By Emmanuelle Delescolle and Leila Verhaegen
Django REST Framework
Hit the ground running with your
API
Who are we?
- Co-founders of LevIT
- Small Belgian company
- Django and Ember remote consulting
- OpenSource libararies authors
Getting your computer ready for the workshop
Please, follow the instructions on http://bit.ly/drf_cc
Slides at http://bit.ly/htgr_drf
Code at http://bit.ly/htgr_drf_commits
sudo pip install cookiecutterDocker container?
If you have trouble getting your computer up and running, you can try the docker image here under.
We also have a couple bootable USB sticks
git clone https://bitbucket.org/levit_scs/djangoconeu2018.git
cd djangoconeu2018
sudo docker-compose run webGetting started with a CookieCutter
$ cookiecutter https://bitbucket.org/levit_scs/cc_htgr_drf.git
Cloning into 'cc_htgr_drf'...
remote: Counting objects: 407, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (296/296), done.
remote: Total 407 (delta 202), reused 189 (delta 75)
Receiving objects: 100% (407/407), 58.77 KiB | 0 bytes/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (202/202), done.
Checking connectivity... done.
project_name [Project name]: My Webshop
repo_name [my_webshop]:
author [Your Name]: Emma
username [emma]:
email [you@domain.com]:
python [python3.6]:
create_superuser [no]: yes
Start things up
$ ./run.shIn shell, launch Django with
Windows user other than Windows 10 Pro, please raise your hand
What did we install?
- Django
- Django Rest Framework
- Django Filter
- Django CORS headers
- DRF-Schema-Adapter
Django REST Framework
- Build Serializer
- Build ViewSet's
- Build EndPoints (urls) through routers
Used to:
Documentation:
Django Filter
Used to easily create filters with DRF
Django CORS header
Used to allow access to Django from another domain
DRF-Schema-Adapter
An extra layer on top of Django REST Framework to facilitate creating endpoints the way you would create Django Admin classes
Documentation on Read The Docs
DRF-Schema-Adapter is also useful to close the bridge between your backend and your frontend and do things like exporting your serializers and viewsets definitions to frontend models or helper so that you don't have to do convert them manually.
(This feature will not be covered by this workshop)
Let's look at what has been created for us
Regular ViewSet and Serializer
# my_webshop/views.py
class UserViewSet(ModelViewSet):
serializer_class = UserSerializer
queryset = get_user_model().objects.all()
filter_backends = (DjangoFilterBackend, )
filter_fields = ('first_name', 'last_name')# my_webshop/serializers.py
class UserSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = get_user_model()
fields = (
'id',
'username',
'email',
'first_name',
'last_name'
) Catalog application
$ ./manage.py startapp catalogINSTALLED_APPS = (
...
'catalog',
)In your venv-activated shell
settings.py
*All commands should be run in a "venv-activated" shell.
To activate a venv, from the back directory, run
You will know that you are in a venv-activated shell because your prompt will be prefixed with (venv) or [venv] depending on your computer.
$ source ../venv/bin/activateModels
For this workshop we will be creating 2 models: Product and Category
from django.db import models
class Category(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=255)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class Product(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=255)
category = models.ForeignKey(Category, related_name='products', on_delete=models.CASCADE)
description = models.TextField()
image = models.URLField()
price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=6, decimal_places=2)
likes = models.SmallIntegerField(default=0)
views = models.PositiveSmallIntegerField(default=0)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
catalog/models.py
Models
$ ./manage.py makemigrations
Migrations for 'catalog':
0001_initial.py:
- Create model Category
- Create model Product
$ ./manage.py migrate
Operations to perform:
Apply all migrations: auth, sessions, catalog, kombu_transport_django,
admin, contenttypes
Running migrations:
Rendering model states... DONE
Applying catalog.0001_initial... OK
in your venv-activated shell
ModelAdmins
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Category, Product
admin.site.register(Category)
admin.site.register(Product)catalog/admin.py
Endpoints
(Think of them as Django admin classes) We will be creating one for each model
from drf_auto_endpoint.router import router
from .models import Category, Product
router.register(Category)
router.register(Product)catalog/endpoints.py
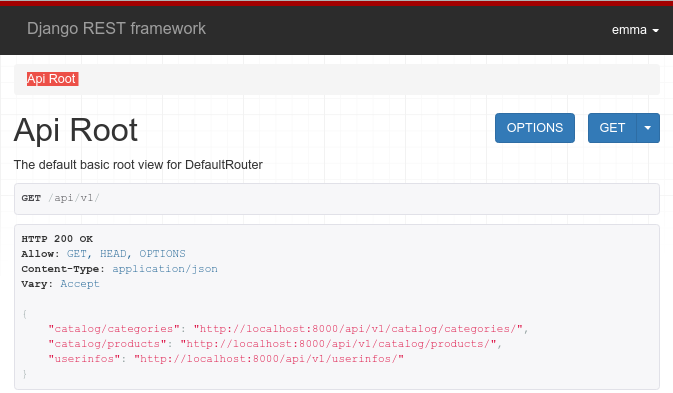
🎉 We now have a fully functional API 🎉
In your browser on http://localhost:8000/api/v1/.
(You may need to restart your Django server)
Customizing Endpoints
(still very similar to Django admin classes)
from drf_auto_endpoint.endpoints import Endpoint
from drf_auto_endpoint.router import register
from .models import Category, Product
@register
class ProductEndpoint(Endpoint):
model = Product
read_only = True
search_fields = ('name', )
filter_fields = ('category_id', )
ordering_fields = ('price', 'name', )
@register
class CategoryEndpoint(Endpoint):
model = Category
search_fields = ('name', )
read_only = True
catalog/endpoints.py
Customizing ViewSets
from rest_framework import viewsets
from .models import Category, Product
class ProductViewSet(viewsets.ReadOnlyModelViewSet):
def retrieve(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
obj = self.get_object()
obj.views += 1
obj.save()
return super(ProductViewSet, self).retrieve(request, *args, **kwargs)catalog/views.py
...
from .views import ProductViewSet
...
@register
class ProductEndpoint(Endpoint):
...
base_viewset = ProductViewSetcatalog/endpoints.py
Customizing Serializers
from rest_framework import serializers
from .models import Category, Product
class SimpleCategorySerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Category
fields = ('id', 'name', )
class ProductSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
category = SimpleCategorySerializer()
catalog/serializers.py
...
from .serializers import ProductSerializer
...
@register
class ProductEndpoint(Endpoint):
...
base_serializer = ProductSerializercatalog/endpoints.py
Customizing Serializers
Made Simple
from drf_auto_endpoint.factories import serializer_factory
from rest_framework import serializers
from .models import Category
class ProductSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
category = serializer_factory(model=Category, fields=('id', 'name'))()catalog/serializers.py
Using different serializers
for different actions
from drf_auto_endpoint.factories import serializer_factory
from .serializers import ProductSerializer
...
class ProductViewSet(viewsets.ReadOnlyModelViewSet):
...
def get_serializer_class(self):
if getattr(self, 'action', None) == 'retrieve':
return serializer_factory(self.endpoint, base_class=ProductSerializer)
return super(ProductViewSet, self).get_serializer_class()catalog/views.py
catalog/endpoints.py
...
@register
class ProductEndpoint(Endpoint):
...
# base_Serializer = ProductSerializer🎉 We now have a fully customized CRUD API 🎉
Can we go beyond CRUD?
Actions
Simple "detail" action
from django.shortcuts import get_object_or_404
from drf_auto_endpoint.decorators import custom_action
from rest_framework.response import Response
...
@register
class ProductEndpoint(Endpoint):
...
@custom_action(method='POST')
def like(self, request, pk):
obj = get_object_or_404(self.model, pk=pk)
obj.likes += 1
obj.save()
return Response(self.get_serializer(obj).data)catalog/endpoints.py
Actions
from drf_auto_endpoint.decorators import custom_action, wizard
from .serializers import LikeCountSerializer
...
@register
class ProductEndpoint(Endpoint):
...
@wizard(LikeCountSerializer)
def dislike(self, request, pk):
obj = get_object_or_404(self.model, pk=pk)
obj.likes -= request.validated_data['amount']
obj.save()
return Response(self.get_serializer(obj).data)catalog/endpoints.py
...
class LikeCountSerializer(serializers.Serializer):
amount = serializers.IntegerField(min_value=1)
class Meta:
fields = ('amount', )catalog/serializers.py
"detail" action with input data
Actions
Simple "list" action
from drf_auto_endpoint.decorators import bulk_action, custom_action, wizard
...
@register
class ProductEndpoint(Endpoint):
...
@bulk_action(method='POST')
def reset_likes(self, request):
self.model.objects.all().update(likes=0)
return Response(status=204)catalog/endpoints.py
Actions
"list" action with input data
from django.db.models import F
...
@register
class ProductEndpoint(Endpoint):
...
@wizard(LikeCountSerializer, meta_type='list')
def cheatlikes(self, request):
self.model.objects.all().update(
likes=F('likes') + request.validated_data['amount']
)
return Response(status=204)catalog/endpoints.py