Informatik I
Übung 3 : Datentypen und Funktionen
11. März 2015
Daniel Hentzen
dhentzen@student.ethz.ch

Heute
- Nachbesprechung Übung 2
- Theorie
- Vorbesprechung Übung 3
Übung 2 : Programmieren in Eclipse
Projekt in Eclipse erstellen...
Input
3 Methoden, um Variablen zuzuweisen :
- im Programm
- mit Programmargumenten
- mit cin
Temperaturumwandlung
atof - Funktion
#include<iostream>#include<stdlib.h>...float a = atof( argv[1] )
Fehler
Integer-Division !!
(int) / (int) = (int)
t_f = 9 / 5 * t_c + 32; // FALSCH !!t_f = (9 / 5) * t_c + 32; // FALSCH !!
(float) / (int) = (float)
t_f = (9 * t_c) / 5 + 32; // RICHTIG !t_f = (9.0f / 5) * t_c + 32; // RICHTIG !t_f = (9f / 5) * t_c + 32; // FALSCH !t_f = float(9) / 5 * t_c + 32; // RICHTIG !
Eclipse Fehlermeldungen
Problem : File nicht korrekt gespeichert
Lösung 1 : Speichern, Kompilieren
Lösung 2 : "Project > Clean...> OK"
"Build All"

Problem : C++ wird nicht mehr erkannt
Lösung : "Run Configurations" > C++ auswählen
evtl Clean... / Build...
using namespace std;
falls Fehlermeldung : Zeile löschen, neu tippen, speichern, kompilieren...
Theorie
- Datentypen und Variablen (2)
- Funktionen
Datentypen
int (integer)
- Speicherung ganzer Zahlen (mit Vorzeichen)
- Speicher ist endlich gross --> endlich grosse Zahlen
- 2, 467467, -7263, 0
char
(character)
- Speichern eines einzelnen Zeichens
char x = 'y';
- Zeichen werden in eine Zahl umgewandelt
- ASCII-Tabelle
- + ► 43
- A..Z ► 65..90
- a..z ► 97..122
float / double
- Speichern von Kommazahlen
float a = 3.14;float x = 0.1E-4;
- Suffix zur Spezifizierung : f
9.0f / 5 //9 wird als float abgespeichert
- begrenzte Präzision !!
- bei numerischen Operationen : double benutzen
bool (boolean)
- kann true / false abspeichern
- 1 / 0
bool test1 = 10; // test 1 = truebool test2 = 0; // test 2 = false
Hauptspeicher
- Daten im Speicher als Bitfolge abgelegt
- 1 Bit : 2 mögliche Zustände (0/1)
- 1 Byte : Kombination von 8 Bits
- 2^8 (256) mögliche Zustände
- 1 Word : Kombination von Bytes
- 32-bit : 1 Word = 4 Bytes
- 64-bit : 1 Word = 8 Bytes
32 bit
- 1 Word = 4 Bytes = 32 bit
- 2^32 verschiedene Bytes
- ~= 4.000.000.000 Bytes = 4GB
- = Grösse des zugreifbaren Arbeitsspeichers
64 bit
- 1 Word = 8 Bytes = 64 bit
- 2^64 verschiedene Bytes
- ~= 16 Exabyte = 16.000.000.000 GB
- = Grösse des (theoretisch) zugreifbaren Arbeitsspeichers
Binary

Datentypen
-
sinnvolle Interpretation des Speicherinhalts
- Basistypen (int, double, float, bool,...)
- abgeleitete Typen (arrays, structs) (später)
Wiederholung : Variablen
int a; // Definitiona = 5; // Zuweisungint b = 3; // Definition und Zuweisungint c,d,e; // in Seriec = d = e = 7;
nicht erlaubte Namen
int a!;int ä;int 1a;int for;int main;int __a:int _B;
Modifiers / Specifiers
<modifier> <type> <name>;- optional
- ändern den Datentypen
- Speicher
- Vorzeichen
long int a; // integer Variable a mit 2 x 2 Byte = 4 Byte Speicherplatzshort int b; // integer Variable b mit 1 Byte Speicherplatzunsigned int c; // c ohne Vorzeichenconst int d = 5; // d hat im ganzen Programm den Wert 5
Zuweisungen / Typenumwandlung
float / double --> int
float a = 3.14;int b = a; // a = 3int a = 3;float b = a; // b = 3.0
char --> double / float / int
(siehe ASCII Tabelle)
char a = 'q';int b = a; // b entspricht dem ASCII Code von 'q'
int / float / double --> char
int a = 127;char b = a; // b ist das ASCII Zeichen von 127
! Achtung : ergibt falsche Werte für Werte über 255 !
int / float / double --> bool
int a = 0;bool b = a; // b = FALSE (0)int a = 2;bool b = a; // b = TRUE (1)
bool --> int / float / double
bool a = true;int b = a; // a = 1bool a = false;int b = a; // a = 0
Achtung!!
long int a = 100000000000000;int b = a; // falsche Werte!!long int a = 10000000000000;short int b = a; // falsche Werte
Bits werden abgeschnitten, ergibt falsche Werte für grosse Zahlen
float a = 3.14;long int b = a; // a wird abgerundet
OK!
type cast
(<type>) Wert/Variable; // C und C++<type> (Wert/Variable); // nur in C++float f = float(3/2 + 4.0f); // f=5.0float f = float(3)/2 + 4.0f; // f=5.5
Funktionen
- Bausteine / Module
- vordefinierte / eigene
- mit / ohne Rückgabewert
- Vorteile :
- Code wiederverwendbar
- Lesbarkeit
Vordefinierte Funktionen
Beispiel 1 : sqrt()
(vordefiniert in cmath)
float a = sqrt(81); // "function call", a = 9Beispiel 2 : atof()
(vordefiniert in stdlib.h)
float b = atof("32"); // b = 32Eigene Funktionen
- müssen deklariert werden (ausserhalb von main)
- --> "Prototyp"
- müssen definiert werden (ausserhalb von main)
- können in main aufgerufen werden
Deklaration
<type> <name> ( <type> ) // Prototyp
Definition
Funktionskopf :
<type> <name>(arguments)
Funktionskörper :
{ statements;return <Wert/Variable>; // (optional)}
Beispiel : Temperaturumwandlung
Vorgehen :
- Rückgabetyp ?
- Name ?
- Argumente / Parameter ?
- Anweisungen ?
-
float
- t_umwandlung
- 1 float Argument : t_c
float t_umwandlung(float); // Deklaration, Prototypint main(){...}float t_umwandlung(float t_c) //Definition{...}
Funktionsaufruf in main()
<name> (argument1, argument2,...)float c;cin >> c;float f;f = t_umwandlung(c); // function call
Scope (Gültigkeitsbereich)
scope = Gültigkeit / "Sichtbarkeit" einer Variable
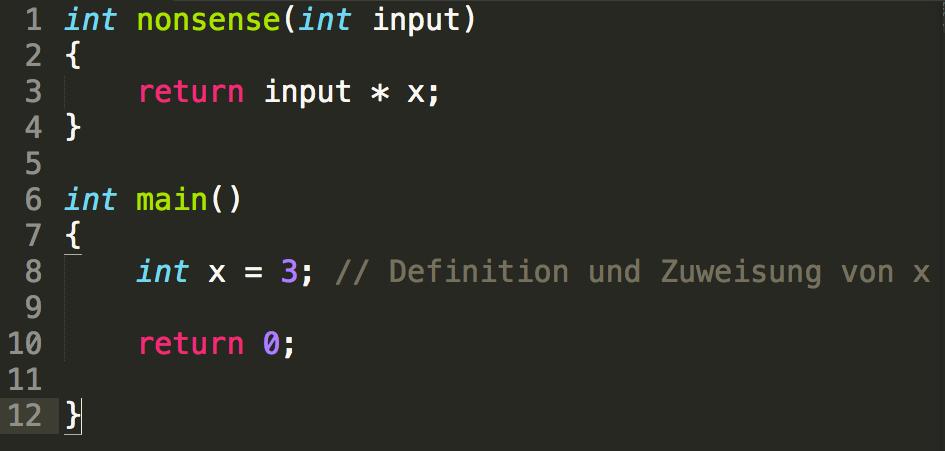
Übung 3 : Datentypen und Funktionen
Aufgabe 1 : Datentypen und Zuweisungen
Aufgabe 2 : UNIX On-line Hilfe
Was bewirkt ein Kommando ?
--> man <Kommando>
--> info <Kommando>
Aufgabe 3 : Typenumwandlung
- Zeile für Zeile vorgehen
- Variablentabelle erstellen
- Tipp : Zufallswerte für nicht initialisierte Variablen


