Covering allbases
Edwin Fuquen
edwin@somespider.com
@efuquen
UUIDs in URLs
www.themid.com/culture/what-you-need-to-know-this-week?u=de305d54-75b4-431b-adb2-eb6b9e546013
Deuglify
Remove dashes and
a more efficient encoding.
to
de305d54-75b4-431b-adb2-eb6b9e546013
3jBdVHW0QxutsutrnlRgEw==
Can we do better?
Do we really need 128 bits?
- p(n) - probability of collision after n UUIDs generated
- m - permutations of the ID (i.e. for UUIDs 2122)
- denominator will be fixed for an ID
- for a UUID it will equal 2 * 2122 which equals 2123
| n | probability |
|---|---|
| 68,719,476,736 = 236 | 0.0000000000000004 (4 × 10−16) |
| 2,199,023,255,552 = 241 | 0.0000000000004 (4 × 10−13) |
| 70,368,744,177,664 = 246 | 0.0000000004 (4 × 10−10) |
where
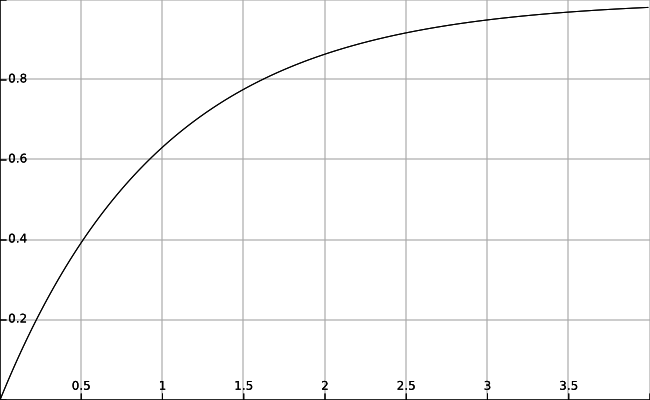
The smaller the x, the lower the probability of collision.
where
| n | x |
|---|---|
| x | collision |
|---|---|
| 1 / 23 | 11.75% |
| 1 / 25 | 1.55% |
| 1 / 27 | 0.79% |
| 1 / 211 | 0.049% |
Assume we're fine with probability of collision of 0.79% after an n of 2^28 (over 268 million) ids.
- m - size of id needed
- n - number of ids generated
- x - variable dependent on probability of collision, as defined previously.
What do we want?
- Correctly randomly generated ids
- Encodable and decodable to many formats
- To an arbitrarily large size
Most libraries that might have worked failed the last criteria, because ...
Number is 64 bits
Any transformation that goes above 64 bits will would give incorrect results.
Character Classes
// 0 15
var HexChars = "0123456789abcdef";
// 0 10 20 30 40 50 61
var Base62Chars = "0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";Indices reperesent the decimal, or base 10, values of each character in the class.
All the bases can be represented this way and then the same base algorithms can be used to encode and decode.
Encode
//num is a bignum to decode
//chars is a string representing the character class
function encode(num, chars) {
var len = chars.length;
var indices = [];
do {
indices.push(num.mod(len));
num = num.div(len);
} while (num.gt(0));
var str = [];
while (indices.length > 0) {
str.push(chars[indices.pop()]);
}
return str.join("");
}Let's turn 10 into binary
indicies = [0];
num = 10 / 2 = 5;indices = [0, 1];
num = Math.floor(5/2) = 2indices = [0, 1, 0];
num = 2/2 = 1;indices = [0, 1, 0, 1]str = [1, 0, 1, 0];
str = str.join("") = "1010";Decode
//str: string to decode
//chars: string representing character class
function decode(str, chars) {
str = esrever.reverse(str);
var num = bignum("0");
var len = chars.length;
for (var i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
var ch = str[i];
var chIndex = chars.indexOf(ch);
var placeNum = bignum.pow(len, i).mul(chIndex);
num = num.add(placeNum);
}
return num;
}Let's decode base62 D4x7
str = str.reverse() = "7x4D"| i | calc | sum |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 7 * 620 | 7 |
| 1 | 33 * 621 | 2046 |
| 2 | 4 * 622 | 15376 |
| 3 | 39 * 623 | 9294792 |
0 10 20 30 40 50 61
"0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"num = 7 + 2046 + 15376 + 929472 = 9312221
Random
function genRandom(numberOfBytes, chars, rand) {
var buf = rand(numberOfBytes);
return encode(bignum.fromBuffer(buf), chars);
}
function random(size, opts) {
var len = opts.chars.length;
var combos = Math.pow(len, size);
if (combos === Infinity) {
throw "Too large of a size, can't estimate needed bytes"
}
var bits = Math.ceil(log(2, combos));
var numberOfBytes = Math.ceil(bits / 8);
return genRandom(numberOfBytes, opts.chars, opts.rand);
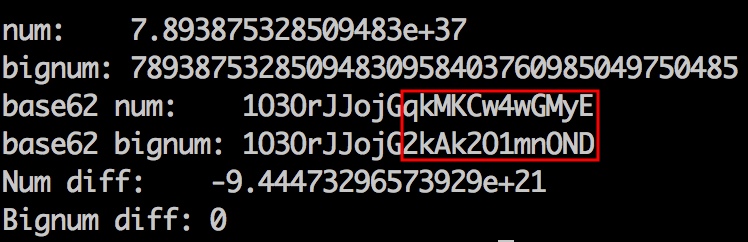
}But, isn't a problem here? I'm using Number ...
Number.MAX_VALUE
- 1.7976931348623157e+308
- base62 can't generate more then 171 characters.
- Big Decimal? big.js library
- But, it doesn't have a log implementation
- Two possible solutions:
- Find a good log estimate for large decimals
- Use big.js to detect large combos and break it down to smaller numbers < Number.MAX_VALUE
Conclusions
- You can't shove everything into Number
- Be careful, encoding/decoding bases one of many issues.
- A little rigor can go a long way.
- Warn your users, they don't need any extra rope from you. Plenty of other dragons to deal with already.