Duality of Firms and Individuals
in Corporate Networks
Diliara Valeeva
KU Leuven
University of Amsterdam
Mitchell Center for Network Analysis | University of Manchester | 18 Nov 2020


Board interlock



Takes, F.W. & Heemskerk, E.M. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. (2016) 6: 97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-016-0402-5
“Interlocks occur between organizations,
but they are created by individuals”
(Mizruchi 1996: 277)

1-mode
2-mode
2
FIRMS
A
B
2
INDIVIDUALS
X
Y
FIRMS
INDIVIDUALS
A
B
Y
X
How do board interlock ties form?

Valeeva, D., Heemskerk, E. M., & Takes, F. W. (2020). The duality of firms and directors in board interlock networks:
A relational event modeling approach. Social Networks, 62, 68-79.
Open access: https://bit.ly/2HeF9s6
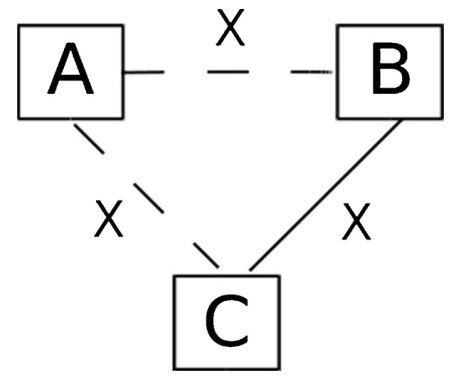
Broken ties argument
A
B
FIRMS
fast tie reconstruction
slow tie reconstruction
firms matter more
individuals matter more
"Duality of persons and groups"
Breiger (1974)
1-mode
2-mode
2
FIRMS
A
B
2
INDIVIDUALS
X
Y
FIRMS
INDIVIDUALS
A
B
Y
X
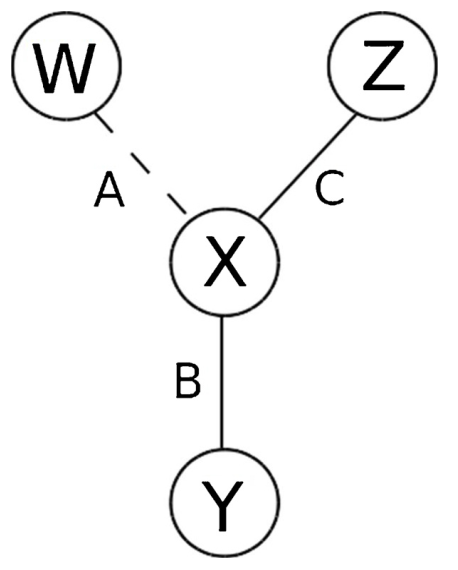
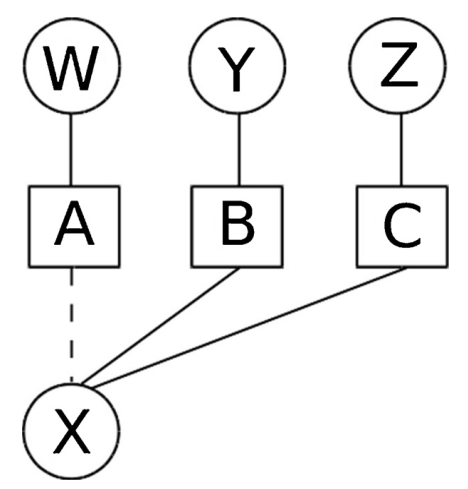
Strategies to form ties
(1) reinforcement
(2) expansion
X
X
Y
Z
X
Y
Z
Problem
reinforcement
expansion
one-mode FIRMS
one-mode INDIVIDUALS
two-mode
FIRMS and INDIVIDUALS
Data and Methods
- Denmark
- 1994-2014
- 3,304 firms
- 10,377 individuals
- 14,893 board appointments
- Relational Event Modeling
Hypotheses
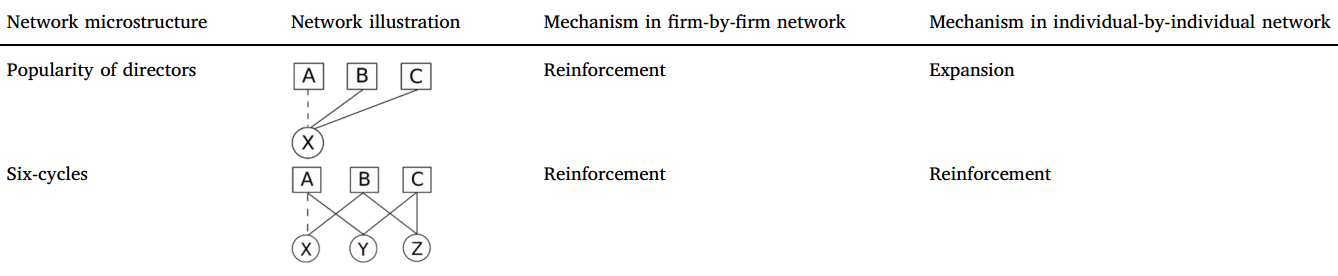
Predictors of new ties

- Popularity of directors
- Six-cycles
- Danish and male directors
- Banks and financial firms
Conclusions
- Complementary rather than conflicting interests of firms and individuals
- Duality of agents is typical for social systems and should not be ignored
Other projects




Diliara Valeeva
@diliara_valeeva
dlliara.valeeva.com
CORPNET
@uvaCORPNET
corpnet.uva.nl
