Magnetic Pendulum
#1
Ernest Wong
Macleans College
The Problem
Make a light pendulum with a small magnet at the free end.
An adjacent electromagnet connected to an AC power source of a much higher frequency than the natural frequency of the pendulum can lead to undamped oscillations with various amplitudes.
Study and explain the phenomenon.
#2
Make a light pendulum with a small magnet at the free end.
An adjacent electromagnet connected to an AC power source of a much higher frequency than the natural frequency of the pendulum can lead to undamped oscillations with various amplitudes.
Study and explain the phenomenon.
#3
Key Conditions
Maximum amplitude near natural frequency
#4
Difference to FOrced Harmonic Oscillator
Harmonic
This Oscillator
Various undamped amplitudes driven by higher frequencies.
Driving force only time dependent.
Smaller sized EM field means force diminishes rapidly with displacement.
#5
Setup
Setup
Low & uniform friction bearing
Coil perpendicular to motion
#6
Magnet poles vertical
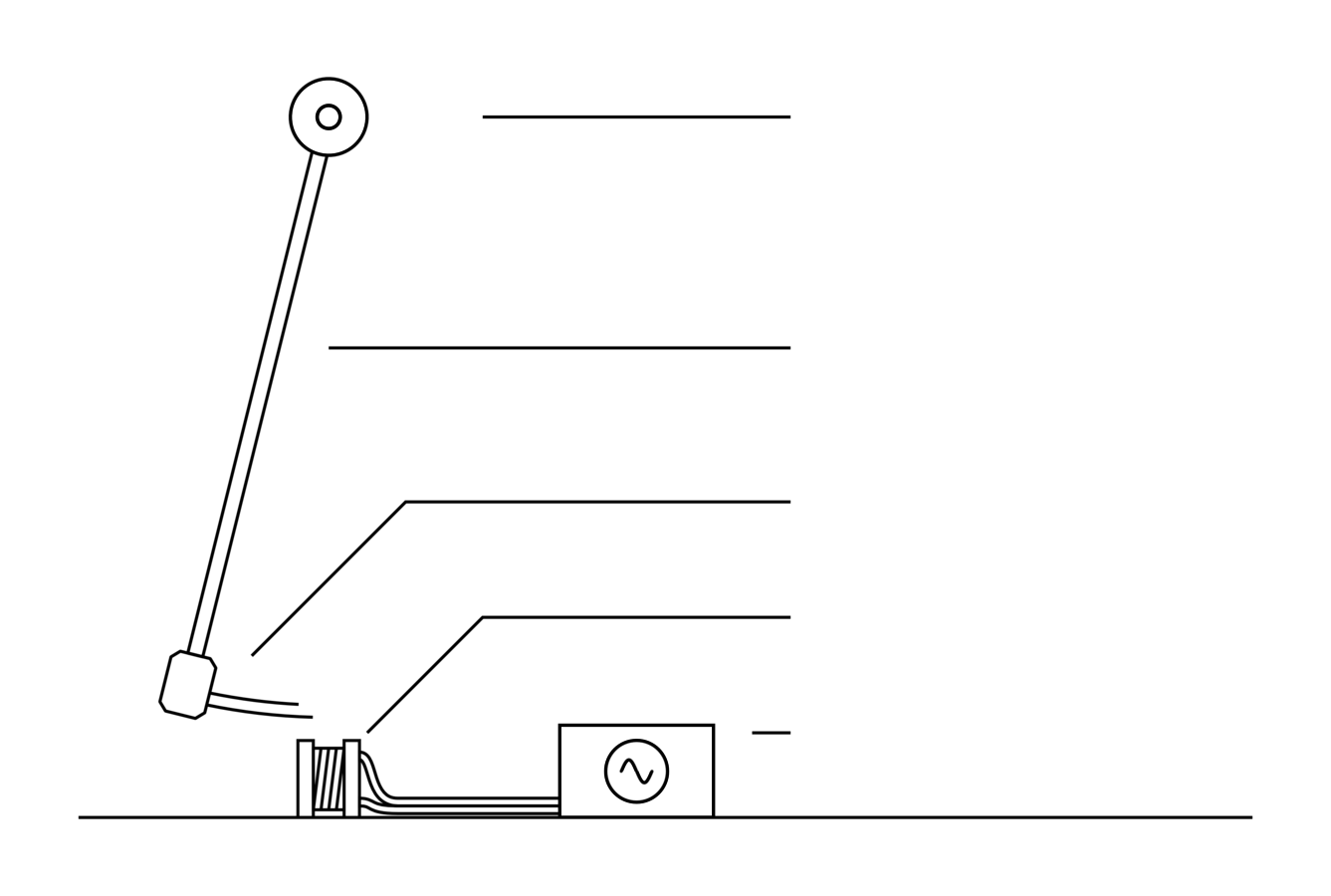
Rigid arm
AC signal
Rigid Arm
#7
Keeps magnet orientation constant.
Bob confined to arc with 1 degrees of freedom.
Setup
Solenoid Orientation
#8
Possible configurations:
1.
Coils parallel to motion
2.
Coils perpendicular to motion
Forces act perpendicular, no effect
Forces acts with motion, maximum effect
Setup
3.
Coil angle in between
Adds complexity to the system
Solenoid Specs
#8
Setup
Magnet Orientation
#9
Possible configurations:
1.
Poles horizontal
2.
Poles vertical
Force on each pole cancels, or causes torque.
Force on lower pole stronger than upper.
Resultant force parallel to motion.
Setup
Bearing, Pendulum Suspension
#10
If friction is too large,
weaker electromagnetic field could not compensate the energy dissipated by friction.
Setup
Pendulum interpretation: suspension needs to limit the motion onto a 2D plane.
#11
This setup is similar to that of a pendulum by Doubochinski.
Dynamical System
Doubochinski pendulum is known for having discrete stable amplitudes.
#11
Proposed Mechanisms
1. Velocity modulation
2. Phase regulation
Proposed by Doubochinski et al
#11
Proposed Mechanisms
1. Velocity modulation
#11
Proposed Mechanisms
2. Phase regulation
#11
Damping
For practicality, we investigated the pendulum in an overdamped configuration for initial amplitudes at angles within 90deg from vertical.
Overdamped
#13
Two amplitudes where damping has lesser effect.
Two regions where damping is more significant
Approx 20 Hz
Over Damped
#14
Overdamped
#13
Undamped regions: amplitude momentarily increases.
Pendulum entry into interaction zone shifted in-phase (constructive), then shifted out of phase (destructive)
Conclusions from overdamp
#13
In the overdamped configuration, velocity modulation had a great affect, but the phase regulation was not effective.
From different Frequencies
#13
Other frequencies (15 to 50Hz) resembled an ordinary damped oscillator.
Note the smaller fluctuations
Suggests that the smaller amplitudes increased interaction time amplified the velocity modulation, but kept shifting in and out of phase.
From different Frequencies
#13
Other frequencies (15 to 50Hz) resembled an ordinary damped oscillator.
Fluctuations present, but less
Suggests that the smaller amplitudes increased interaction time amplified the velocity modulation, but kept shifting in and out of phase.
Conclusion
#13
For overdamped configuration of the Doubochinski's pendulum, phase regulation seems less apparent.
Increasing frequency creates smaller fluctuations, whose effect diminishes with frequency.