
A Full Day of Vue.js
Day 1 - Extras
Component Templates
In simple standalone Vue applications, we can declare the template of a component in:
Vue.component('name-of-component', {
template: '<p>Hello World</p>',
});
- Single Line Strings
- Multiline format with back-ticks
- Inline Templates
- X-Templates
Component Templates
Vue.component('greetings-component', {
template: '<div>Hello World</div>',
});
Single Line Strings
Component Templates
Vue.component('greetings-component', {
template: `
<div> <h1>Hello World</h1> <p>This is the Hello World component</p> </div> `, });
Multiline format with back-ticks (template literals)
Component Templates
Inline Templates
<div id="app"> <greeting-component inline-template> <div> <h1>Hello World</h1> <p>This is the Hello World component</p> </div> </greeting-component> </div>
The inline-template attribute tells the component to take inner content as the template.
Component Templates
Inline Templates

Component Templates
X-Templates
<div id="app">
<greeting-component></greeting-component>
<script type="text/x-template" id="greeting-template"> <div> <h1>Hello World</h1> <p>This is the Hello World component</p> </div> </script> </div>
Vue.component('greeting-component', {
id: '#greeting-template'
});
The text/x-template type attribute tells the component to take inner content of a separate script element with same id.
Component Templates
X-Templates

Component Templates
Best Practice
- Stick with template option for simple standalone components
- Use Single File Components if building a Webpack bundled larger app.
Render Functions
At build times, Vue compiles instance templates to something known as render functions. At these render functions, Vue builds an in-memory view (i.e. the Virtual DOM) that is maintained/managed and tracked.
We can also use these render functions to craft the DOM/markup of our instances!
Render Functions
Vue.component('name-of-component', {
render(createElement) {
},
});
Render functions always have access to the createElement function as a payload.
Render Functions
createElement(' ',{ },[ ]);
createElement is the function that creates the virtual node - part of the virtual DOM tree
createElement has three arguments:
HTML Tag Name for Node
OR a components options object
Data object to specify attrs of constructed node
Child Nodes of the Parent Node
Render Functions
Vue.component('name-of-component', {
render(createElement) {
return createElement('div');
},
});
Render Functions
Vue.component('name-of-component', {
render(createElement) {
return createElement(
'div', {'attrs': {class: 'heading'}}
);
},
});
Render Functions
Vue.component('name-of-component', {
render(createElement) {
return createElement(
'div', {'attrs': {class: 'heading'}}, 'Hello World!'
);
},
});
Render Functions
Vue.component('name-of-component', {
render(h) {
return h(
'div', {'attrs': {class: 'heading'}}, 'Hello World!'
);
},
});
Render Functions
😅
Render functions aren't easy to use - hence why Vue recommends sticking with templates unless you want to do certain things that render functions may be of better help.
Render Functions
Render functions can output JSX if an appropriate babel plugin is used.
Vue.component('name-of-component', {
render(h) {
return (
<div>Hello World!</div>
)
},
});
Render Functions
Closing Remark. Good to know about render functions.... but you don't usually need to worry about them.
CSS Frameworks



Some popular CSS frameworks
Bulma
Bootstrap
Semantic UI
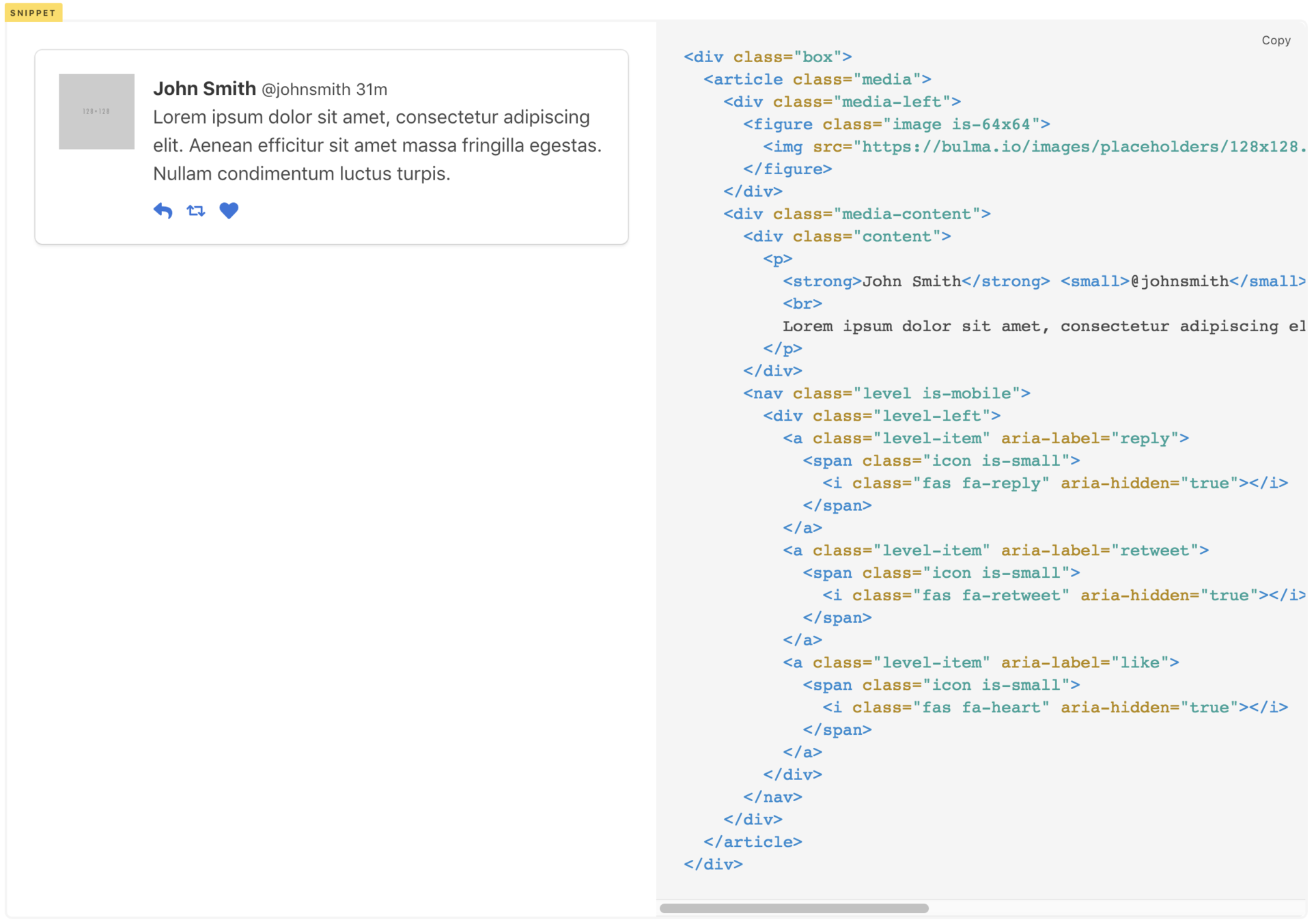

BoxComponent
CSS Frameworks
CSS Frameworks
Simple ways of introducing CSS frameworks to
Webpack Applications
CSS Frameworks
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="icon" href="<%= BASE_URL %>favicon.ico">
<title>Project Two: Calendar App</title>
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="<%= BASE_URL %>bulma/bulma.css">
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="<%= BASE_URL %>font-awesome/css/font-awesome.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<noscript>
<strong>We're sorry but Project Two: Calendar App doesn't work properly without JavaScript...</strong>
</noscript>
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- built files will be auto injected -->
</body>
</html>
- index.html is processed with html-webpack-plugin
- Uses lodash templates to interpolate values like <%= BASE_URL %>
- BASE_URL the application will be deployed at - by default is the root of the domain (https://example.com/)
Direct reference to file paths
CSS Frameworks
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="icon" href="<%= BASE_URL %>favicon.ico">
<title>Project Two: Calendar App</title>
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/bulma/0.5.3/css/bulma.css">
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="https://use.fontawesome.com/releases/v5.0.6/css/all.css">
</head>
<body>
<noscript>
<strong>We're sorry but Project Two: Calendar App doesn't work properly without JavaScript...</strong>
</noscript>
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- built files will be auto injected -->
</body>
</html>
Direct reference to CDN
CSS Frameworks
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
import 'semantic-ui-css/semantic.css';
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')