Green Bytes
How Enhancing Web Vitals Contributes to Environmental Sustainability
Dimitris Kiriakakis
Fullstack Developer @ ZEAL
Who am I
-
Writing code professionally since 2013
-
Sharing blog posts about web vitals, web performance, sustainability and other topics on Medium and Dev.To (@dimeloper)

Overview
-
The carbon footprint of Web Activities
-
Web Vitals review
-
Web Vitals and carbon footprint (use cases)
-
Useful tools and websites
The internet consumes a lot of electricity.
Electricity means emissions.
a. 1.5% of global CO2 emissions
b. 2.5%
c. 3.5%
3.7%* of worldwide CO2 emissions
That's almost equal to the emissions
of the aviation industry.
*source: bbc.in/35mLuxM
Carbon footprint of Websites
-
Caused by infrastructure, data transfer, device usage
-
Page weight impacts all footprint factors
Page weight refers to the total size of a webpage, including all the files, images, scripts, and other content downloaded when a user visits a website.
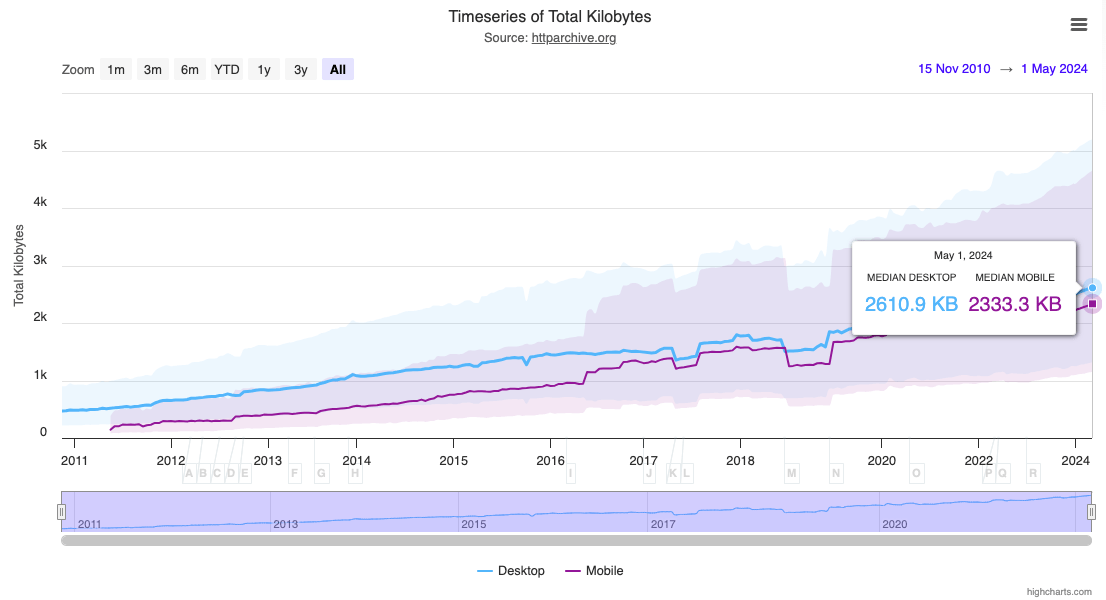
A website's average page weight has steadily increased over the years.
2011: 524.4 KB (desktop) and 202.5 KB (mobile)
2024:
"Shaving off 1 kilobyte in a file that is being loaded on 2 million websites reduces CO2 emissions by an estimated 2950kg per month.*"
"Like cancelling 5 flights from AMS to NYC."
*source: dannyvankooten.com
Web Vitals
A set of metrics that measure real-world user experience for loading performance, interactivity and visual stability of a web page.
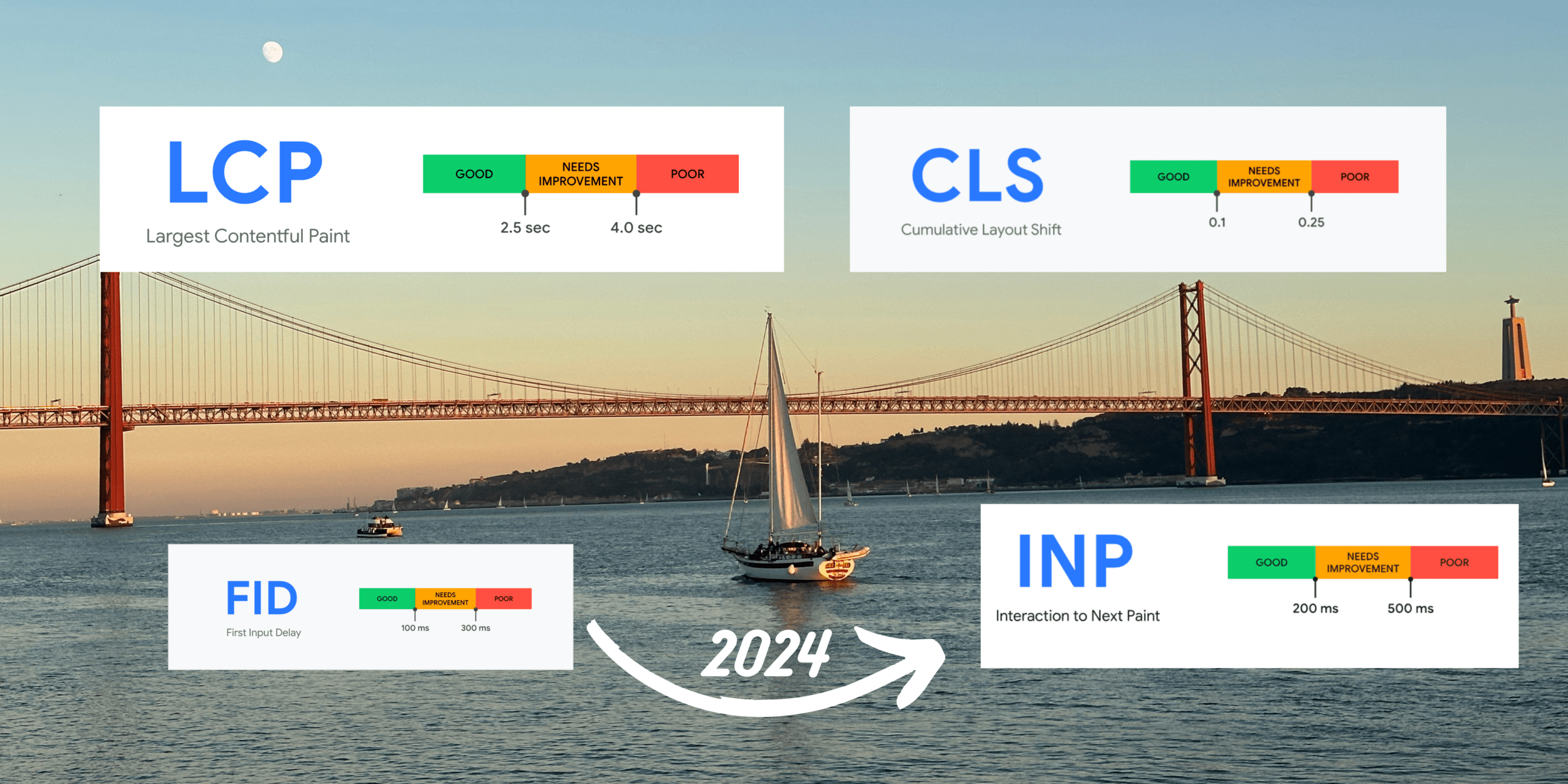
Loading Performance
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) is the Core Web Vital metric for measuring load speed.
It reports the render time of the largest image or text block visible in the viewport, relative to when the user first navigated to the page.
To provide a good user experience, sites should have an LCP score of 2.5 seconds or less.

Interactivity
Interaction to Next Paint (INP) is the Core Web Vital metric for measuring interactivity.
INP observes the latency of all click, tap, and keyboard interactions with a page throughout its lifespan, and reports the longest duration.
An INP equal to or less than 200 ms means our page has good responsiveness.

Visual Stability
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) is the Core Web Vital metric for measuring visual stability.
It helps quantify how often users experience unexpected layout shifts.
To provide a good user experience, our site must have a CLS score of 0.1 or less.

Use Case 1: A sample web app
Actions taken to improve Web Vitals
-
Reduced the size of images, converted to webp format
-
Prioritised LCP image loading
-
Deferred loading of other elements
-
Eliminated layout shifts
-
Page weight was decreased by ~70%
More details: dimeloper.com/angular-optimization
Performance impact
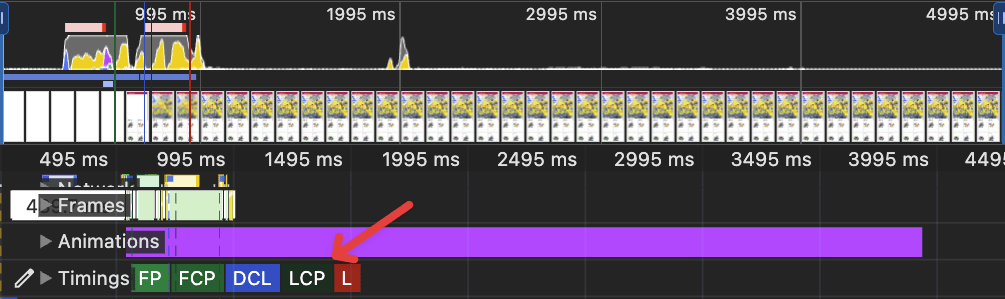
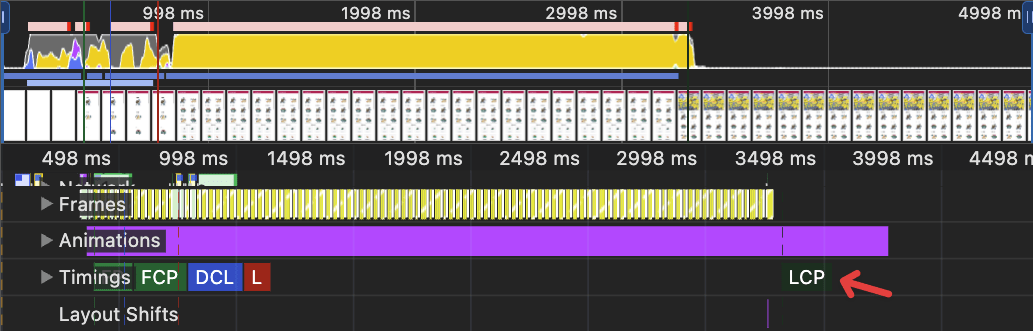
before
after
Carbon footprint impact


*source: digitalbeacon.co
Use Case 2: Lotto24
In early 2021 we started optimising the ZEAL websites to improve their performance and web vitals scores.
source: google lightouse, best run out of 10 runs
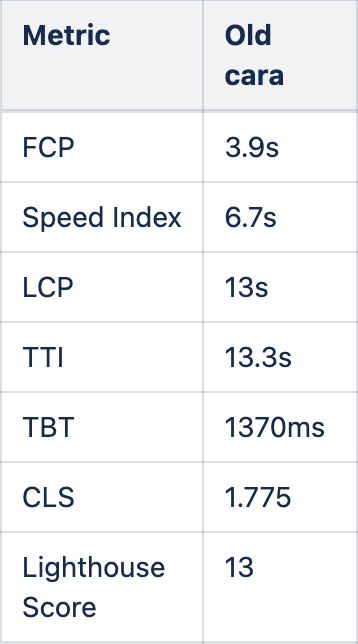
Back then, the carbon footprint for Lotto24 was 1.13g of CO2 per page load*.

*source: websitecarbon.com
..and if we consider that in 2022 the page was loaded 22 million* times, it generated:
~25 tonnes of CO2 emissions
That's the equivalent of burning
~10.000 litres (3000 gallons) of gasoline.
*source: our data team :)
Fast forward to 2024, now we finally have websites that are about to pass the assessment.
source: pagespeed.web.dev
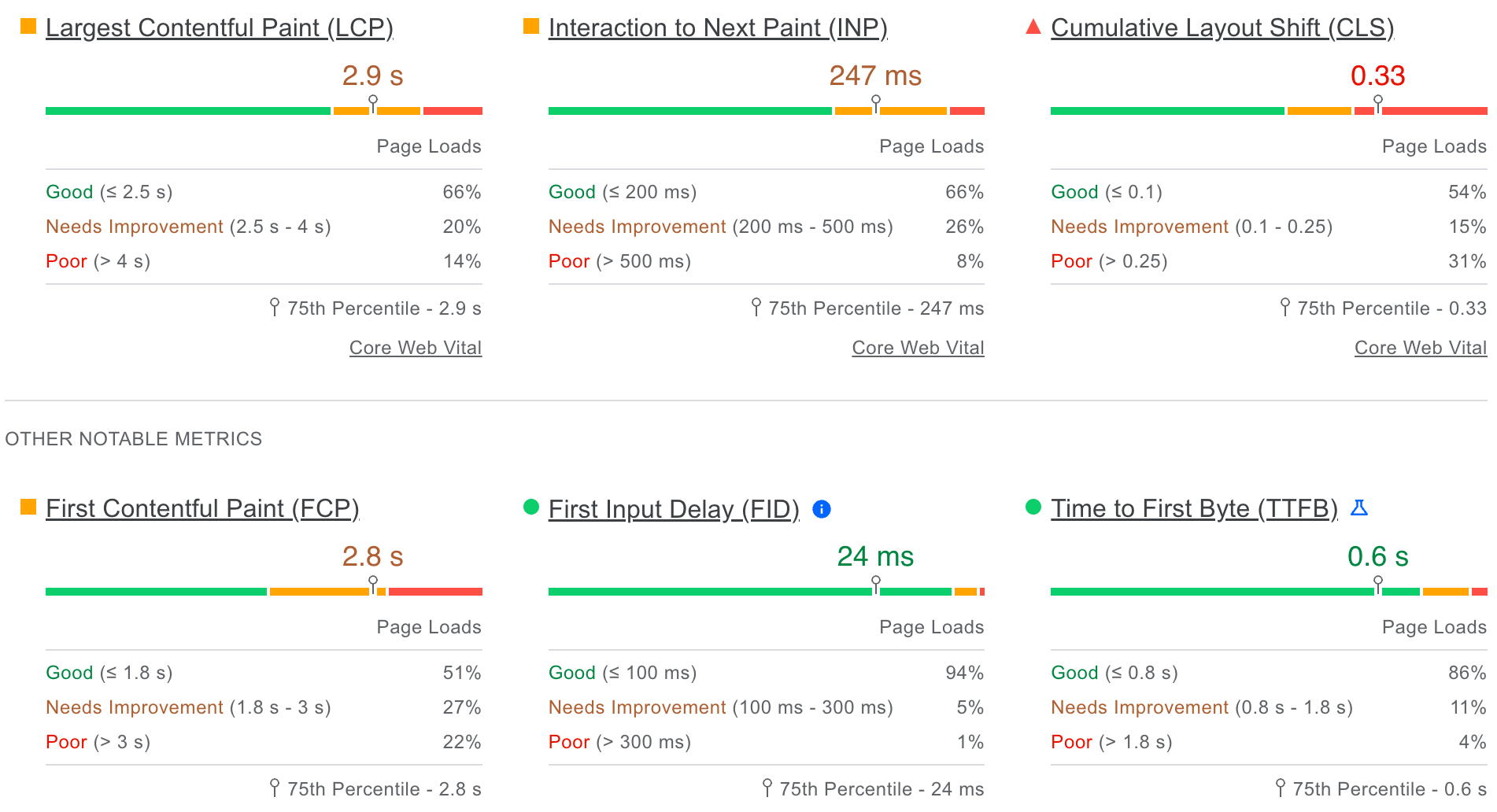
..and our carbon footprint has been reduced to 0.39g of CO2 per page load.
source: websitecarbon.com

..this already translates to an annual reduction of..
~16 tonnes of CO2 emissions
That's the equivalent of saving ~7000 liters (2000 gallons) of gasoline..
..every year.

Summary
Improving the Web Vitals scores of a website leads to smaller page weight and significant carbon footprint reduction.
-
Improving the LCP of a website is not possible without assets optimisation and deferred loading of other elements.
-
Better INP score means less processing power is required in client devices.
-
Eliminating layout shifts (CLS) ensures the stability of viewport elements and efficient lazy loading.
Summary
Other things that can help reducing the carbon footprint:
- Switch to green hosting providers.
- Serve assets via CDN to reduce the distance that data has to travel between servers and users' devices.
- Efficient caching policies (return visits).
Useful Tools & Websites
Measuring carbon footprint:
-
digitalbeacon.co (+return visit)
-
ecoping.earth (enterprise)
Green hosting directory:
Community:
Questions?

Slides
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/kiriakakis
Twitter: @dimeloper

