Ruby on Rails 網站程式設計基礎班
第一課:Introduction

簽到
門禁卡
200元,不收大鈔
FB 社團
Wifi
R223 A & B:
Name: CSIE_Train
Pass: csietrain1223
Wifi
R108:
Name: CSIE_guest
User ID: html-student
Pass: Y3RBV6E7
課程目標
- 學會基礎 Ruby 語法
- 能獨立用 Ruby on Rails 架站
- 將 Rails 專案上架到雲端
About Me
- 張佑成 a.k.a Eugene (唸起來像是 ’有勁‘)
- 現職是 Ruby on Rails 工程師
年齡:關你啥事體重:秘密
Let's Get Started!
What is Ruby?
• 松本行弘 (Matz) 於 1994 年開發
• 直覺的語法
• 高生產力

松本行弘 (Matz)


松本行弘 (Matz)

Ruby Conf TW 2016 小筆記:
Karoshi - 過勞死
Prevent Alpha Syndrome
Be Lazy, work less, code in Ruby
直覺的語法
int main () {
int a;
for(a = 0; a < 3; a++){
printf("Hello World!");
}
return 0;
}3.times do
print "Hello World!"
endC
Ruby


高生產力
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello! World!");
}
}puts "Hello World!"JAVA
Ruby


高生產力
"A little knowledge of Python, Ruby, or some other scripting language works wonders in comparison to compiled languages like C++ or Java when you do need to get something quick and dirty done."
- Edmond Lau, The Effective Engineer

What is Rails?
- David Heinemeier Hansson (DHH) 在 2005 年開發
- Ruby 語言的網頁程式開發框架
- Dry: Don't Repeat Yourself
- Convention Over Configuration

DHH


什麼是框架?

制定好一套軟體開發的規範和慣例,讓開發者基於該框架進行開發
著名 Rails 專案

著名 Rails 專案

著名 Rails 專案

著名 Rails 專案

著名 Rails 專案

著名 Rails 專案

著名 Rails 專案

著名 Rails 專案
心理建設
心理建設
-
環境很難裝 -
要學的東西很多 (html, css, javascript, sql, etc)
-
會經歷一段痛苦期
Rails 科技樹
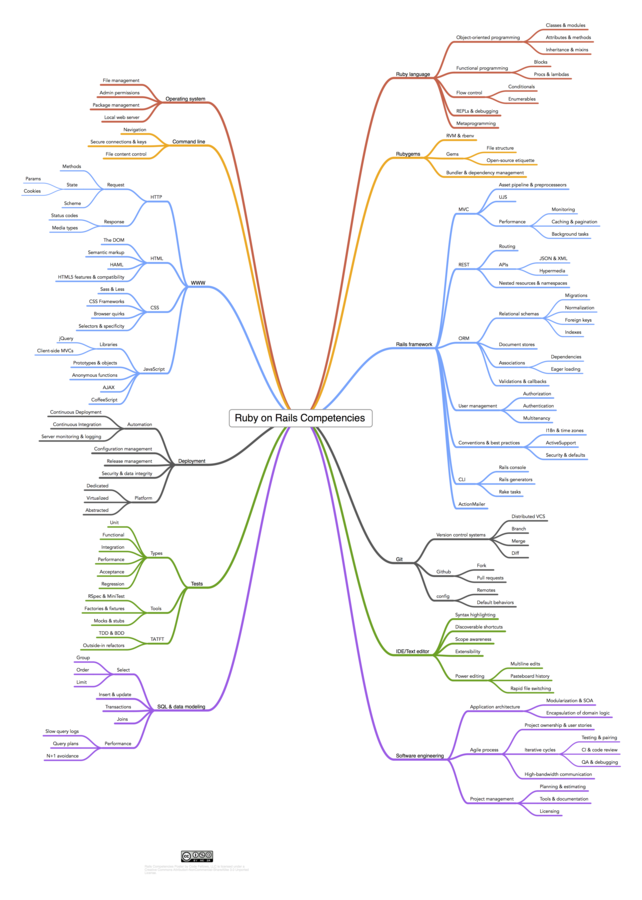
但你若克服了所有的困難...
- 擁有自已架站的能力
- 能快速 prototype 出自己的想法
- 自由 (可以 Remote 工作, 接案, etc.)
- 謎之好處
謎之好處...

課程大綱
Lesson 1 & 2 : 安裝環境 & Ruby 語法
Lesson 3 & 4 : Ruby 與物件導向 & SQL
Lesson 5 & 6 : MVC 與 ActiveRecord
課程大綱
Lesson 7 : Bootstrap 美化網頁
Lesson 8 : Heroku 部署
Lesson 9 : 使用者認證
Lesson 10: 多型關聯與 Ajax
考核規定
作業 (程式,10%)
小考 (每週四公佈,10%)
課程專案 (有交才能及格,80%)
功課規定
統一用 git 繳作業
每一個新功課請開一個 github 新專案
傳一個新專案到 github 上
把 github 連結貼到 FB 社群上
發問題方式
非程式問題,請發至 FB
程式相關問題(debug, 卡關, 環境出錯),發至 github AMA
歡樂裝機趴踢
若你要用隨身碟:
1. 請將裡面的資料夾複製到學校電腦的D槽
2. 再用 VM WorkStation開啟
ubuntu 密碼:student
歡樂裝機趴踢
註冊 Github 帳號
Github 註冊完後 帳號密碼不要忘囉!我們之後還需要用到它
Visual Studio Code

展示一下 Rails 的魔力
某慣老闆:現在 11:45 分,給我在 12:00 作出 一個定便當系統給所有參加公司活
動的來賓使用
此時你的反應...


但是你若是會 Rails...

但是你若是會 Rails...
# 使用 scaffold 指令
$rails new dinbento
$rails g scaffold order name:string phone:string description:text
$rake db:migrate
$rails server
# 做完這些事後應該還有 5~10 分鐘的時間可以喝茶、看 FB十五分鐘後...


一般工程師
你
Hello World!
打開終端機,輸入以下:
mkdir lesson1
cd lesosn1
touch hello_world.rb
將 hello_world.rb 這個檔案用 VS Code 開啟,輸入:
string = "Hello World!"
puts stringString (字串)
# 宣告一個 string (字串) 這樣做,記得字串一定要包在 " " 裡面
str = "Welcome to NTU Rails!"
# 若要把兩個 string 接在一起,可直接用加號 +
str1 = "Welcome to"
str2 = " NTU Rails!"
# irb 輸入
str1 + str2
# 就會得到:
# Welcome to NTU Rails!
# 用 puts 印出結果:
puts str1 + str2
String (字串)
# 但是用 + 號連接字串會多耗記憶體,所以我們可以用字串內差(string interpolation)的方式連接字串
# 用法就是 "#{這邊放你的字串或數字}"
# irb 輸入:
str1 = "Welcome to"
str2 = " NTU Rails 265!"
puts "#{str1}#{str2}"
# 會得到 Welcome to NTU Rails 265!
# ruby 字串也會包含型別轉換,所以你若是從 gets.chomp 得到字串型別的數字
number_str = "5"
# 你就可以用 .to_i 把這個字串轉成整數
number_str.to_i
# 會得到 5
印出字串
# print 是把任何物件轉成字串印出
number = 5
string = "Hello"
print number
print string
# =>5string
# puts 是把任何物件轉成字串,加上斷行,再印出
number = 5
string = "Hello"
puts number
puts string
# =>5
# =>Hello
數字
# 數字主要分為整數與浮點數
# 1, 101, 888 為整數
# 檢查資料型別的方式: 用 .class
1.class
# =>Fixnum
# 0.05, 3.14, 0.00001 是浮點數
(3.14).class
# =>Float
數字可用 to_s 轉成字串
5.to_s
# =>"5"數字運算
# 加法
1 + 1
# => 2
# 減法
2 - 1
# => 1
# 乘法
3 * 3
# => 9
# 除法
9 / 3
# => 3
# 餘數
10 % 3
# => 1
# 平方
2 ** 3
# => 8
Boolean (布林值)
true 和 false 是布林值,是電腦用來表示 '是' 和 '否' 的資料型別
1 == 1
# => true
1 == 2
# => false
Method (方法)
# method 方法,我們經常遇到一個程式裡面會有許多不斷重複的程式碼,我們可以把它們打包起來使用
# 可以把 method 想像成數學公式:X + Y = Z,你只要輸入 X 和 Y,這個公式就可幫妳算出 X 和 Y 的和,也就是 Z
# 若我們今天需要寫一個經常會用到計算園面積的程式,我們就可以把計算園面積的程式碼寫成一個 method:
# 宣告程式要用 def 關鍵字,加上你幫 method 取得名字,這裏我幫它取名叫 area_of_circle
def area_of_circle(radius) # (你要丟給方法的輸入,也就是參數,要寫在括弧裡)
return radius * radius * 3.14 # 計算式,注意你要計算的變數需要和括弧裡你設定的參數名一樣
end
# 我接下來可在程式任何一個地方呼叫我的方法
cicrle1 = area_of_circle(3)
irb(main):015:0> cicrle1 = area_of_circle(3)
# 放進 irb 裡面算,就可得出半徑是 3 的圓面積
# => 28.26Method (方法)
# 寫出方法後,我就可以呼叫它很多次、代入不同的參數
circle2 = area_of_circle(5)
# => 78.5
circle2 = area_of_circle(8)
# => 200.96
circle2 = area_of_circle(10)
# => 314.0
# 我也可以算長方形的面積
def area_of_rectangle(width, height) # 這時我就需要兩個參數,寬與高
return width * height
end
# 呼叫它的方法就是
area_of_rectangle(5,6)
# 傳進兩個參數
# => 30Comparisons (邏輯運算)
# 電腦用來代表是或否的資料型別是
true
false
# 他們叫做布林值(Boolean)
# 另外,nil 則是 ruby 用來表示空值的資料型別
nil
# 若想知道一個變數是否為空值,可用 nil? 方法
var = nil # 設定 var 為 nil
var.nil? # 變數 var 是否為空值?
#=> true
# 回傳 true,代表 var 是空值
# A == B 是比較 A 和 B 是否相同
if 5 == 5
puts "5 等於 5"
endComparisons (邏輯運算)
# A != B 是比較 A 和 B 是否不同
if 4 != 5
puts "4 不等於 5"
end
# A < B 是比較 A 是否小於 B
if 4 < 5
puts "4 小於 5"
end
# A > B 是比較 A 是否大於 B
if 5 > 4
puts "5 大於 4"
end
# A >= B 是比較 A 是否大於等於 B
if 5 >= 4
puts "5 大於等於 4"
endComparisons (邏輯運算)
if 4 >= 4 #若這樣比
puts "5 大於等於 4" #這行也會被印出
end
# A <= B 則是比較 A 是否小於等於 B
if 5 <= 6
puts "5 小於等於 6"
end
if 6 <= 6 #若這樣比
puts "5 小於等於 6" #這行也會被印出
endComparisons (邏輯運算)
# A && B 則是指 A 必須成立而且 B 也必須成立,我才會回傳 true
if (4 < 5) && (5 < 6)
puts "兩者都成立"
end
if (4 < 5) && (5 > 6) #這樣就不會印出任何東西,因為( 5 > 6 )不成立
puts "兩者都成立"
end
# A || B 則是指只要 A 或 B 其中一方成立,我就會回傳 true
if (4 < 5) && (5 < 6) #這樣會印出東西,因為兩者皆成立
puts "兩者都成立"
end
if (4 < 5) || (5 > 6) #這樣也會印出東西,因為兩者其中一方成立
puts "兩者都成立"
endComparisons (邏輯運算)
# !A 則是取身為布林值 A 的反值,所以
!(4 < 5) # 放入 irb 裡會回傳 false
# (4 < 5) 會回傳 true, 但前面加的 ! 會取 true 的相反值,也就是 false
# 在 ruby 裡,變數前面有兩個驚歎號代表會把判斷這個變數是否有值
!!5
# =>true 5並非空值
str = "p"
!!str
# =>true str, 也就是"p",並非空值
# ruby 語言裡唯二會被判斷成 false 的值分別是 false 和 nil
!!false
# => false
!!nil
# => falseCondition(判斷式)
input = 6
if input < 5 # 如果 if 後面判斷式成立
puts "#{input} is less than 5" # 就執行這邊
else # 不成立的話
puts "#{input} is greater than or equal to 5" # 只好執行這邊
end
# => 6 is greater than or equal to 5Condition(判斷式)
operation = 3
if operation == 1 #判斷式不成立,會接下去看下一個 elsif
result = num1 + num2
puts "your answer is: #{result}"
elsif operation == 2 #判斷式還是不成立,會接下去看下一個 elsif
result = num1 - num2
puts "your answer is: #{result}"
elsif operation == 3 # 成立!,印出 num1 x num2 的結果
result = num1 * num2
puts "your answer is: #{result}"
else
result = num1.to_f / num2.to_f
puts "your answer is: #{result}"
endCondition(判斷式)
# ternary operator 簡單來說,就是讓你用更簡潔的方法來寫 if...else 判斷式
# 語法是 判斷式 ? 成立要執行或回傳的程式碼 : 不成立要執行或回傳的程式碼
puts true ? "this is true" : "this is false"
# => "this is true"
puts false ? "this is true" : "this is false"
# => "this is false"Condition(判斷式)
# case...when,用敘述來測試一連串條件
operation = 5
case operation #case 關鍵字後面要加上被判斷的變數
when 1 # 到這裡,ruby 會去判斷 when 後面的參數是否等於 case 後面的變數
# 就等同於執行 operation == 1 (但請不要把判斷式寫在這裡喔)
puts "operation is equal to 1" # 若 operation 等於 when 後面的結果,執行這段程式碼
when 2 # 到這裡,ruby 會去執行 operation == 2
puts "operation is equal to 2" # 若 operation 等於 when 後面的結果,執行這段程式碼,以此類推
when 3 # 以此類推...
puts "operation is equal to 3"
when 4 # 以此類推...
puts "operation is equal to 4"
else # 預設項目,若上面所有的 case 都不成立時,就執行預設項目裡的程式碼
puts "operation is equal to 5"
endCondition(判斷式)
# when 後面要被比較的結果也可以是字串
operation = "3"
case operation #case 關鍵字後面要加上被判斷的變數
when "1" # 到這裡,ruby 會去執行 operation == 1 (請不要把判斷式寫在這裡喔)
puts "operation is equal to 1" # 若 operation 等於 when 後面的結果,執行這段程式碼
when "2" # 到這裡,ruby 會去執行 operation == 2
puts "operation is equal to 2" # 若 operation 等於 when 後面的結果,執行這段程式碼,以此類推
when "3"
puts "operation is equal to 3"
when "4"
puts "operation is equal to 4"
endCondition(判斷式)
# 當然,Ruby 是講求程式碼精簡的語言,所以我們可以把 case when 的程式碼變得更簡潔一點:
operation = 3
case operation
when 1 then puts "operation is equal to 1" # 加上 then 關鍵字,可直接把要執行的程式碼寫在 then 後面
when 2 then puts "operation is equal to 2"
when 3 then puts "operation is equal to 3"
when 4 then puts "operation is equal to 4"
endHomework
安裝開發環境