Mortality statistics capture a vital dynamic in a population system.
It measures how frequently individuals leave the system through death, who leaves and how they leave.
Mortality statistics is of 3 types:
1. Crude death rate
2. Mortality by population groups (eg Infant mortality rate)
3. Mortality by cause
Leading Causes of Death in the US
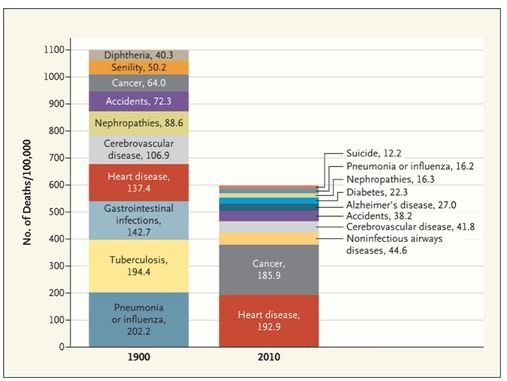
A comparison of cause-specific mortality fractions in the USA between 1900 and 2010 is illustrative of the changes in society that have occurred in the course of the century.The mortality burden of infectious diseases, more than a third of all deaths in 1900, has decreased considerably while that due to heart diseases and cancers have increased.
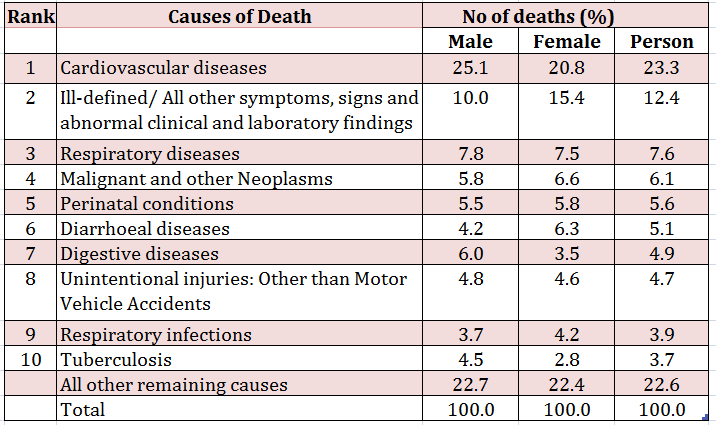
Leading Causes of Death in India: 2010-2013
Causes of death in 21st century India have some diseases (eg cardiovascular diseases) in common with those seen in contemporary USA as well as those that were common in USA over a hundred years back (eg. infectious diseases).
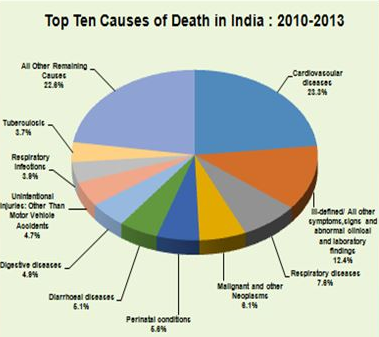
Leading Causes of Death in India: 2010-2013
Uses of mortality statistics
a. Health planning and administration
- Prioritize investments in control and research
- Evaluate control programmes
- Improve health care delivery and quality
- Investigate role of risk factors
- Investigate impact of interventions
b. Health Research -Monitor trends in mortality and diseases
Users of mortality statistics
-
Clinicians
-
Community health physicians
-
Epidemiologists
-
Social scientists
-
Biostatisticians/Demographers/ Medical records personnel
-
Programme managers
-
Policy-makers
Reporting of Cause of death
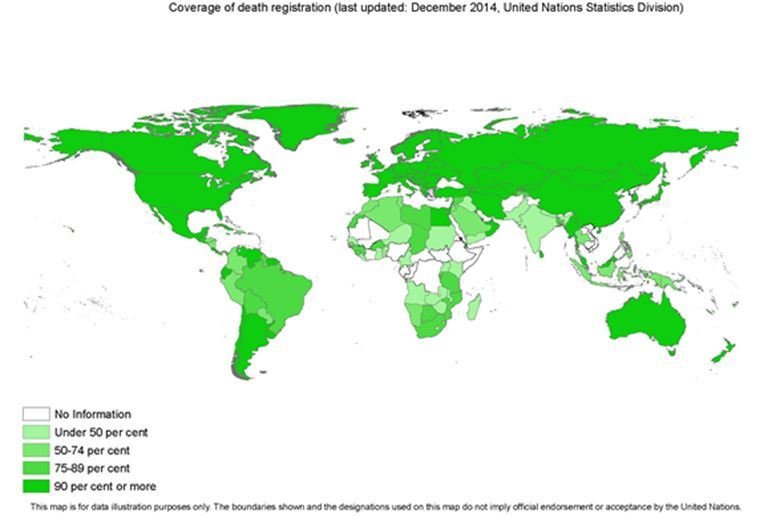
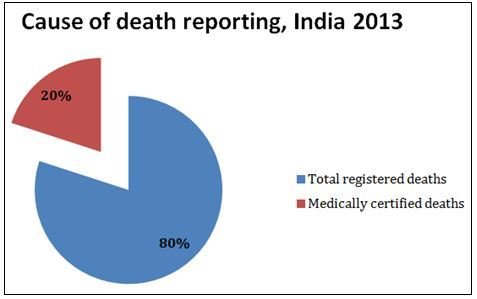
Only about 1 in 5 deaths in India have a cause of death identified for them
Sources of CoD data
CoD data is obtained through -
-
Civil Registration systems (CRS)
-
Sample Registration systems (SRS)
-
Medical Certification of Cause of Death (MCCD)
1. Civil Registration systems (CRS)
-
It is a passive system comprising of registration of all births and deaths by the government
-
Data is collected by non-medical personnel
-
Aim: mainly for statistical purposes by registering the fact of death (and not the cause of death)
-
Status report in India –
-
Sample is incomplete and non-representative since only ~5.5 out of 10 lakh estimated deaths are reported per year
-
2. Sample Registration systems (SRS)
-
This is a subset of CRS wherein from ~7500 small representative geographic areas of the country the fact of death and the cause of death data are collected for a sample size of ~0.5 lakhs/year
-
It comprises of enumeration of deaths in sample villages / urban areas
-
It includes investigation of causes of mortality through verbal autopsy by trained non-medical personnel
-
Aim: for statistical purposes to assign a cause-of-death
-
Status report in India –
-
This system generates reliable community-based information on death rates as well as the causes of death by age-and-sex groups for the country as a whole and for different regions of India
-
3. Medical Certification of Cause of Death (MCCD)
-
This is hospital-based certification of deaths by physicians
-
Aim: It is used both for patient-oriented quality improvement and for statistical purposes
-
Status report in India –
-
It is non-representative since only 22 lakhs (22%) of the nearly 100 lakh deaths are certified per year; it suffers from incomplete and inaccurate reporting of causes of deaths in hospital certificates
-
-
Medical Certification of Cause of Death [MCCD] scheme was proposed by WHO as a tool to obtain scientific and reliable information in terms of causes of mortality
-
It was accepted formally by the Government of India as The Registration of Births and Deaths Act, 1969
MCCD scheme in India
-
Under Registration of Births & Deaths Act, 1969
-
All hospitals are required to submit cause of death data
-
All hospitals will be prescribed punitive action for neglect / refusal of the above
-
Implementation of MCCD scheme is being done in a phased manner since the 1970s
-
As of date about 20% of hospitals across the country have been covered under MCCD
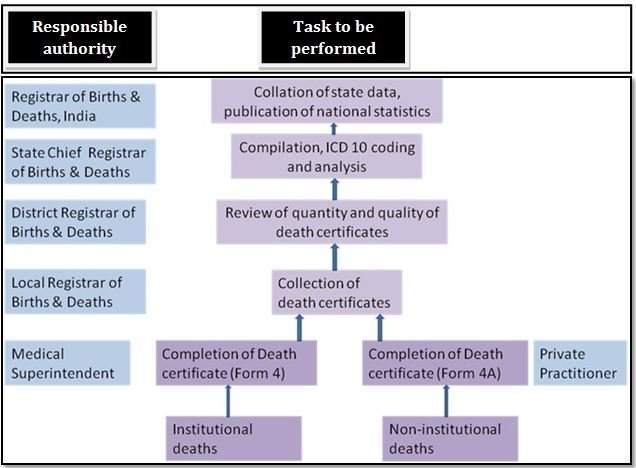
Flow of activities in MCCD
Legal issues with MCCD
Often relatives may plead, persuade, pressurize, offer a price or threaten to obtain a death certificate or make changes to the information that needs to be written on death certificate. In such scenarios, remember that
-
Death certificate is legal document which is a proof of death
-
Failure to provide death certificate and cause of death or filling incorrect information can lead to prosecution of the physician under section 39 CrPC, 175 IPC or 176 IPC