Dom Taylor
Religion and Social Work Librarian
What does reliable information look like?
November 28, 2017
Evaluating sources
Student Nights Against Procrastination series
Overview
-
Disinformation online
-
Social media as evidence
-
Overview of our own biases
-
3 ways to filter out disinformation and bias
There seems to be a lot of disinformation on the Internet
Disinformation:
false information deliberately presented as true or real
Misinformation:
false information unintentionally presented as true or real
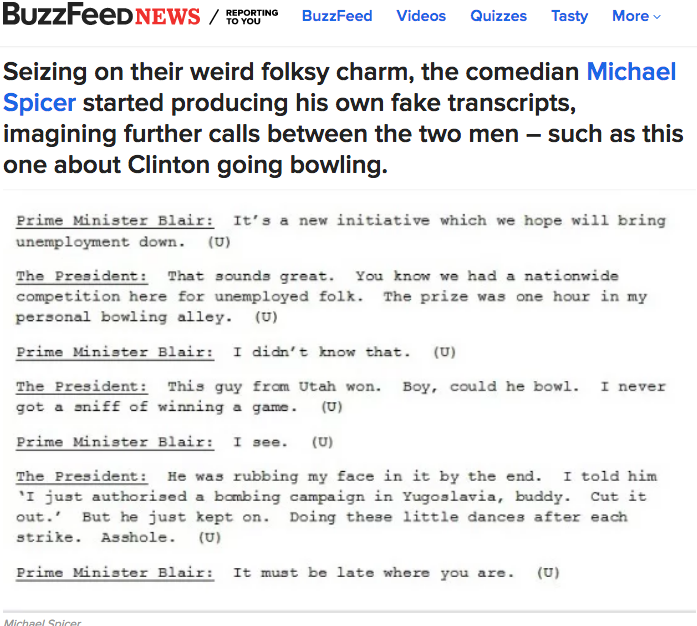
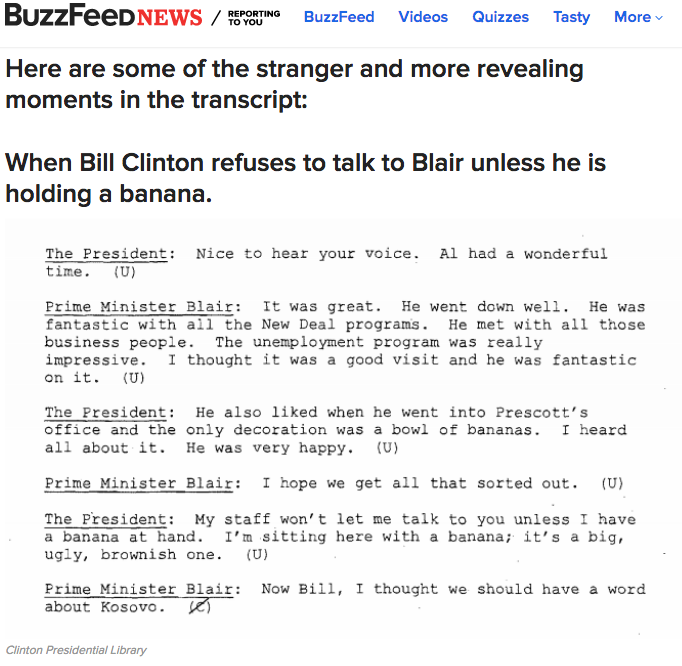
It's tough to figure out
Especially when the truth is bizarre
Here is the link to a digitized version of the original transcripts from the William J. Clinton Presidential Library & Museum
We are bombarded by manipulated information
At least there's the trusty paper...
Even established newspapers now publish "advertorials"/sponsored content. It can sometimes be hard to spot. Look for clues in the header or the footer of the article. Find out who the author is.
To make things more complicated, social media can be used as evidence
The Syrian Archive preserves social media evidence of human rights violations for war crimes tribunals.
Oh... and then there's our BRAINS

Cognitive biases
Humans have a tendency to believe or look for information that:
(1) confirms the beliefs they already believe
(2) makes them feel good about themselves
(3) makes people they care about look good
Humans have a tendency to discount information that:
(1) questions things they already believe
(2) makes them feel bad about themselves
(3) makes people they care about look or feel bad
Photo credit: FOTO:FORTEPAN / MHSZ (2016, CC BY-SA 3.0)
Source: Lenker, M. (2016). Motivated Reasoning, Political Information, and Information Literacy Education. portal: Libraries and the Academy, 16(3), 511-528. https://doi.org/10.1353/pla.2016.0030
Takeaway: we sometimes believe things without good evidence and we sometimes believe things in spite of evidence.

How to deal with disinformation and bias
1.
Get some context: Look at the bigger picture
- How does the article/book/website relate to other information? How does it fit into the larger world?
- Rather than only analyzing an information source on its own merits (close reading), take a look at similar or related sources (e.g., this is a good time to use GoogleScholar or even just Google [especially if it's a website]).
- If you are reading a book, look at book reviews; these are available through our catalogue. If you are looking at an article look at who cited it and see if there are some differing views.
- Talk to your librarian. They can point you to other sources and/or help flesh out the context of a source.
2.
Distinguish between POV and evidence
- Assuming that all research is trying to show and/or make a case something, it is important to see if the information an author uses:
- Counts as appropriate evidence (e.g.,is it anecdotal, is it based on a study? Is there a review of alternative and similar theories? Is there argumentation for the POV)
- Supports the author's POV (e.g., is the argumentation linked to the POV? Is the author provided related, but not supportive, information?)
- Having a POV is not problematic in and of itself, but it needs to be supported by appropriate evidence to be credible.
3.
Check yourself
- Avoid cherry picking: Don't just look for information that supports your hypothesis/argument. Go broader and look at the context surrounding your POV.
- Strength in multiple perspectives: Even if you are sure your POV is right, think of plausible and credible counter-arguments or alternative perspectives. See if these alternative views have been written about. Addressing them usually makes the evidence supporting your POV stronger.
- Remember that we all have biases and that we tend to gravitate toward information that reflects those biases (this goes for accomplished scholars too).
Questions?
Dom Taylor
Religion and Social Work Librarian
Elizabeth Dafoe Library
dominique.taylor@umanitoba.ca
204-474-9184
THANKS!!!
Student Night Against Procrastination
Monday: Search like a pro
Tuesday: Evaluating sources
Wednesday: When to cite
Thursday: How to cite
Credits
All icons are from the Noun Project through a Creative Commons license (CC BY 4.0):
- Brain icon by Laymilk
- Newspaper icon by Andrey Vasiliev