Async
JaxNode October 2018
Happy Birthday!!!
JaxNode 5th year!
Concurrency is Hard!



Concurrency should be as easy as riding a bicycle
Why is concurrency important?

State of Computing today
- Processors aren't getting faster
- Still adding more transistors to piece of silicon
- More cores being added to processors
- Speed is coming from being able to do many things concurrently

Ryan Dahl
Introduced Node.js in 2009
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('World!');
}, 2000);
console.log('Hello ');Intro
- How Node handles Async work
- Error first callbacks
- Promises
- Generators
- Async/Await
- Async module
JavaScript
- Single Threaded
- Non-blocking
- Callbacks
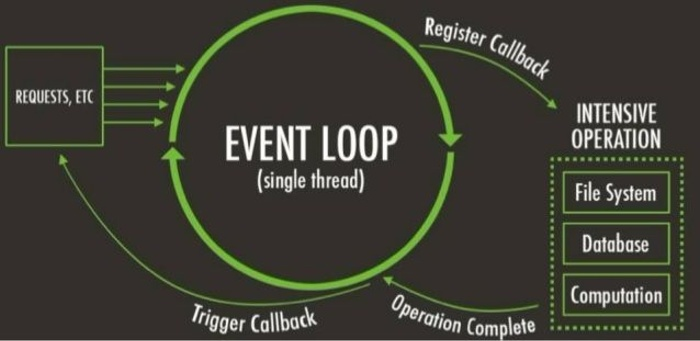
* https://www.codementor.io/theresamostert/understanding-non-blocking-i-o-in-javascript-cvmg1hp6l
Async API
- When Node starts, it starts Event Loop
- LibUV concurrency library part of Node
- Event Loop looks at timers first
- Then handles event callbacks
- Enters idle phase, internal only
- Then handles I/O callbacks queue
- close callbacks
Timers
- setImmediate(fn)
- setTimeout(fn, milliseconds)
- setInterval(fn, milliseconds)
- process.nextTick(fn)
Demo 1
Error First Callbacks
- Instead of returning a value, functions will expect parameter takes a another function
- The function or lambda will contain an error parameter, and a results parameter
- function query('Arg', function (err, data) {...})
Error first callbacks
function callFn(err, result) {
if (err) console.error(err);
console.log(result);
}
function makeDatabaseQuery(params, cb) {
// ...Do your magic
const result = magicIsCompleted();
if (error) {
cb(error, null);
} else {
cb(null, result);
}
}
makeDatabaseQuery(['12', false, 'Larry'], callFn);Demo 2
Callback Hell
- JavaScript allows inline functions or lambda
- Developers can wind up having massive trees of callbacks inside one method
- Hard to read and unintuitive
fs.readdir(source, function (err, files) {
if (err) {
console.log('Error finding files: ' + err)
} else {
files.forEach(function (filename, fileIndex) {
console.log(filename)
gm(source + filename).size(function (err, values) {
if (err) {
console.log('Error identifying file size: ' + err)
} else {
console.log(filename + ' : ' + values)
aspect = (values.width / values.height)
widths.forEach(function (width, widthIndex) {
height = Math.round(width / aspect)
console.log('resizing ' + filename + 'to ' + height + 'x' + height)
this.resize(width, height).write(dest + 'w' + width + '_' + filename, function(err) {
if (err) console.log('Error writing file: ' + err)
})
}.bind(this))
}
})
})
}
})Streamline Callbacks
- Inline functions are hard to debug
- if you use inline functions, consider naming
- Define separate function and use for the callback
fs.readdir(source, handleFiles);
function handleFiles(err, files) {
if (err) {
console.log('Error finding files: ' + err)
} else {
files.forEach(forEachFile)
}
}
function forEachFile(filename, fileIndex) {
console.log(filename)
gm(source + filename).size(handleSize)
}
function handleSize(err, values) {
if (err) {
console.log('Error identifying file size: ' + err)
} else {
console.log(filename + ' : ' + values)
aspect = (values.width / values.height)
widths.forEach(handleWidth.bind(this))
}
}
function handleWidth(width, widthIndex) {
height = Math.round(width / aspect)
console.log('resizing ' + filename + 'to ' + height + 'x' + height)
this.resize(width, height).write(dest + 'w' + width + '_' + filename, function(err) {
if (err)
console.log('Error writing file: ' + err)
})
}Generators
- Generates values when needed
- '*' used after 'function' keyword
- Use the 'yield' keyword to return values
- generator results.next().value
- Typically used for iterators
function* simpleGenerator() {
yield 1;
yield 5;
}
const g = simpleGenerator();
const v1 = g.next().value; // --> 1
const v2 = g.next().value; // --> 5
const v3 = g.next().value; // --> undefined
function* myGenerator() {
let i = 0;
while(i < 2) {
i += 1;
yield i;
}
}
const g = myGenerator();
const v1 = g.next(); // --> { value: 1, done: false }
const v2 = g.next(); // --> { value: 2, done: false }
const v3 = g.next(); // --> { value: undefined, done: true }function* withReturn() {
yield 1;
yield 55;
return 250;
yield 500;
}
const g = withReturn();
const v1 = g.next().value; // --> 1
const v2 = g.next().value; // --> 55
const v3 = g.next().value; // --> 250
const v4 = g.next().value; // --> undefinedDemo 3
Promises
- A type of Monad
- Built in type in Node and JavaScript
- Can chain and nest Promises
- Handling functions with .then and .catch
- Avoids callback Hell, but can still be tricky
const promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
// do a thing, possibly async, then…
if (/* everything turned out fine */) {
resolve("Stuff worked!");
}
else {
reject(Error("It broke"));
}
});
promise.then(result => {
console.log(result);
}).catch(err => {
console.error(err);
});const promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
resolve(1);
});
promise.then(function(val) {
console.log(val); // 1
return val + 2;
}).then(function(val) {
console.log(val); // 3
})Handle multiple Promises
- Promise.all()
- Can pass multiple promises, and call then handler when every promise has been fulfilled
const promise1 = Promise.resolve(3);
const promise2 = 42;
const promise3 = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(resolve, 100, 'foo');
});
Promise.all([promise1, promise2, promise3]).then(function(values) {
console.log(values);
});Promise Support
-
Chrome 32, Opera 19, Firefox 29, Safari 8 &
Microsoft Edge - Node 0.12
- Q module
- Util.Promisify added in Node v8
Convert error first Callbacks to Promises
const util = require('util');
const fs = require('fs');
const stat = util.promisify(fs.stat);
stat('.').then((stats) => {
// Do something with `stats`
}).catch((error) => {
// Handle the error.
});
// Or
const stat = util.promisify(fs.stat);
async function callStat() {
const stats = await stat('.');
console.log(`This directory is owned by ${stats.uid}`);
}Demo 4
Async Await Keywords
- 'async/await' added Node and JavaScript in Node v8
- To make any function asynchronous, place 'async' keyword to the beginning of function
- Place 'await' keyword in front of asynchronous calls like promises instead of using '.then()' handler
- Allows JavaScript developers to write their code in a more synchronous way
- Also available in C# and coming to Swift
function resolveAfter2Seconds() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('resolved');
}, 2000);
});
}
async function asyncCall() {
console.log('calling');
var result = await resolveAfter2Seconds();
console.log(result);
// expected output: 'resolved'
}
asyncCall();Async/Await behind the scenes
- Async tells the compiler to expect awaits on function
- Await proceeds Promises, but allow synchronous style syntax
- Compiler will divide functions into starting and callback functions
- If you have one 'await' keyword function will be divided into two functions
Demo 5
Async Framework
- Works in Node or Browser
- Parallel workflow
- Waterfall workflow
- forEach workflow
- race workflow
async.map(['file1','file2','file3'], fs.stat, function(err, results) {
// results is now an array of stats for each file
});
async.filter(['file1','file2','file3'], function(filePath, callback) {
fs.access(filePath, function(err) {
callback(null, !err)
});
}, function(err, results) {
// results now equals an array of the existing files
});
async.parallel([
function(callback) { ... },
function(callback) { ... }
], function(err, results) {
// optional callback
});
async.series([
function(callback) { ... },
function(callback) { ... }
]);Demo 6
Resources
- https://github.com/jaxnode-UG/async
- https://slides.com/davidfekke/async
- https://medium.com/@ajmeyghani/async-javascript-a-pocket-reference-2bb16ac40d21
Questions?
Contact Me
- David Fekke at gmail dot com
- Twitter @jaxnode and @davidfekke
- Skype: davidfekke
- http://jacksonville-tech.com/ Slack Group