Social Network Analysis in Gephi
Diliara Valeeva
University of Warsaw | 18 April 2024
Introductions
Plan for today
1. Basic network terminology
2. Key network actors
3. Communities
4. Visualization

What is a network?
Nodes
are entities with the network
e.g. people
organizations
countries
Edges
are connections or relationships between the nodes
e.g. friendship
communication
a business transaction
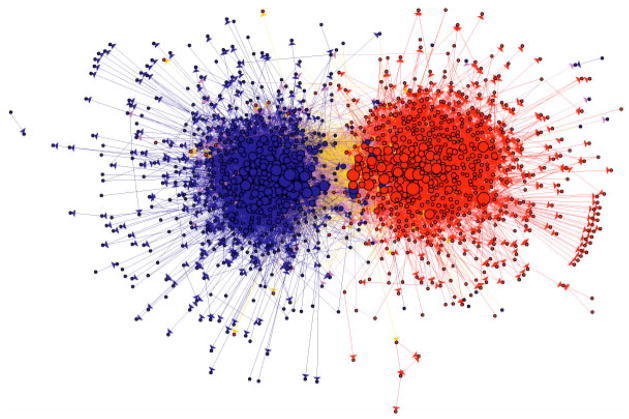
Political blogs
Adamic & Glance (2005)
Racial segregation in school
Moody (2001)
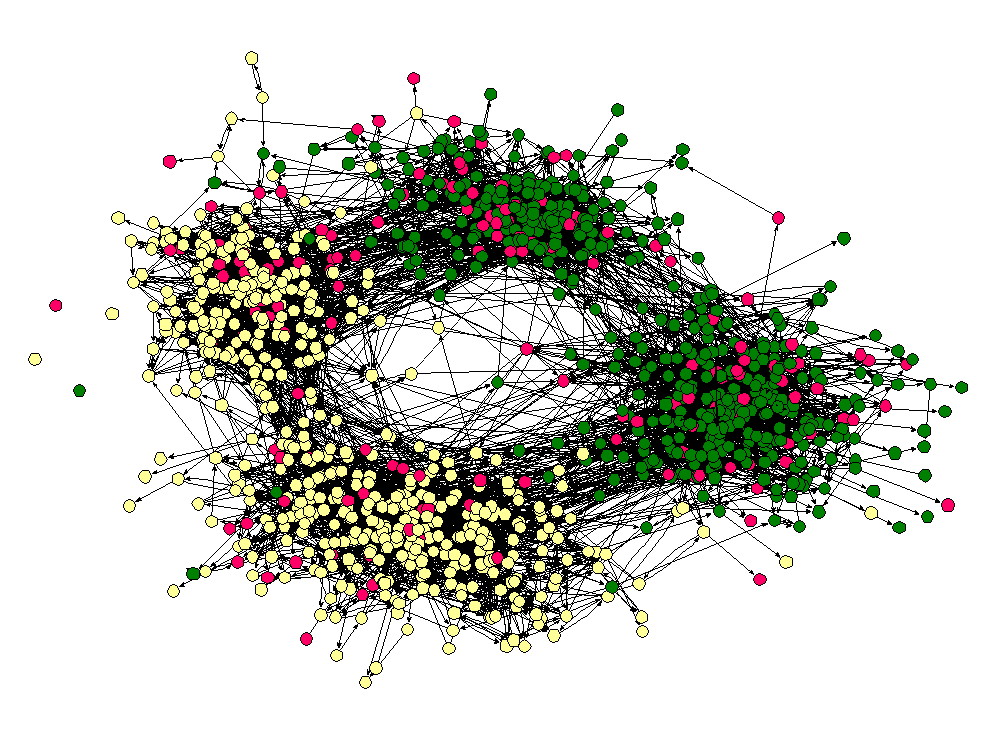
Kilpatrick & Randolph (2012)
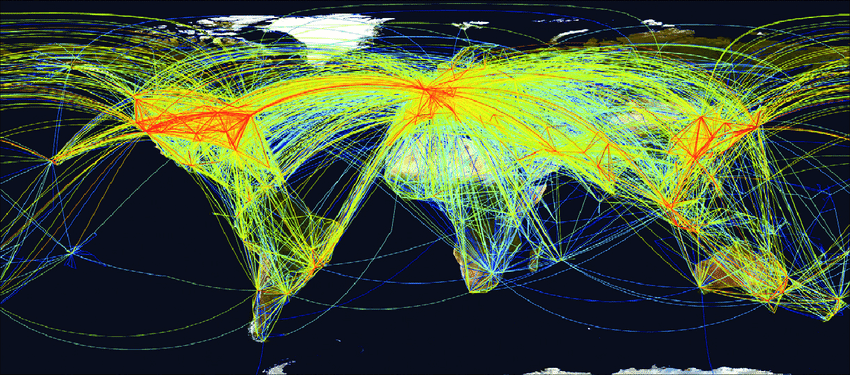
Airline network
Network types
Directed networks
Directed: edges have a direction, indicating the relationship flows from one node to another (e.g. Twitter followers, sanctions between countries)
* opposite is undirected
directed
undirected
Weighted networks
Weighted: edges carry a value that represents the strength of interaction between nodes (e.g. the number of emails exchanged between co-workers)
* opposite is unweighted
unweighted
weighted
One-mode and two-mode
One-mode: has only one type of node, and all connections occur between these similar nodes e.g. friendship
Two-mode: has two different types of nodes, and connections occur between nodes of different types e.g. countries and international organizations
one-mode
two-mode
Ego-networks
Ego-networks: focus on a single node (the ego) and all the nodes to which it is directly connected, as well as the connections between them e.g. ego-network of a country and its trade treaties with other countries
ego
Signed networks
Signed networks: edges have values that denote positive or negative relationships e.g. social media likes and dislikes
+
+
+
-
-
... and many more
Title Text
Data
#biden2020
#bloomberg2020
#buttigieg2020
#gabbard2020
#klobuchar2020
#sanders2020
#steyer2020
#warren2020
#trump2020
#weld2020

#biden2020
#bloomberg2020
#buttigieg2020
#gabbard2020
#klobuchar2020
#sanders2020
#steyer2020
#warren2020
#trump2020
#weld2020

node: user
edge: retweet
hashtag
How is 2020 US presidency
discussion network structured?

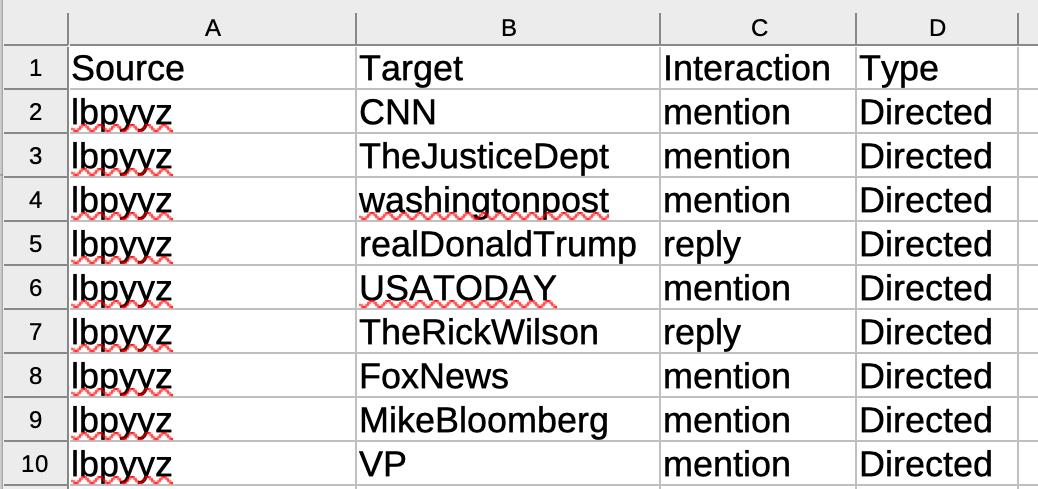
Download datasets
Nodelist
Edgelist
Gephi Tutorial
Step 1:
Create a Gephi project
Title Text
By SlvrKy - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=50571810
Title Text

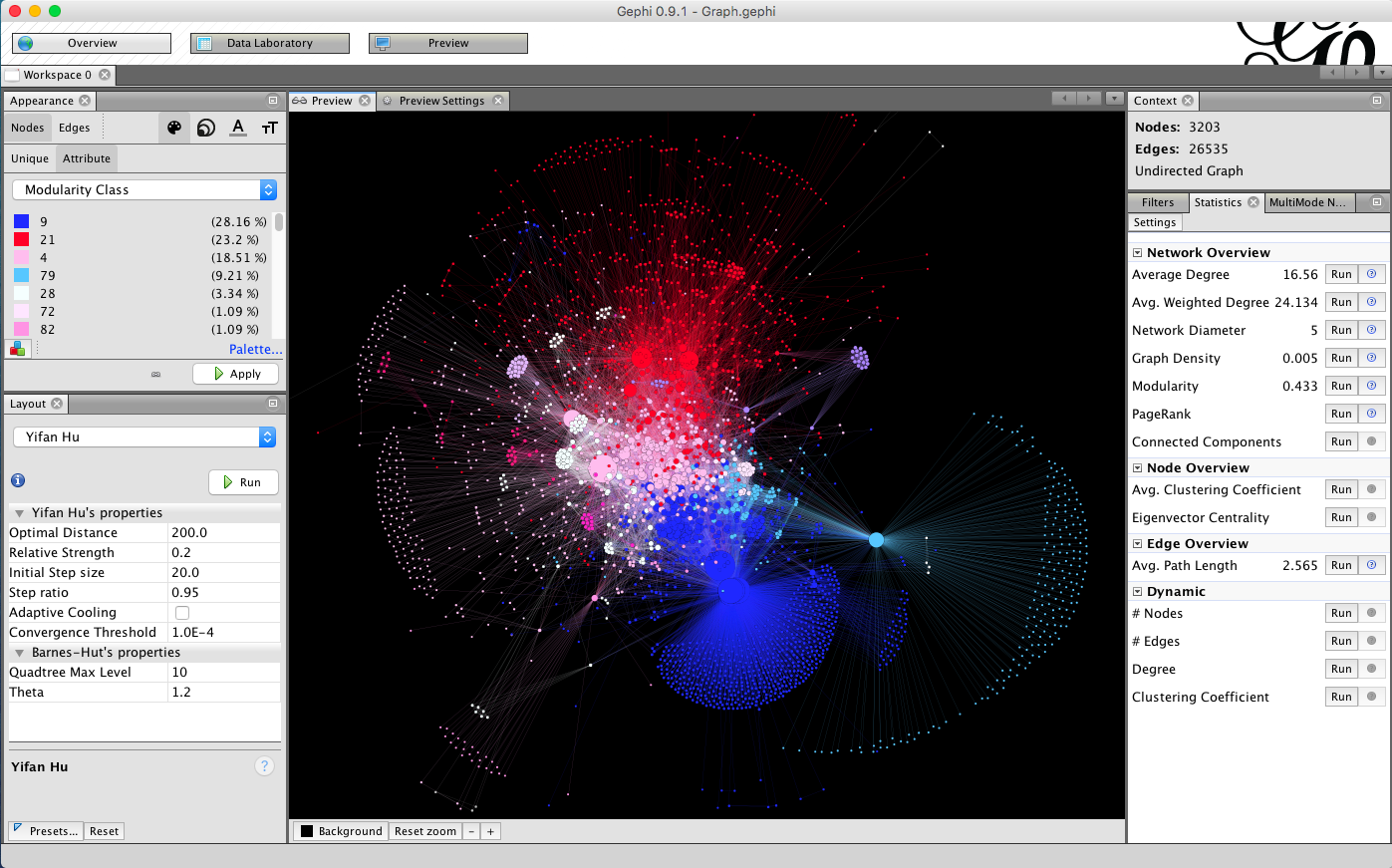
for network statistics
for data import/export
for adjusting visualization
Step 2:
First network visualization
Step 3:
Network centralities
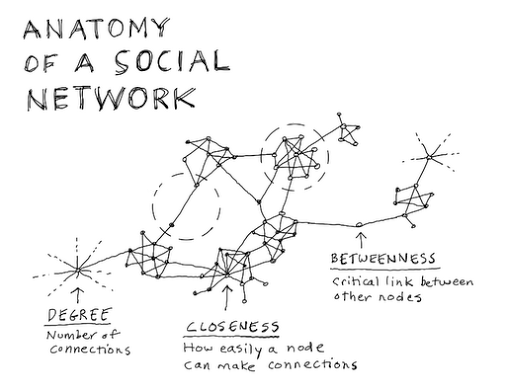
Degree centrality of a node is the number of connections it has to other nodes
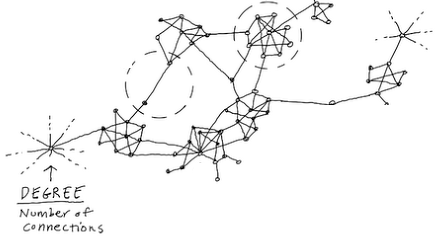
Degree centrality
In directed networks, degree centrality is a sum of indegree and outdegree
Indegree centrality: number of incoming ties
Outdegree centrality: number of outcoming ties

Degree centrality
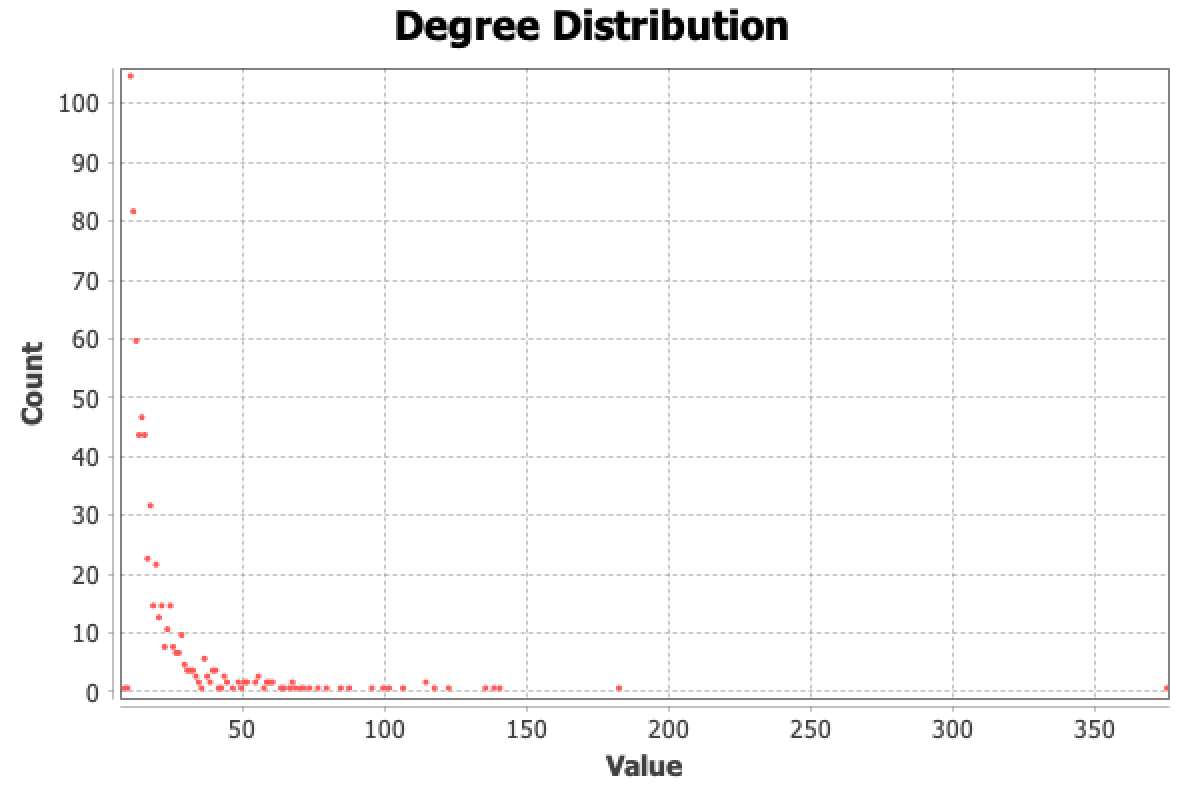
In many real-world social networks, the degree distribution follows a power law
It means that most nodes have relatively few connections, but a few nodes (hubs) have a large number of connections
This is often referred to as a scale-free network
Typical degree distribution

Closeness centrality is the reciprocal of the sum of the length of the shortest paths between the node and all other nodes in the network.
Closeness centrality
Shortest path: the minimum path of edges that must be traversed in a network to travel from one node to another.

Network paths
Shortest path: the minimum path of edges that must be traversed in a network to travel from one node to another.

10
Network paths
Shortest path: the minimum path of edges that must be traversed in a network to travel from one node to another.

9
10
Network paths

Betweenness centrality quantifies the number of times a node acts as a bridge along the shortest path between two other nodes in the network
Betweenness centrality
Average path length is the average number of steps along the shortest paths for all possible pairs of network nodes. Most real networks have a very short average path length
Network paths
Network diameter is the longest of all the shortest paths between any pair of nodes in the network

Continue working on Step 2
and explore the most central nodes
Small world networks
Have you ever heard about the six handshakes rule?
Small-world networks have high clustering coefficient and close distances.
High clustering: high probability that two friends of one person are friends themselves.
Close distances: there is a short path of connections between any two people
Small world networks
Step 4:
Update network visualization
Step 5:
Filters
Step 6:
Network community detection
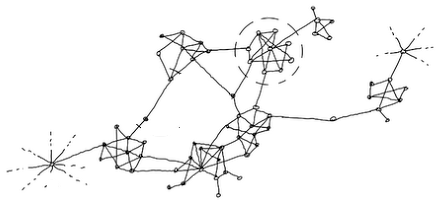
Network communities
Community detection helps in identifying the clusters of nodes that are more densely connected to each other than to other nodes in the network
Modularity detects network communities
High modularity: dense intra-community, sparse inter-community ties


Qualitative interpretation is the key to community detection

democrats
Trump-related
influencers
news media
mixed
Step 7:
Final touches
What we did today
1. Basic network terminology
2. Key network actors
3. Communities
4. Visualization

Would like to learn more?
Check "Awesome Network Analysis" list of resources: