HTML 2


Formatting Elements
Built in Style Tags
- We often want to apply styles to text to emphasize a certain point or have the text jump out on the page
Applying Custom Styles Using Span Tags
- Sometimes we want to be more specific with the styles applied
- The span tag is perfect for applying custom css to a subsection of text
- The span tag applies no visual changes by itself
URLs and Linking
U(niform) R(esource) L(ocator) anatomy
In order to request information on the World Wide Web, resources must have an address they can be located at. This address is located using a URL. An example of a URL is https://google.com?search_term=hello%20world.
-
A full URL is made up of the following parts https://user:password@www.example.com:80/search?q=term&lang=en#results
- https is the Protocol to use
- user:password is the user information. Often left out or sent via headers
- www.example.com is the host. This is the DNS name or IP address of the server
- :80 is the port the server is using to listen for incoming requests
- /search is the file name or file extension on the server
- ?q=term&lang=en are the optional queries passed to the server
- #results is the optional anchor, or spot on the page to jump to
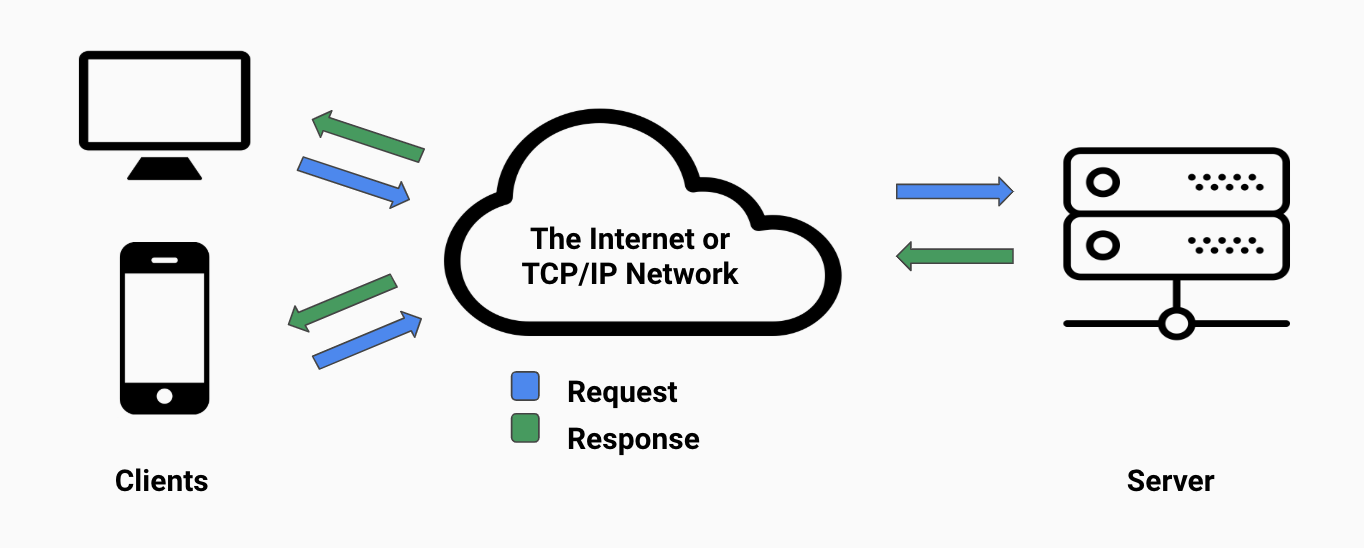
How internet requests are fulfilled
The internet is a complicated construct. Requests and responses moving at nearly the speed of light in some cases zip over the internet cables delivering packets of data between computers. Let's take a short look at how these request/responses find their destinations.
- The client (pc, laptop, iPhone etc.) makes an outgoing request using a URL
- The request is processed by many different servers until a server is found that knows the location of the requested resource
- The request is forwarded on to the server, who processes the request, formats a response and sends it back
- The request is then processed by the same servers until it reaches the client
Hyperlinking: connecting the web
- We can link to other web pages in our document. Either external or internal
- We can use the a tag to create Hyperlinks on our page
- The link address is specified using the href attribute
- Links can be used to open your mail client, jump to a specific section of your webpage or open a new tab
Lists
Ordered List
- It's often useful to create lists on our webpage
- To create an ordered list, we can use the ol and li tags
Unordered List
- Similar to an ordered list, we can create an unordered list using the ul tag
- We can change the type of the bullets by changing the style attribute
Tables
Table Syntax
- The table tag defines the opening and closing of the table
- The tr tag defines rows in the table
- The td tag defines the data
- The th tag defines the table heading
- The caption tag defines the table caption
Table Spans
- the colspan attribute makes cells span multiple columns
- likewise, the rowspan attribute makes cells span multiple rows
Head, body and foote
- Adding tbody, thead and tfoot allows us to structure our tables better
- tbody allows for the browser to scroll in the table body independent of the head or body
- These elements will ensure that large tables that span multiple pages will have the table header and footer printed at the top and bottom of each page