Advanced Android traineship
Program
- android plateform tools
- MVP simple project
- Basic explanation
- first project
- Parse.com
- First injection with ButterKnife
- Dagger2
- Create a real project (Chat)
Android studio
- New android platform
- Based by JetBrains' IntelliJ IDEA
- Build system : Graddle
- Support Google TV, Google Wear, Google Glasses, ...
but don't support NDK ...
MVC => MVP
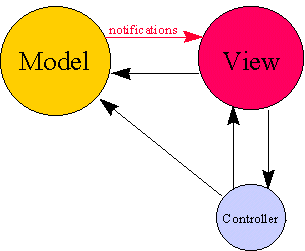
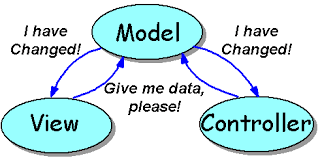
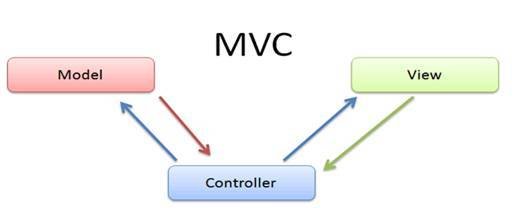
MVC
Model - View - Controller
View
What the user see
Model
Business data, databases interaction, Http request, local storage, ...
Controller
It's the glue between View and Model. It map data to send to View. It control user interaction and may change model's data
Interaction
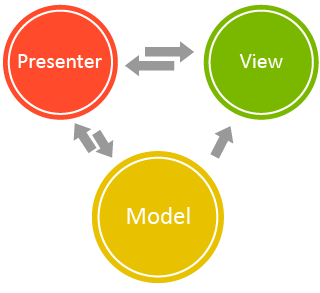
MVP
Model - View - Presenter
All presentation logic is pushed to presenter
View
The view is a passive interface that displays data (the model) and routes user commands (events) to the presenter to act upon that data.
Model
The model is an interface defining the data to be displayed or otherwise acted upon in the user interface.
Presenter
The presenter acts upon the model and the view. It retrieves data from repositories (the model), and formats it for display in the view.
The current activity or fragment
Business data, databases interaction, Http request, local storage, ...
The brain
public class MainActivity extends Activity implement ICustormerView
{
CustomerPresenter mCustomerPresenter;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mCustomerPresenter = new CustomerPresenter(this);
}
MVP
Let's code
New project
Project name : First Mvp
Blank Activity
Activity Name : MainActivity
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity">
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="25dp">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge"
android:text="id"
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_gravity="left" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="195dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="number"
android:ems="10"
android:id="@+id/idText"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_alignParentEnd="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="0dp"
android:layout_marginRight="0dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="25dp">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge"
android:text="lastname"
android:id="@+id/textView3" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="195dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="text"
android:ems="10"
android:id="@+id/lastNameEditText"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_alignParentEnd="true"/>
</RelativeLayout>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="25dp">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge"
android:text="firstname"
android:id="@+id/textView2" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="195dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="text"
android:ems="10"
android:id="@+id/firstNameEditText"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_alignParentEnd="true"/>
</RelativeLayout>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="100dp">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Save"
android:id="@+id/saveButton" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Load"
android:id="@+id/loadButton"
android:layout_gravity="right"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_alignParentEnd="true"/>
</RelativeLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>private EditText mFirstNameEditText, mLastNameEditText, mIdEditText;
private Button mSaveButton, LoadButton;
CustomerPresenter mCustomerPresenter;Add into MainActivity Class
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mIdEditText = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.idText);
mFirstNameEditText = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.firstNameEditText);
mLastNameEditText = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.lastNameEditText);
mSaveButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.saveButton);
mLoadButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.loadButton);
mCustomerPresenter = new CustomerPresenter(this);
mSaveButton.setOnClickListener(this);
mLoadButton.setOnClickListener(this);
}Add into onCreate
public CustomerPresenter(MainActivity mainActivity) {
}
public void saveCustomer (String firstName, String lastName) {
}
public void loadCustomer (int id) {
}Create customerPresenter
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements ICustomerView, View.OnClickListener {Go back on MainActivity
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.saveButton:
mCustomerPresenter.saveCustomer(mFirstNameEditText.getText().toString(),
mLastNameEditText.getText().toString());
break;
case R.id.loadButton:
String id = mIdEditText.getText().toString();
if (id.isEmpty()) { Toast.makeText(this, "Need to enter id", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); return ; }
mCustomerPresenter.loadCustomer(Integer.parseInt(mIdEditText.getText().toString()));
break;
}
}public interface ICustomerView {
void setLastName (String lastName);
void setFirstName (String firstName);
void setId(Integer id);
}Let's create ICustomerView
And create implement methods on MainActivity
@Override
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
mLastNameEditText.setText(lastName);
}
@Override
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
mFirstNameEditText.setText(firstName);
}
@Override
public void setId(Integer id) {
mIdEditText.setText(id.toString());
}public class CustomerPresenter {
private ICustomerView mCustomerView;
private ICustomerModel mCustomerModel;
public CustomerPresenter(ICustomerView view) {
mCustomerView = view;
mCustomerModel = new CustomerModel();
}
public CustomerPresenter(MainActivity mainActivity) {
mCustomerView = (ICustomerView)mainActivity;
mCustomerModel = new CustomerModel();
}
public void saveCustomer (String firstName, String lastName) {
mCustomerModel.setFirstName(firstName);
mCustomerModel.setLastName(lastName);
mCustomerModel.save();
}
public void loadCustomer (int id) {
mCustomerModel.load(id);
mCustomerView.setId(mCustomerModel.getId());
mCustomerView.setFirstName(mCustomerModel.getFirstName());
mCustomerView.setLastName(mCustomerModel.getLastName());
}Replace the CustomerPresenter
public interface ICustomerModel {
void setFirstName(String firstName);
void setLastName(String lastName);
void setId(Integer id);
String getFirstName();
String getLastName();
Integer getId();
ICustomerModel load(Integer id);
void save();
}Last but not the least, the Model !
ICustomerModel
public class CustomerModel implements ICustomerModel {
String firstName;
String lastName;
Integer id;
public CustomerModel() {
}
public CustomerModel(Integer id) {
}
@Override
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
@Override
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
@Override
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
@Override
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
@Override
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
@Override
public ICustomerModel load(Integer id) {
// read on db
this.id = 1;
firstName = "first";
lastName = "last";
return null;
}
@Override
public void save() {
// write on db
}
}
CustomerModel
Running MVP
Parse
No more backend developpement
What parse can do ?
- Databases
- ACL
- Notification
- Analytics
Running on many platform
Even physical
- Arduino
- Embedded C
Running on many language
Cost ? It's free ! ... until
- 30 requests per seconds
- 1 000 000 first push notification
- Analytics, unlimited free
More over
- Really easy to use
- No backend dev
- No server to manage
- Free until your application is really used
Parse
Let's dev
First create an account
Go on : https://www.parse.com
... and "sign up for free"
Create your application
You suppose to be on the dashboard
- Select "Data"
- Select "Mobile"
- Select "Android"
- Select "Native (Java)"
- Select "Existing project"
Download the SDK
Download the SDK, and put all file on app/libs

Add permission
And permission on AndroidManifest.xml, on <manifest></manifest>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />And add parse's init
Create new class CustomerApplication.java
public class CustomerApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Parse.enableLocalDatastore(this);
Parse.initialize(this, getString(R.string.parse_app_id), getString(R.string.parse_client_key));
ParseObject.registerSubclass(Customer.class);
}
}On strings.xml, add ...
<string name="parse_app_id">xCoCH4Ct98vUSr8wpBp3Ej9riw5nVM4qx9oi76nw</string>
<string name="parse_client_key">WUqycIkrmBjtbgMtQT939yuaxNtMzAtfv1Uuxd0t</string>Done, parse is set and up, let's use it
On acitvity_main, change for ...
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme"
android:name=".CustomerApplication">Save customers
We want to display the objectId on idText
- The user clic on save
- The view catch the click and call the presenter
- The presenter call the model
- The model communicate with parse
Let's return objectId
- Model callback presenter
- Presenter call the view
- ObjectId is displayed on idText
CustomerPresenter.java
public void saveCustomer (String firstName, String lastName) {
mCustomerModel.setFirstName(firstName);
mCustomerModel.setLastName(lastName);
mCustomerModel.save(new CustomerModelSaveCallback() {
@Override
public void done(CustomerModel customer) {
mCustomerView.setId(customer.getId());
}
});
}CustomerModelSaveCallback
public interface CustomerModelSaveCallback {
void done(CustomerModel customer);
}ICustomerModel
void save(CustomerModelSaveCallback callback);CustomerModel
@Override
public void save(final CustomerModelSaveCallback callback) {
customer.setFirstName(firstName);
customer.setLastName(lastName);
customer.saveInBackground(new SaveCallback() {
@Override
public void done(ParseException e) {
self.setId(customer.getObjectId());
callback.done(self);
}
});
}That's all

Code : load
CustomerModelLoadCallback
public interface CustomerModelLoadCallback {
void done(CustomerModel customer);
}CustomerPresenter
public void loadCustomer (String id) {
mCustomerModel.load(id, new CustomerModelLoadCallback() {
@Override
public void done(CustomerModel customer) {
mCustomerView.setId(customer.getId());
mCustomerView.setFirstName(customer.getFirstName());
mCustomerView.setLastName(customer.getLastName());
}
});
}ICustomerModel
void load(String id, CustomerModelLoadCallback callback);CustomerModel
@Override
public void load(String id, final CustomerModelLoadCallback callback) {
ParseQuery<Customer> query = ParseQuery.getQuery(Customer.class);
query.whereContains("objectId", id);
query.findInBackground(new FindCallback<Customer>() {
@Override
public void done(List<Customer> list, ParseException e) {
self.customer = list.get(0);
self.setId(self.customer.getObjectId());
self.setFirstName(self.customer.getFirstName());
self.setLastName(self.customer.getLastName());
callback.done(self);
}
});
}Code injection
Dagger / Butterknife
Code injection is done on compiling ...
Thing you should know
... so dependency and initialisation are checked on compilation
Module injection are done with singleton ...
... so you can get you modules every where in your code
You can inject different module following you environement ...
... one module for production using real API
... one module for developpement using fileDB
ButterKnife
View "injection" library for Android

Annotate fields with @InjectView and a view ID
class ExampleActivity extends Activity {
@InjectView(R.id.title) TextView title;
@Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.simple_activity);
ButterKnife.inject(this);
}
}Listener injection
@OnClick(R.id.submit)
public void submit(View view) {
// TODO submit data to server...
}Argument are optional
@OnClick(R.id.submit)
public void submit() {
// TODO submit data to server...
}Select multiple IDs
@OnClick({ R.id.door1, R.id.door2, R.id.door3 })
public void pickDoor(DoorView door) {
if (door.hasPrizeBehind()) {
Toast.makeText(this, "You win!", LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "Try again", LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}And more ...
@InjectViews({ R.id.first_name, R.id.middle_name, R.id.last_name })
List<EditText> nameViews;View list
ButterKnife.apply(nameViews, DISABLE);
ButterKnife.apply(nameViews, ENABLED, false);And apply action on them
@Optional @InjectView(R.id.might_not_be_there) TextView mightNotBeThere;By default, if target is not exist on the view, ButterKnife will throw an error. To suppress this behavior : @Optional
@OnItemSelected(R.id.list_view)
void onItemSelected(int position) {
// TODO ...
}Event on list
ButterKnife
Let's code
Gradle configuration
compile 'com.jakewharton:butterknife:6.1.0'Dagger
Dagger keyword
- @Inject
- @Module
- @Provide
- @Component
@Inject
We indicate to dagger we request this depedency injection. Dagger will construct instances of this annitated calsses and satisfy their dependencies.
@Module
Modules are classes whose methods provide dependencies, so we define a class and annotate it with @Module
@Provide
Inside modules we define methods containing this annotation which tells Dagger how we want to construct and provide those mentioned dependencies.
@Module
Components basically are injectors, its main responsibility is to put together @Inject and @Module
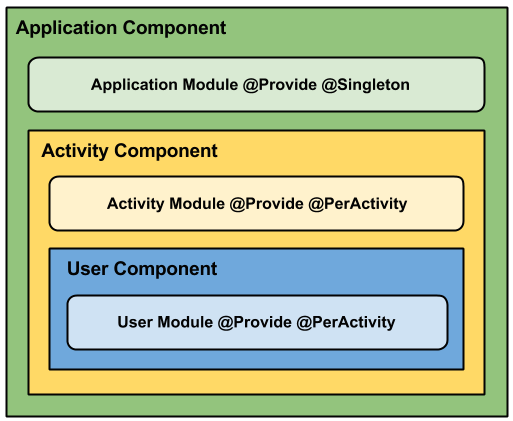
@Scope
Permit to define boundaries to injection. In other words, we can define the granularity of your scopes (@PerFragment, @PerUser, etc).
@Qualifier
Define context @ForApplication, @ForActivity
And more, there is @Scope, @Qualifier
Dagger2
Let's code
Dagger
Configuration
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
apply plugin: 'com.neenbedankt.android-apt'
android {
compileSdkVersion 22
buildToolsVersion "22.0.1"
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.meuuh.test.firstmvp"
minSdkVersion 16
targetSdkVersion 22
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
}
dependencies {
compile 'com.parse.bolts:bolts-android:1.+'
compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: 'Parse-*.jar')
compile 'com.jakewharton:butterknife:6.1.0'
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:22.1.1'
compile 'com.google.dagger:dagger:2.0'
apt 'com.google.dagger:dagger-compiler:2.0'
provided 'org.glassfish:javax.annotation:10.0-b28'
}
// Top-level build file where you can add configuration options common to all sub-projects/modules.
buildscript {
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:1.2.2'
// NOTE: Do not place your application dependencies here; they belong
// in the individual module build.gradle files
classpath 'com.neenbedankt.gradle.plugins:android-apt:1.4'
}
}
allprojects {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
maven{
url 'https://oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots/'
}
}
}build.gradle (Project)
build.gradle (Module)
Inject presenter
@Module
public class CustomerPresenterModule {
@Provides
@Singleton
CustomerPresenter provideCustomerPresenter() {
return new CustomerPresenter();
}
}CustomerPresenterModule.java
@Singleton
@Component(modules = {CustomerPresenterModule.class})
public interface CustomerPresenterComponent {
CustomerPresenter provideCustomerPresenter();
}
CustomerPresenterComponent.java
@Inject CustomerPresenter mCustomerPresenter;MainActivity
How and where to use it ?
Create Chat Application
Tests
Unit test
Unit testing is a procedure that checks a specific piece of software is abstracted from everything else in the application
Integration test
The integration test consolidates several changes to check if there are any errors during compilation of all these changes. (Jenkins, git)
Functional test
The functional test is a user scenario applied to a application screen. It simulates user interactions and audits on the data displayed on the graphical components that interfaces after testing.
Acceptance test
The acceptance test is designed to ensure that the project complies with the specifications. This step involves the presence of a work of mastery (entity providing technical expertise as required) and a project owner (carrier entity needed) by performing procedures of functional and technical tests.
(human)
Android studio
Android studio manage unit test by default.
- Class need to be ended by xxxTests
- Class need to be public
- Assert on return classes (not really easy with callback)
Unit test

How it work ?
//mock creation
List mockedList = mock(List.class);
//using mock object
mockedList.add("one");
mockedList.clear();
//verification
verify(mockedList).add("one");
verify(mockedList).clear();Mockito
Warehouse project
New project
Project name : Warehouse
Blank Activity
Activity Name : MainActivity
Module: app
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
android {
compileSdkVersion 22
buildToolsVersion "22.0.1"
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.meuuh.test.myapplication"
minSdkVersion 19
targetSdkVersion 22
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
packagingOptions {
exclude 'LICENSE.txt'
exclude 'META-INF/DEPENDENCIES'
exclude 'META-INF/ASL2.0'
exclude 'META-INF/NOTICE'
exclude 'META-INF/LICENSE'
}
}
dependencies {
compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:22.1.1'
androidTestCompile 'org.mockito:mockito-core:1.9.5'
androidTestCompile 'com.google.dexmaker:dexmaker:1.0'
androidTestCompile 'com.google.dexmaker:dexmaker-mockito:1.0'
androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:2.0'
androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test:testing-support-lib:0.1'
}
Warehouse.java
public interface Warehouse {
boolean hasInventory(String product, int quantity);
void remove(String product, int quantity);
}RealWarehouse.java
public interface Warehouse {
boolean hasInventory(String product, int quantity);
void remove(String product, int quantity);
}public class RealWarehouse implements Warehouse{
public RealWarehouse() {
products = new HashMap();
products.put("Talisker", 5);
products.put("Lagavulin", 2);
}
public boolean hasInventory(String product, int quantity) {
return inStock(product) >= quantity;
}
public void remove(String product, int quantity) {
products.put(product, inStock(product) - quantity);
}
private Integer inStock(String product) {
Integer quantity = (int)products.get(product);
return quantity == null ? 0 : quantity;
}
private HashMap products;
}Order.java
public class Order {
public Order(String product, int quantity) {
this.product = product;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
public void fill(Warehouse warehouse) {
if (warehouse.hasInventory(product, quantity)) {
warehouse.remove(product, quantity);
filled = true;
}
}
public boolean isFilled() {
return filled;
}
private boolean filled = false;
private String product;
private int quantity;
}MainActivity
public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity {
private Warehouse warehouse = new RealWarehouse();
private EditText productEditText;
private EditText quantityEditText;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
productEditText = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.product);
quantityEditText = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.quantity);
}
public void placeOrder(View view) {
String product = productEditText.getText().toString();
int quantity = Integer.parseInt(quantityEditText.getText().toString());
Order order = new Order(product, quantity);
order.fill(warehouse);
String message = order.isFilled() ? "Success" : "Failure";
Toast toast = Toast.makeText(this, message, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT);
toast.show();
}
}The mock : MainActivityTests
public class MainActivityTests extends ActivityInstrumentationTestCase2<MainActivity> {
public MainActivityTests() {
super(MainActivity.class);
}
public void testInStock() {
Warehouse mockWarehouse = mock(Warehouse.class);
when(mockWarehouse.hasInventory("Talisker", 50)).thenReturn(true);
Order order = new Order("Talisker", 50);
order.fill(mockWarehouse);
assertTrue(order.isFilled());
verify(mockWarehouse).remove("Talisker", 50);
}
public void testOutOfStock() {
Warehouse mockWarehouse = mock(Warehouse.class);
when(mockWarehouse.hasInventory("Talisker", 50)).thenReturn(false);
Order order = new Order("Talisker", 50);
order.fill(mockWarehouse);
assertFalse(order.isFilled());
}
}Now we can create run the test
What about documentation ?
What about callback ?
Functional test

Espresso
Entry point to interactions with views (via onView and onData). Also exposes APIs that are not necessarily tied to any view (e.g. pressBack).
Basics
ViewMatchers
You can pass one or more of these to the onView method to locate a view within the current view hierarchy
ViewActions
A collection of ViewActions that can be passed to the ViewInteraction.perform method (for example, click).
ViewAssertions
The matches assertion, which uses a View matcher to assert the state of the currently selected view
Example
Espresso.onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.my_view)) // withId(R.id.my_view) is a ViewMatcher
.perform(ViewActions.click()) // click() is a ViewAction
.check(ViewAssertions.matches(ViewMatchers.isDisplayed())); // matches(isDisplayed()) is a ViewAssertionClick
onView(withId(R.id.button)).perform(click());Check text
onView(withId(R.id.spinnertext_simple)).check(matches(withText(containsString("Americano"))));Perform an action
onView(...).perform(click());Perform an assertion
onView(...).check(matches(withText("Hello!")));Click on list (Adapter)
onData(allOf(is(instanceOf(String.class)), is("Americano"))).perform(click());Documentation
Espresso
On ChatApp
MainActivityTests
public class MainActivityTests extends ActivityInstrumentationTestCase2<MainActivity> {
public static String uuid = null;
public static String username;
public static String password;
public static String pseudo;
public MainActivityTests() {
super(MainActivity.class);
ParseUser user = ParseUser.getCurrentUser();
if (user != null) user.logOut();
if (this.uuid == null) {
this.uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 8);
this.username = this.uuid + "@meuuh.com";
this.password = this.uuid;
this.pseudo = "test_" + this.uuid;
}
}
@Override
public void setUp() throws Exception {
super.setUp();
getActivity();
}
public void testCreateLogin() throws InterruptedException {
Espresso.onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.parse_login)).check(ViewAssertions.matches(ViewMatchers.isDisplayed()));
Espresso.onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.parse_signup_button)).perform(ViewActions.click());
/**/
}
}Template
Java
ITemplate
public class ImplementDog implements ITemplate<Dog> {
Dog dog;
public ImplementDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
@Override
public void call() {
dog.doIt();
}
@Override
public void init(Dog object) {
}
@Override
public Dog returnObject() {
return null;
}
}DogImplementation
public interface ITemplate<T> {
public void init(T object);
public void call();
public T returnObject();
}public class Dog {
public void doIt() {
Log.e("test_template", "I'm a dog");
}
}Dog class
public class ImplementCat implements ITemplate<Cat> {
Cat cat;
public ImplementCat(Cat cat) {
this.cat = cat;
}
@Override
public void init(Cat object) {
}
@Override
public Cat returnObject() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void call() {
cat.doIt();
}
}CatImplementation
public class Cat {
public void doIt() {
Log.e("test_template", "I'm a cat");
}
}
Cat class
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ImplementDog implementDog = new ImplementDog(new Dog());
implementDog.call();
ImplementCat implementCat = new ImplementCat(new Cat());
implementCat.call();
}