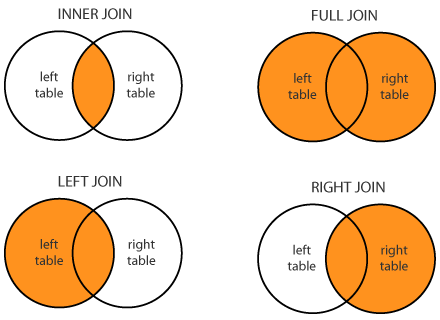
Joins
to combine data from two sets of data (i.e. two tables).
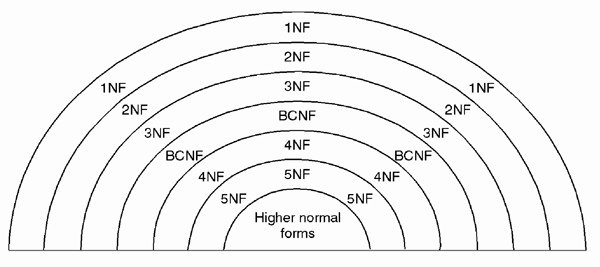
Normalization
- Normalization is a database design technique which organizes tables in a manner that reduces redundancy and dependency of data.
- It divides larger tables to smaller tables and links them using relationships.
Database Design
- The process of producing a detailed data model of a database.
- This data model contains all the needed logical and physical design choices and physical storage parameters needed to generate a design, which can then be used to create a database.
- Overview
- Determine the data to be stored in the database.
- Determine the relationships between the different data elements.
- Superimpose a logical structure upon the data on the basis of these relationships.
1. Determine the purpose of the database - This helps prepare for the remaining steps.
2. Find and organize the information required - Gather all of the types of information to record in the database, such as product name and order number.
3. Divide the information into tables - Divide information items into major entities or subjects, such as Products or Orders. Each subject then becomes a table.
4. Turn information items into columns - Decide what information needs to be stored in each table. Each item becomes a field, and is displayed as a column in the table. For example, an Employees table might include fields such as Last Name and Hire Date.
5. Specify primary keys - Choose each table’s primary key. The primary key is a column, or a set of columns, that is used to uniquely identify each row. An example might be Product ID or Order ID.
6. Set up the table relationships - Look at each table and decide how the data in one table is related to the data in other tables. Add fields to tables or create new tables to clarify the relationships, as necessary.
7. Refine the design - Analyze the design for errors. Create tables and add a few records of sample data. Check if results come from the tables as expected. Make adjustments to the design, as needed.
8. Apply the normalization rules - Apply the data normalization rules to see if tables are structured correctly. Make adjustments to the tables, as needed.
Steps in Database Design
Questions?
References
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/sql-ddl-dml-dcl-tcl-commands/
- http://www.sql-join.com/sql-join-types/
- https://www.guru99.com/database-normalization.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Database_design