HTTP/2 + Node.js

Intro

What is a Protocol?
Is a set of rules that allow two or more entities to transmit and receive information, it defines the syntax, semantics, and synchronization of communication and possible error recovery methods.

What is TCP/IP?
Is the protocol that governs the connection of computer systems to the Internet.It has a special mechanism that ensures data is safely transferred without errors from one point to another.

What is HTTP/2?
Is a major revision of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), the protocol used by the World Wide Web. this protocol uses TCP/IP to transfer its information between computers (usually Web servers and clients).

HTTP1.1 - How the Web used to work


History

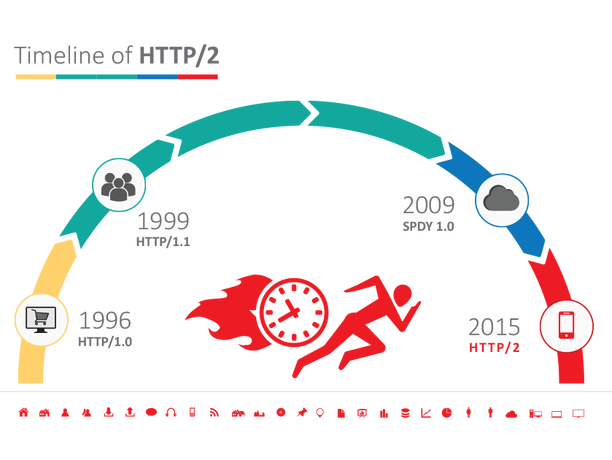
Features

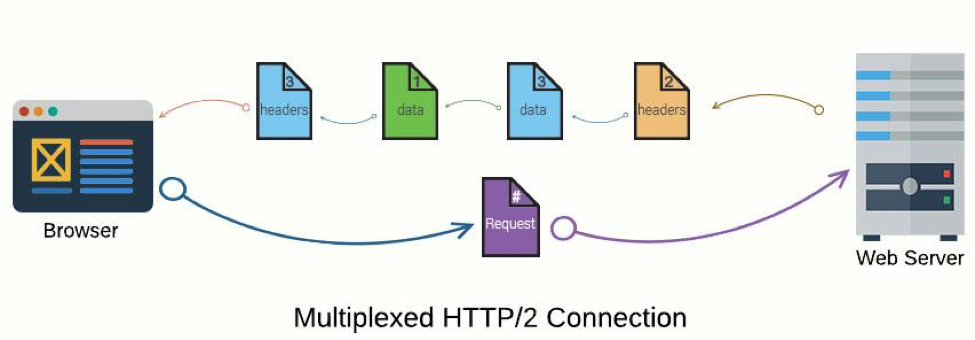
Multiplexing
Multiple HTTP requests can be sent and responses can be received asynchronously via a single TCP connection.

Header Compression
HTTP/2 compresses the individual value of each header before it is transferred to the server, which then looks up the encoded information in list of previously transferred header values to reconstruct the full header information.


Server Push
HTTP/2 allows the server to send additional cacheable information to the client that is not requested but is anticipated in future requests.

Stream prioritization
HTTP/2 includes the ability to send "hints" indicating the importance of a given stream (priority) relative to other streams on the same connection, so that resources can be allocated appropriately.


Binary protocol
HTTP1.x used to process text commands to complete request-response cycles. HTTP/2 can use binary commands to execute the same tasks.


Benefits

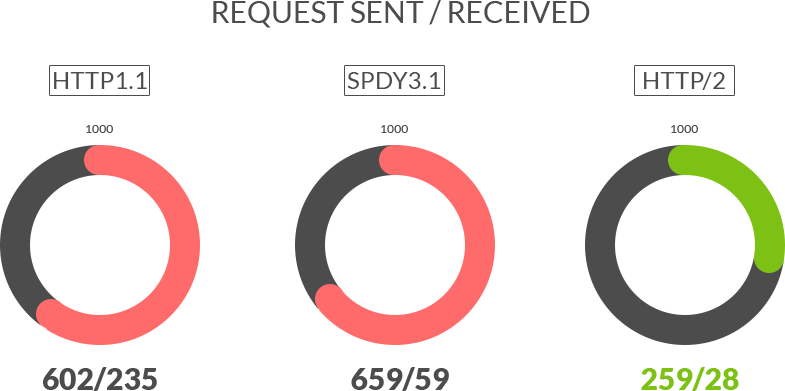
Faster Load Times

More Secure
HTTP/2 prevent multiple attacks possible today with HTTP 1.1 because the way it handles the headers with HPACK and the mandatory use of encryption, HTTPS is required

Mobile Friendly
The header compression feature allows mobile sites with high amount of requests to prevent wasted megabytes from the headers from being downloaded.

Less dependency on hacks
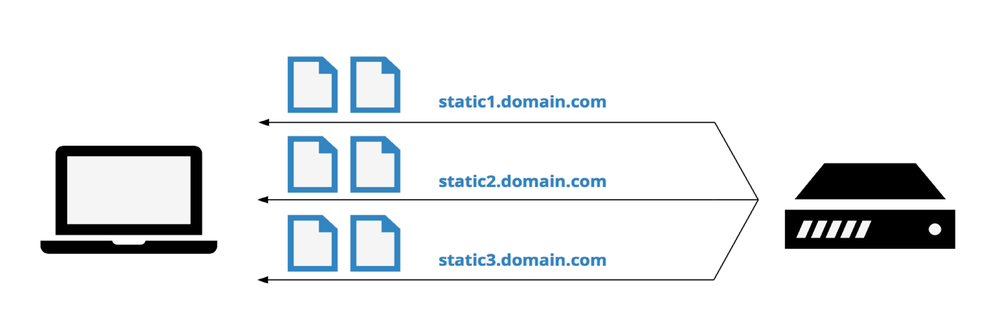
Common practices like Spriting, Concatenating, Domain sharding and others are not longer needed

HTTP/1.1 Compatibility
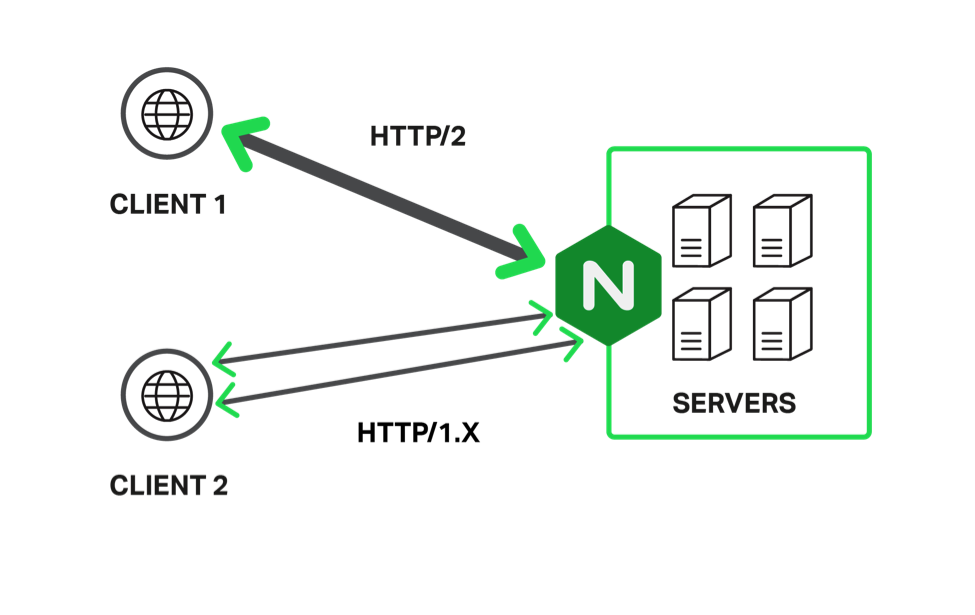
HTTP/2 is fully backwards-compatible with HTTP/1.1, meaning websites will work the same with either protocol.

Cons

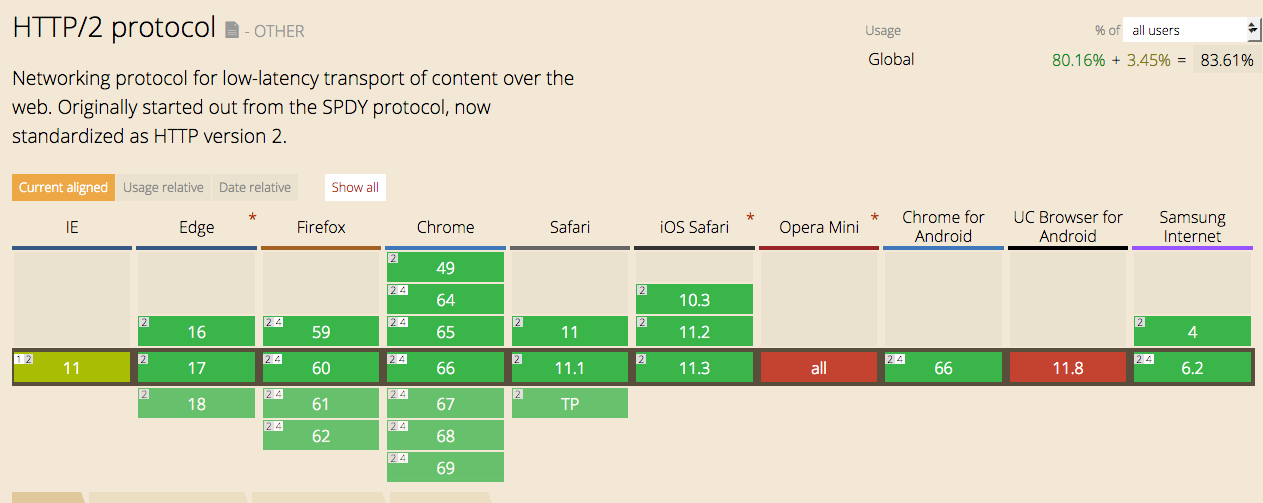
Browsers compatibility

Text
HTTPS Prerequisite
SSL certificates could be expensive if not using letsencrypt.org and will require some setup.


Performance impact could be minimal
In case your website’s optimization is good, you may not find the improvements in your performance so impressive.

HTTP/2 Unknowns
The protocol is still relatively new; a lot of studies will have to be conducted in order to determine best practices and possible pitfalls.

HTTP/2 in Node

Support
Experimental support in Node v8 Carbon, Stable in Node v10 Dubnium


Implementation details
- Full support for stream multiplexing
- Push Stream Support
- respondWithFile() and respondWithFD() APIs
- TLS and Plain-text connections
- HTTP/2 Prioritization and Flow Control
- Support for HTTP/2 trailers
- HPACK header compression support
- Compatibility API layer for HTTP/1 API

Native module

const http2 = require('http2')
const server = http2.createSecureServer(options);
server.on('stream', (stream, requestHeaders) => {
stream.respond()
stream.end('HTTP/2 hello world!')
})
server.listen(4300)Frameworks
- Hapi
- Koa
- Fastify
- Express (not quite there yet)

Demo time

Resources
- API docs: https://nodejs.org/api/http2.html
- HTTP/2 initial implementation: https://medium.com/the-node-js-collection/say-hello-to-http-2-for-node-js-core-261ba493846e
- HTTP/2 Push with Node: https://medium.com/the-node-js-collection/node-js-can-http-2-push-b491894e1bb1
- HTTP/2 in frameworks: https://dexecure.com/blog/native-http2-support-node-frameworks-hapi-koa-express/
- Demos: https://github.com/edsadr/http2-demos

Thanks
