Role of Mortality data in
Public Health
Uses of mortality statistics - These include
a. Health planning and administration
- Prioritize investments in control and research
- Evaluate control programmes
- Improve health care delivery and quality
- Investigate role of risk factors
- Investigate impact of interventions
b. Health Research -Monitor trends in mortality and diseases
Users of mortality statistics include
-
Clinicians
-
Community health physicians
-
Epidemiologists
-
Social scientists
-
Biostatisticians/Demographers/ Medical records personnel
-
Programme managers
-
Policy-makers
Reporting of Cause of death
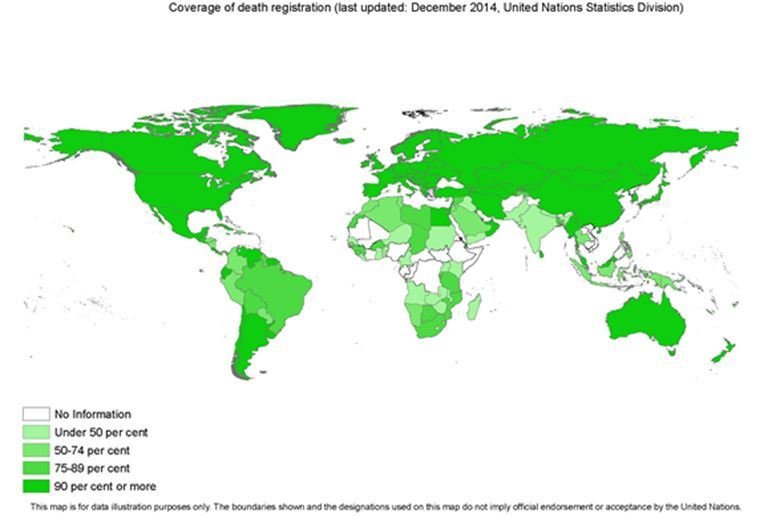
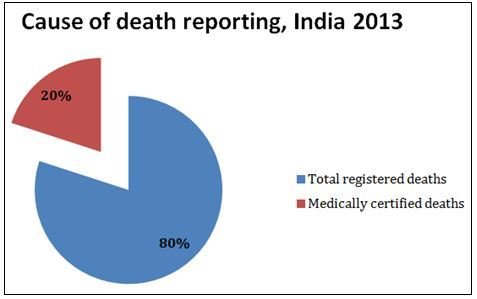
Only about 1 in 5 deaths in India have a cause of death identified for them
Sources of CoD data
CoD data is obtained through -
-
Civil Registration systems (CRS)
-
Sample Registration systems (SRS)
-
Medical Certification of Cause of Death (MCCD)
1. Civil Registration systems (CRS)
-
It is a passive system comprising of registration of all births and deaths by the government
-
Data is collected by non-medical personnel
-
Aim: mainly for statistical purposes by registering the fact of death (and not the cause of death)
-
Status report in India –
-
Sample is incomplete and non-representative since only ~5.5 out of 10 lakh estimated deaths are reported per year
-
2. Sample Registration systems (SRS)
-
This is a subset of CRS wherein from ~7500 small representative geographic areas of the country the fact of death and the cause of death data are collected for a sample size of ~0.5 lakhs/year
-
It comprises of enumeration of deaths in sample villages / urban areas
-
It includes investigation of causes of mortality through verbal autopsy by trained non-medical personnel
-
Aim: for statistical purposes to assign a cause-of-death
-
Status report in India –
-
This system generates reliable community-based information on death rates as well as the causes of death by age-and-sex groups for the country as a whole and for different regions of India
-
3. Medical Certification of Cause of Death (MCCD)
-
This is hospital-based certification of deaths by physicians
-
Aim: It is used both for patient-oriented quality improvement and for statistical purposes
-
Status report in India –
-
It is non-representative since only ~1.5 out of 10 lakh deaths are certified per year; suffers from incomplete and inaccurate reporting of causes of death in hospital certificates
-
You have now come to the end of this learning activity.
Move on to your next learning activity.