Introduction To JAVA
By:
Anirudh Rajan
Dilsahib Singh
Kamal Kumar Vishwakarma
Sourabh Sharma
Context
- History
- Features
- JVM, JDK and JRE
- Array
- Namming Convention
History
- James Gosling, Mike Sheridan and Patrick Naughton (1991)
- Green Team
- Greentalk (.gt) by James Gosling
- Oak (Green Project) --> Symbol of Strength
- 1995 --> Oak to JAVA
Why name JAVA
- Reflect the essence of Technology
- "JAVA was one of the top choices along with Silk" - James Gosling
- Java Island -> First Coffee -> Java coffee
- Developer - James Gosling at Sun Microsystems (sub. ORACLE Corporation)
- Time Magazine (1995) - "JAVA one of the 10 Best Products of 1995"
- JDK 1.0 - Jan 23, 1996
Features
- Simple
- Object Oriented
- Platform Independent
- Secure
- Robust
- Architecture Neutral
- Portable
- Dynamic
- Interpreted
- High Performance
- Multithreaded
- Dustributed
Simple
- Syntax based on C++
- Removed many confusing or rarely-used features
- explicit Pointers
- operator overloading
- Automatic Garbage Collection
Object-Oriented
- Different type of objects that incorporates both data and behaviour
- Object-Oriented Programming is a methodology
- Basic concepts
- Object
- Class
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Abstraction
- Encapsulation
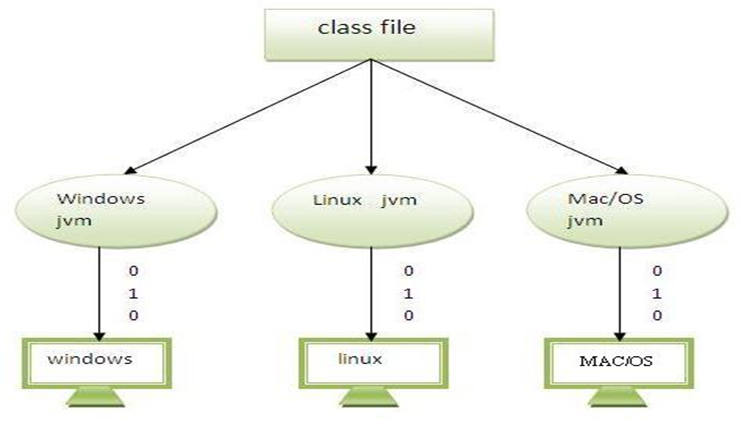
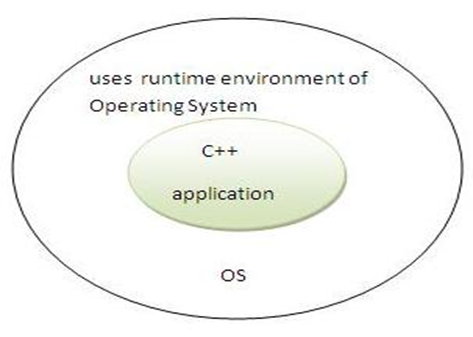
Platform Independent
- Two Types
- Hardware - based
- Software - based
- JAVA provides software - based Platform
- JAVA code can run on multiple platforms(Windows, Linux, etc.)
- Java code is compiled by the compiler and converted into bytecode.
- Write Once and Run Anywhere (WORA)
Secured
- No Explicit Pointer
- Program run inside virtual machine sandbox
- Classloader
- Bytecode Verifier
- Security Manager
- SSL
- JAAS
- cryptography
Robust
- Strong
- Lack of pointers that avoids security problem
- Automatic Garbage collection
- Exception handling and type checking mechanism
Architecture-Neutral
- No Implementation Dependent Features
Portable
- Carry java bytecode to any platform
High - Performance
- Java is faster then traditional interpretation
Distributed
- RMI and EJB are used
- Access files by calling the methods from any machine
Multi - Threaded
- Deal with many tasks by defining multiple threads
- Share same memory
- Multimedia
- Web Application
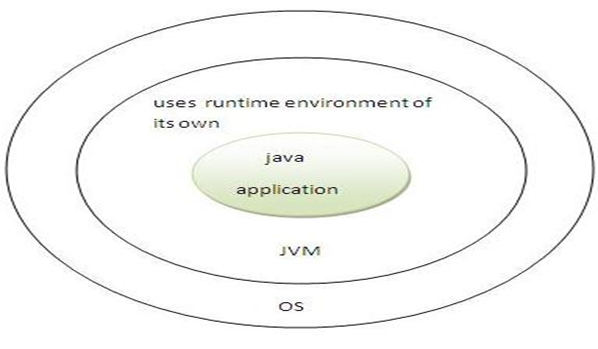
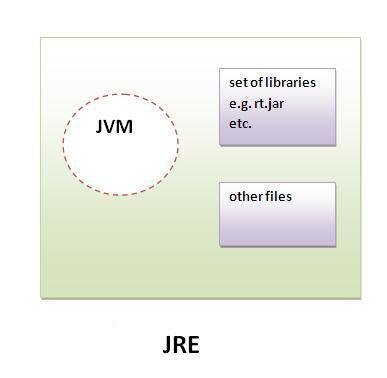
JVM, JDK and JRE
JVM
- Abstract Machine
- Run Time Environment
- Tasks
- Loads code
- Verifies code
- Executes code
- Provides runtime environment
- JVM, JRE and JDK are platform dependent
JDK
- Contains JRE + development tools
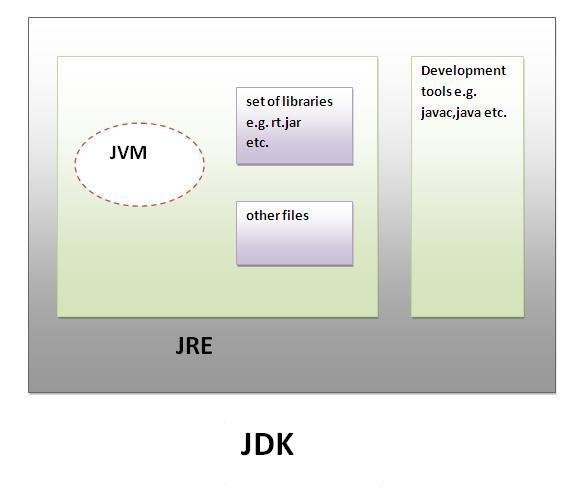
JRE
- Provide Run Time Environment
- Implementation of JVM
- Contains set of libraries + other files that JVM uses at runtime
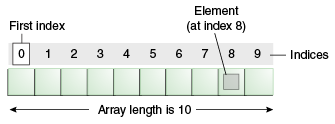
ARRAY in JAVA
- Collection of similar type of elements
- Contiguous memory location
- Java array is an object the contains elements of similar data type
Advantage
- Code Optimization
- Random Access
Disadvantage
- Size Limit
Types of Array
- Single-Dimention Array
- Multi-Dimention Array
Single-Dimention Array
Syntax :
- dataType[] arr;
- dataType []arr;
- dataType arr[];
Instantiation of an Array
Syntax :
- arrayRefVar=new datatype[size];
Declaration, Instantiation and Initialization
Syntax :
- int a[]={33,3,4,5};
Multidimensional array
Syntax :
- dataType[][] arrayRefVar;
- dataType [][]arrayRefVar;
- dataType arrayRefVar[][];
- dataType []arrayRefVar[];
Instantiate Multidimensional Array
Syntax :
- int[][] arr=new int[3][3];
Initialize Multidimensional Array
Syntax :
arr[0][0]=1;
arr[0][1]=2;
arr[0][2]=3;
arr[1][0]=4;
arr[1][1]=5;
arr[1][2]=6;
arr[2][0]=7;
arr[2][1]=8;
arr[2][2]=9;
Naming Conventions
- Pascal Casing
- Camel Casing
