Conditionals & User Inputs

Working with Numbers
In JavaScript, we can assign plain numbers to variables too. We can also reassign them and use them in other places in our JavaScript.
var myNum = 5
var numDisplay = document.querySelector('p')
var button = document.querySelector('button')
function addFive() {
myNum = myNum + 5;
numDisplay.textContent = myNum
}
button.addEventListener('click', addFive)Inputs and Values
In HTML, we can create input fields and drop downs using input and select tags respectively.
<input type="text"/><select>
<option>apples</option>
<option>bananas</option>
<option>oranges</option>
</select>input tag
select and option
Inputs and Values
In JavaScript, we can select the values of inputs or selects using the .value property.
var nameInput = document.querySelector('#name-input')
var userName = document.querySelector('h2')
var btn = document.querySelector('button')
function changeName() {
userName.textContent = nameInput.value
}
btn.addEventListener('click', changeName).value
event.target
We can write one function that will affect multiple elements by using the event parameter and the property target.
var div = document.querySelector('div')
var section = document.querySelector('section')
var aside = document.querySelector('aside')
function changeElemColor(event) {
event.target.classList.add('red')
}
div.addEventListener('click', changeDivColor)
section.addEventListener('click', changeSectionColor)
aside.addEventListener('click', changeAsideColor)Comparison Operators
< less than
> greater than
=== equal to
<= less than or equal to
>= greater than or equal to
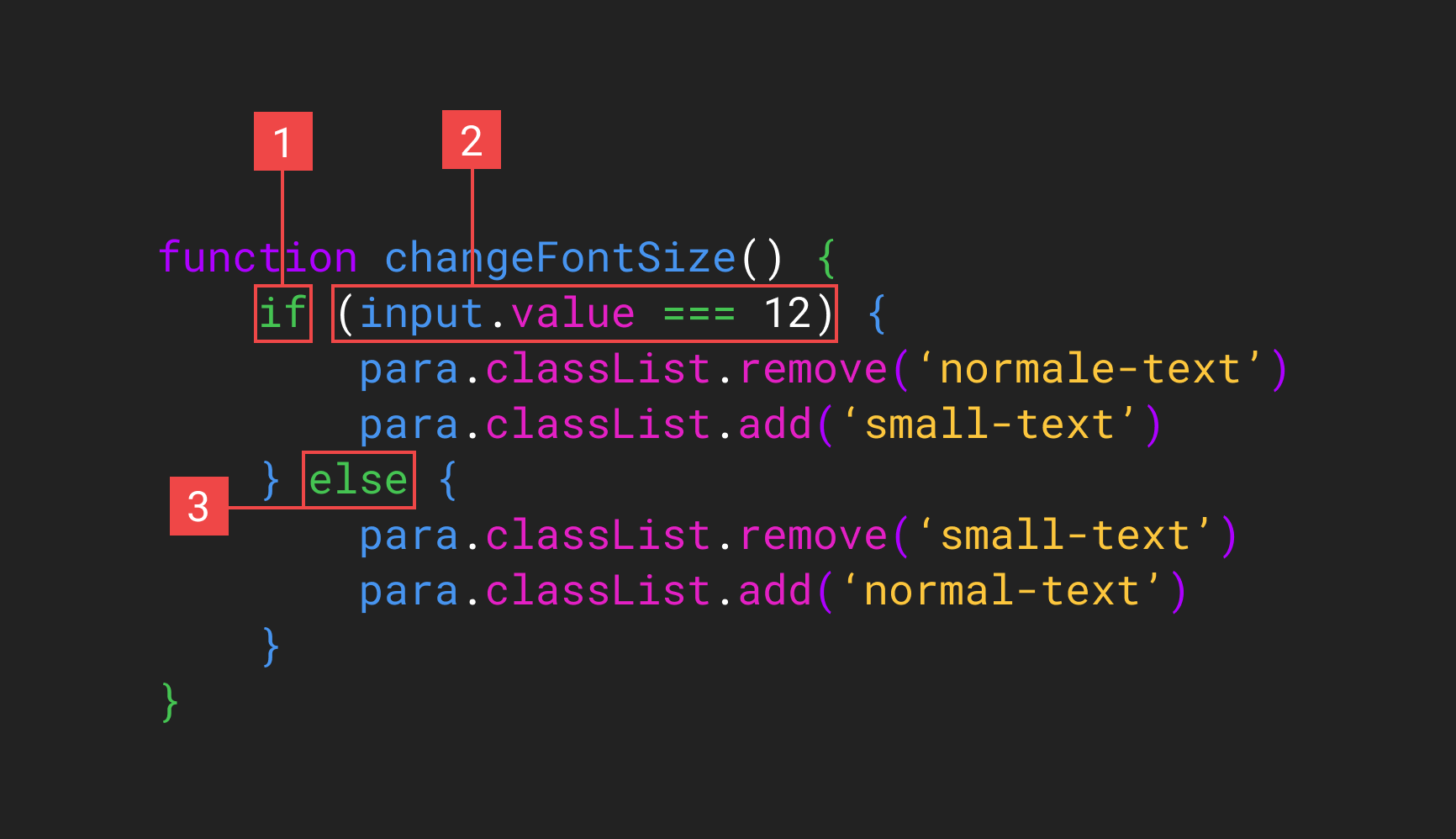
Conditional Statement Structure