the Great Pacific
Garbage Patch
新傳一 周祐徳
Subtitle
What is the Great Pacific Garbage Patch?
The largest of the five offshore plastic accumulation zones .
Located halfway between Hawaii and California also near Japan.
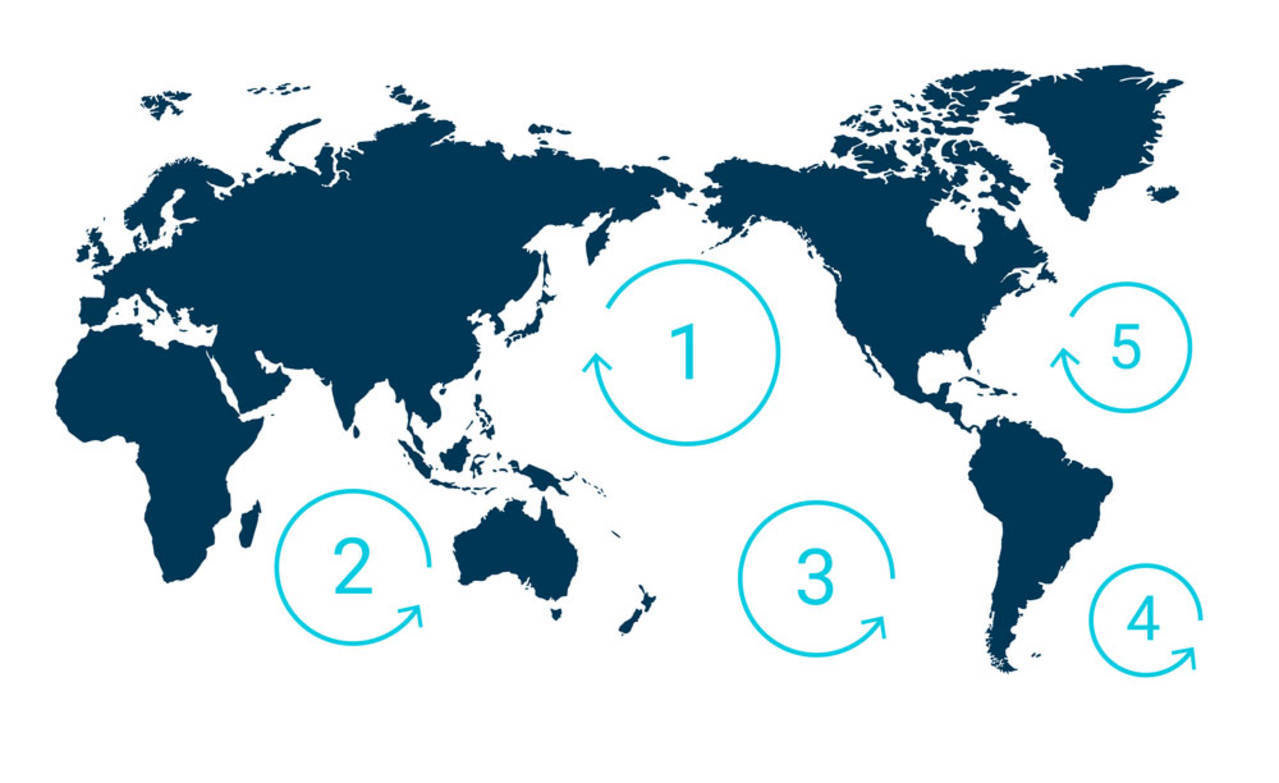
Concentrations of marine debris.



Estimation Of Size
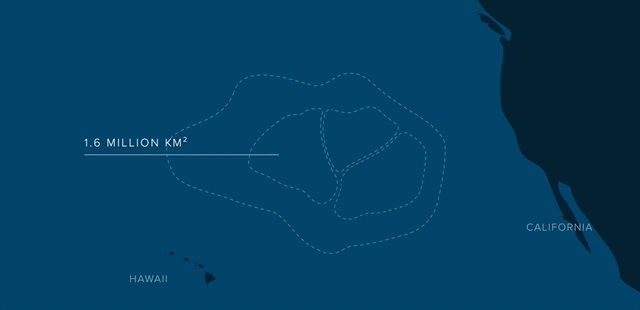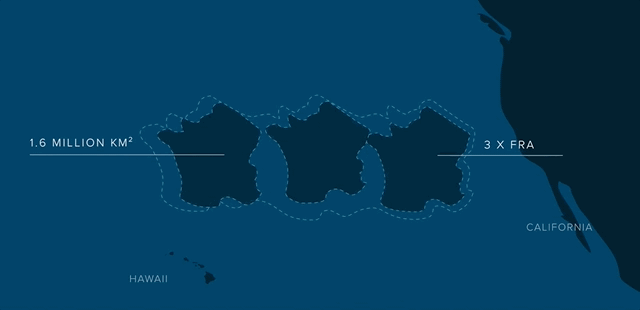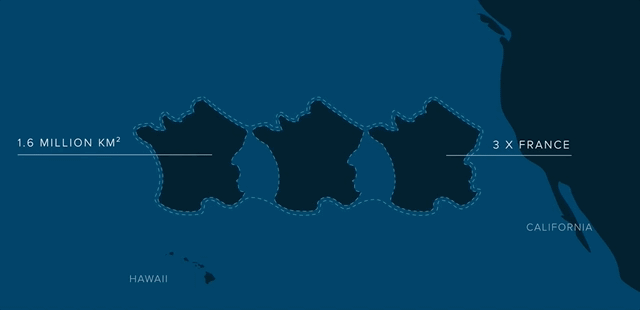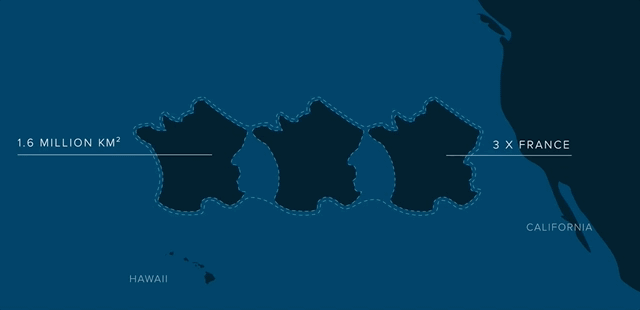
Covers an estimated surface area of 1.6 million square kilometers.
Twice the size of Texas.
Three times the size of France.
44 times the size of Taiwan.
Location
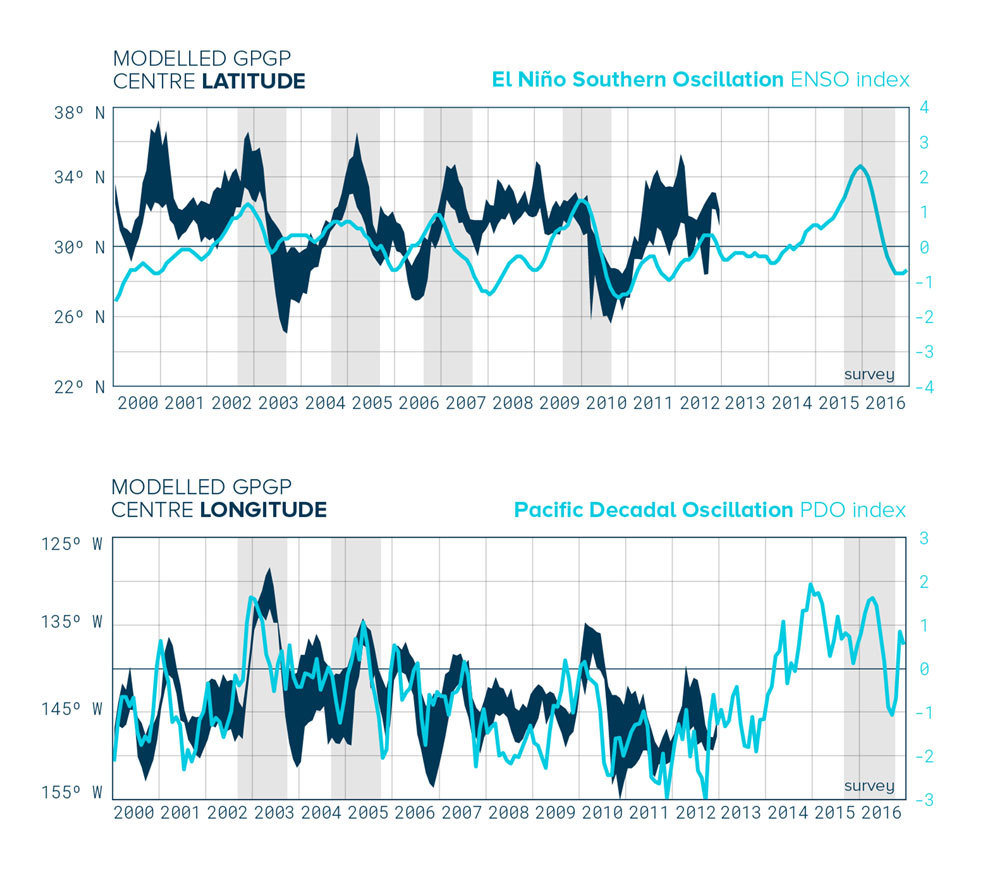
The GPGP's location and shape
are constantly changing.
On average the patch orbits
around 32°N and 145°W.

How much plastic float
in the GPGP?
A total of 1.8 trillion plastic pieces
were estimated to be floating
in the patch.
Weigh an estimated 80,000 tonnes.
This weight is also equivalent
to that of 500 Jumbo Jets.



WHY LARGE DEBRIS MATTER

They will likely break down into smaller plastics while floating in the GPGP.
Microplastics are very difficult to remove and are often mistaken for food by marine animals.
Sun exposure , waves ,
marine life and temperate
changes
What are the effects on marine life and humans?

Animals confuse the plastic for food, causing malnutrition;
it poses entanglement risks and threatens their overall behavior, health and existence.
Interaction with these
discarded nets, often
results in the death of the
marine life involved.
IMPACT ON HUMANS AND SOCIETY
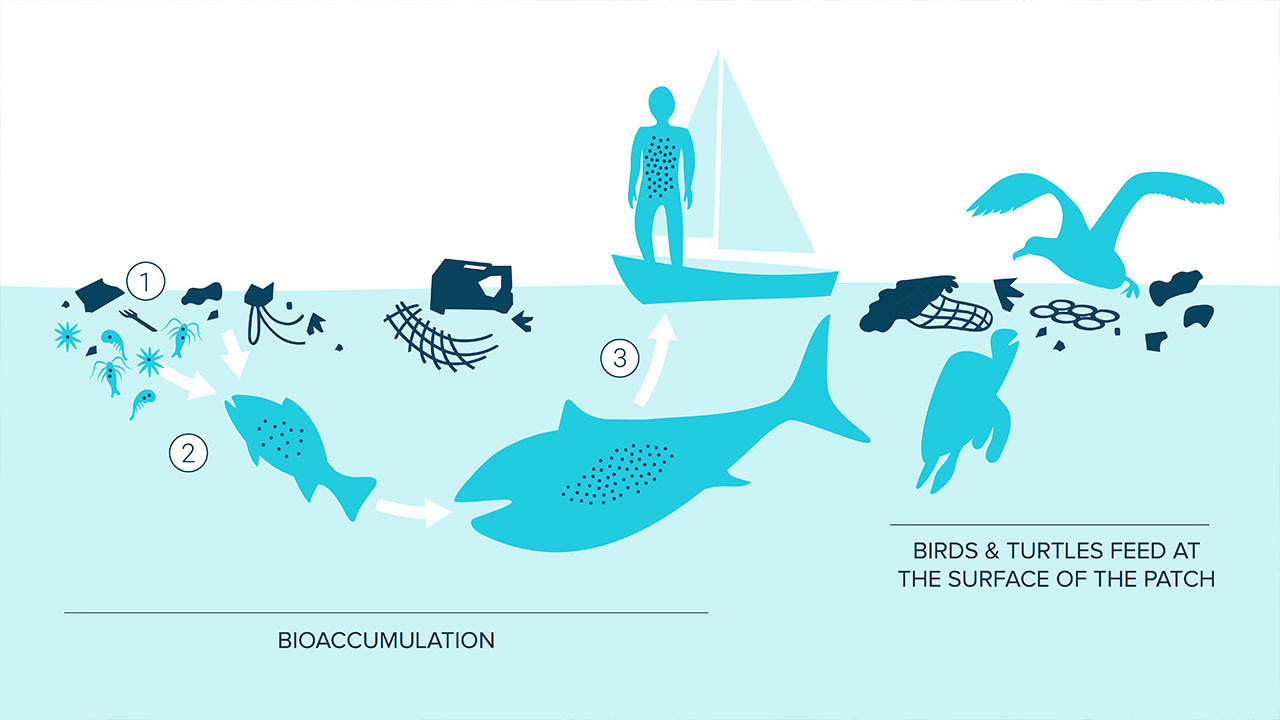
Through a process called bioaccumulation, chemicals in plastics will enter the body of the animal feeding on the plastic, and as the feeder becomes prey, the chemicals will pass to the predator - making their way up the food web that includes humans. These chemicals that affected the plastic feeders could then be present within the human as well.
Solutions
THE OCEAN CLEANUP conducts a containment policy to prevent the garbage from drifting to the windless zone before the garbage is broken down into plastic debris.
Producers reduce the generation of garbage.



Consumers reduce waste.