Java Swing
Content
Intro
MVC Pattern
Basic Components
Layoutmanager
Example: Basic Swing App
Intro
- AWT disadvantages
- OS provides window and dialog elements
- Difficult to achieve unified look and feel
- Porting problems due to OS differences
- Required lots of effort to unify behaviour
- Small set of elements provided by AWT
- Swing characteristics
- Components require minimum amount of platform specific GUI resources
- Besides top-level window, dialogs and primitive operations, all GUI elements implemented in java
- E.g. JButton not provided by Windows UI-Manager, entirely implemented in Java
Swing Characteristics
- Swing codebase is cleaner, since only minimal platform specific code
- Unified look and feel
- Independent of common platform components
- May introduce new components
- Lightweight component
- Paint method not defered to OS specific resources
- Implemented via primitive graphic operations
- AWT components are heavyweight
- Pluggable look and feel
- May change during runtime
Model View Controller
- Divide codebase into three areas
- Modell: holds the data
- View: is concerned about the graphical presentation
- Controller: connects modell with view
- Model-Delegate Pattern
- Similar to MVC
- View and Controller packed in a UI-Delegate
- Easier to implement since view and controller no separate
Basic Swing App
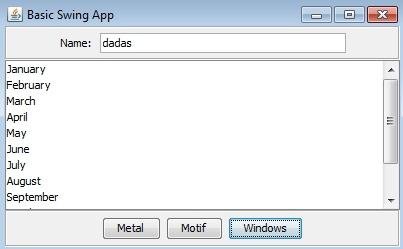
Basic Swing App
public class BasicFrame extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
// ...
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) {
// ...
}
}- Main class extends JFrame
- Implements ActionListener
- Overrides actionPerformed
- Adds known WindowClosingAdapter
JFrame
// JFrame class in JSE
public class JFrame extends Frame implements ... {
// ...
}
// Content pane as container
JPanel namePanel = new JPanel();
namePanel.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder());
getContentPane().add(namePanel, BorderLayout.NORTH);
- Extends an AWT Frame
- Creates a Swing window (JDialog, JWindow, JApplet)
- Container is a content pane
JPanel
// JPanel class in JSE
public class JPanel extends JComponent implements ... {
// ...
}
// Usage
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel();
buttonPanel.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder());
getContentPane().add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);- Extends JComponent
- Allows the usage of another layout manager
- Allows borders
- General purpose container
JLabel & JTextField
// JLabel class in JSE
public class JLabel extends JComponent implements ... {
// ...
}
// JTextField class in JSE
public class JTextField extends JTextComponent implements ... {
// ...
}
// JLabel usage
JLabel nameLabel = new JLabel("Name: ", new ImageIcon("triblue.gif"), SwingConstants.LEFT);
// JTextField usage
JTextField tf = new JTextField(30);- JLabel
- Used to display immutable
- May display an icon
- JTextField
- Simple text input
- Use JPasswordField for password inputs
Tooltip and Borders
// Tooltip on JButton
JButton btn1 = new JButton("Metal");
btn1.setToolTipText("Activate Metal-Look-and-Feel");
// Borders
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel();
buttonPanel.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder());- Tooltip via setToolTipText(...)
- Borders
- Feature of JComponent
- Pass a Border instance
- Created with BorderFactory
JList
String[] MONTHS = {
"January", "February", "March", "April",
"May", "June", "July", "August",
"September", "October", "November", "December",
};
JList list = new JList(MONTHS);- List of values, one or multiple entries selectable
- Pass list of values or
- Pass instance of ListModel to display complex and dynamic data structures
JScrollPane
JList list = new JList(MONTHS);
list.setToolTipText("Choose your birthdate");
getContentPane().add(new JScrollPane(list), BorderLayout.CENTER);- Allows scrolling on bigger components
- Handles scrolling logic
Look and Feel
UIManager.setLookAndFeel("com.sun.java.swing.plaf.windows.WindowsLookAndFeel");
SwingUtilities.updateComponentTreeUI(this);- Use UIManager to set look and feel
- USe SwingUtilities to update component tree to refresh style
Layout Manager
- In some GUI systems absolute coords are used to position components
- AWT designers opted to use a layout manager
- Layout manager handles position of components
- Specify layout manager via setLayout method
- Components are passed to the add method, positions determined by layout manager
Layout Manager Overview
- FlowLayout
- Position elements horizontally
- Jump to next line if no horizontal space left
- GridLayout
- Specify a rectangular grid
- Number of colmuns and rows defined when initializing
- BorderLayout
- Position on borders of container or middle
- CardLayout
- Holds multiple containers, allows to display one component at a time
- GridBagLayout
- Extends functionalities of GridLayout
References
Handbuch der Java-Programmierung
(5. Auflage)
Thank you for your attention!