

Middleware, Validatie & Mailing
Validatie, Authenticate, Authorisatie & Mailing
INTRODUCTIE


Installatie
Installeer express-validator
npm install express-validatorInstalleer de dependencies
npm install
Voorbereiding
Voer de migrations uit, en laat de seeder eenmaal lopen
Vanaf nu heb je een database, met tabellen en gegevens
npx knex migrate:latest
npx knex seed:run 
Start het project
- Start het project, je zal zien dat we volgende pagina's hebben
- Home
- Contact
- Authenticatie:
- Login
- Register
- Logout
- API route (users)
npm run start:devValidatie, Authenticate, Authorisatie & Mailing
MIDDLEWARE

Middleware functions are functions that have access to the request object ( req ), the response object ( res ), and the next function in the application's request-response cycle. The next function is a function in the Express router which, when invoked, executes the middleware succeeding the current middleware.

Middleware
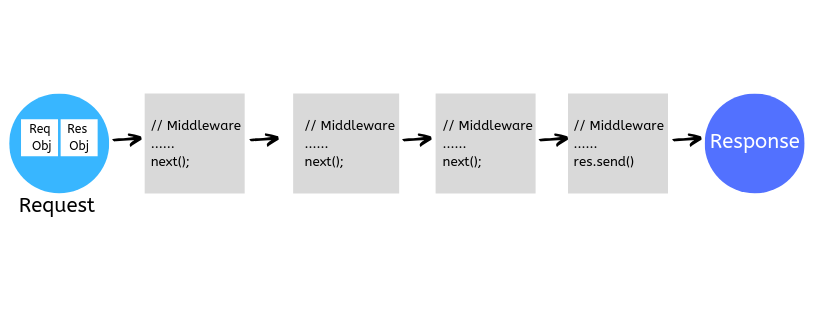

Middleware
- Opmerking: body-parser (PGM2) is deprecated en vanaf Express v4.16 ingebouwd in Express
// Body parsing is built in to Express
app.use(express.json());
app.use(express.urlencoded({extended: true}));
// Deprecated since Express v4.16:
// app.use(bodyParser.json());
// app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended: true}));
Middleware
request
response
express.
json()
express.json() zal data die wordt meegegeven vanaf de client omzetten naar json.

Middleware
-
Deze week schrijven we middleware om
formulieren te valideren -
Volgende week schrijven we middleware voor:
-
Authorisatie
- API requests
- Checken of een user ingelogd is
-
Authorisatie
Validatie, Authenticate, Authorisatie & Mailing
VALIDATIE

Validatie is het controleren van een waarde of een methode op geldigheid of juistheid. Meestal wordt deze werkwijze gebruikt bij het versturen van data met behulp van een formulier.

Validatie
- We gebruiken express-validator om te valideren dat wat wordt verstuurd hetgeen is wat we verwachten.
- We hebben een POST-method, waar we een contact formulier kunnen opvangen.
app.get("/contact", contact);
app.post("/contact", postContact, contact);
express-validator
- Vóór we data doorgeven naar onze postContact-functie, laten we deze controleren door express-validator (middleware).
request
response
express-
validator
postContact
page
controller

express-validator
- De express-validator middleware zal errors toevoegen aan de request van de client wanneer de body niet voldoet aan bepaalde criteria.
- express-validator heeft tal van ingebouwde criteria.
- Stel, je wil een e-mailadres uit je request body valideren. Gebruik de ingebouwde validator als volgt:
body('email').isEmail()
express-validator
- Gebruik
withMessageom een gebruiksvriendelijke foutmelding
toe te voegen:
body('email')
.isEmail()
.withMessage('Onjuist e-mailadres');- Maak nieuwe schakels om te controleren of je e-mail wel is ingevuld én of het ingevulde effectief een e-mailadres is:
body('email')
.notEmpty()
.withMessage('E-mail is een verplicht veld.')
.isEmail()
.withMessage('Onjuist e-mailadres'),
express-validator
- In het voorbeeld op de vorige slide zal de foutmelding de laatste boodschap zijn (Onjuist e-mailadres) TENZIJ je de ketting stopt met
bail
body('email')
.notEmpty()
.withMessage('E-mail is een verplicht veld.')
.bail()
.isEmail()
.withMessage('Onjuist e-mailadres'),
Contactformulier
- In contact.ejs vind je een array die objecten omzet naar HTML input-velden
- Die array definiëren we in de contact-functie
in PageController
<% locals.inputs?.forEach(input => { %>
<%- include('./partials/form-input', input) %>
<% }); %>
Contact
export const contact = (req, res) => {
const inputs = [
{
name: "fullname",
label: "Volledige naam",
type: "text",
},
{
name: "email",
label: "E-mail",
type: "text",
},
{
name: "message",
label: "Bericht",
type: "textarea",
},
];
res.render("contact", {
inputs
});
}
Contact
- Er zal nu een contactformulier verschijnen als je naar /contact navigeert in de browser.
- Tijd om Georgette een gevalideerd berichtje te sturen

Contact Validatie
- We voegen middleware toe via een array aan validatieregels. Daarmee valideren we:
- e-mailadres
- naam
- bericht
- Nieuwe folder middleware
- Nieuwe folder validation
- Nieuwe file
ContactValidation.js
- Nieuwe file
- Nieuwe folder validation


Contact Validatie
- Telkens wanneer we het contactformulier verzenden, zal er een validatie gebeuren
import { body } from "express-validator";
export default [
body("fullname")
.notEmpty()
.withMessage("Volledige naam is een verplicht veld.")
.bail()
.isLength({ min: 2 })
.withMessage("Volledige naam moet minstens twee tekens bevatten."),
body("email")
.notEmpty()
.withMessage("E-mail is een verplicht veld.")
.bail()
.isEmail()
.withMessage("Onjuist e-mailadres"),
body("message")
.notEmpty()
.withMessage("Bericht is een verplicht veld.")
.bail()
.isLength({ min: 10 })
.withMessage("Bericht moet minstens tien tekens bevatten."),
];

Contact Validatie
- Voeg nu de validator middleware(s) toe vlak vóór we de controller postContact ingaan.
-
Let op: zorg dat je
ContactValidationimporteert in app.js
app.post("/contact", ContactValidation, postContact, contact);
postContact
- Eenmaal aangekomen in de postContact action kunnen we het resultaat van de validatie opvragen.
export const postContact = async (req, res, next) => {
const errors = validationResult(req);
// if we have validation errors
if (!errors.isEmpty()) {
console.log("uh oh, we got errors dude");
res.send(errors);
}
};
postContact
- Twee opties:
- validatie loopt fout:
opnieuw de contactpagina tonen vianext() - validatie loopt goed:
email sturen + bevestiging
- validatie loopt fout:
postContact

- We parsen de fouten en geven de foutmeldingen per veld door naar de register route via de
next()functie.
if (!errors.isEmpty()) {
// set the form error fields
req.formErrorFields = {};
errors.array().forEach((error) => {
req.formErrorFields[error.path] = error.msg;
});
// set the flash message
req.flash = {
type: "danger",
message: "Er zijn fouten opgetreden",
};
return next();
}contact

export const contact = (req, res) => {
const inputs = [
{
name: "fullname", label: "Volledige naam", type: "text",
err: req.formErrorFields?.fullname ? req.formErrorFields["fullname"] : "",
value: req.body?.fullname ? req.body.fullname : "",
},
{
name: "email", label: "E-mail", type: "text",
err: req.formErrorFields?.email ? req.formErrorFields["email"] : "",
value: req.body?.email ? req.body.email : "",
},
{
name: "message", label: "Bericht", type: "textarea",
err: req.formErrorFields?.message ? req.formErrorFields["message"] : "",
value: req.body?.message ? req.body.message : "",
},
];
const flash = req.flash || {};
res.render("contact", {
inputs,
flash,
});
};
postContact
- Zijn alle velden correct, dan sturen we een emailtje (todo slides)
export const postContact = async (req, res, next) => {
// [...] (validation)
try {
// let us send an email
console.log('Yay, we could send Georgette an email now');
// set the flash message
req.flash = {
type: "success",
message: "Uw bericht is verzonden",
};
// empty the form fields
req.body = {};
return next();
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}

Oefening


Oefening
-
Validaties
- Cursus
- Vereist
- Minimaal 4 karakters, maximaal 50 karakters
- Email
- Vereist
- Geldig e-mailadres
- Bericht
- Vereist
- Minimaal 10 karakters, maximaal 250 karakters
- Score
- Vereist
- Minimum 0, maximum 10
- BONUS: checkbox met "Ik ga akkoord dat mijn score wordt gebruikt voor de eindevaluatie van dit vak" die verplicht moet aangevinkt worden
- Cursus

Oefening


Oefening
-
Stappen
- Set-up
- Nieuwe folder + npm init
- Dependencies installeren
- express
- express-validator
- ejs
- Server opzetten + homepagina renderen ("Hello world!)
- EJS configureren
- Routes + controller
- GET / (homepagina renderen + formulier)
- POST / (form submit)
- Validaties
- Validation middleware schrijven + toevoegen
- Errors renderen in template
- Set-up
Validatie, Authenticate, Authorisatie & Mailing
MAILING


Nodemailer is a module for Node.js applications to allow easy as cake email sending. The project got started back in 2010 when there was no sane option to send email messages, today it is the solution most Node.js users turn to by default.

Installatie
Installeer nodemailer
npm install nodemailer
Installatie Nodemailer App
Installeer de applicatie nodemailer op je PC of Mac:
https://www.nodemailer.com/app/
Hiermee kunnen we een e-mail server starten en testmails opvangen.


Configuratie Nodemailer App
Maak een nieuw project in nodemailer
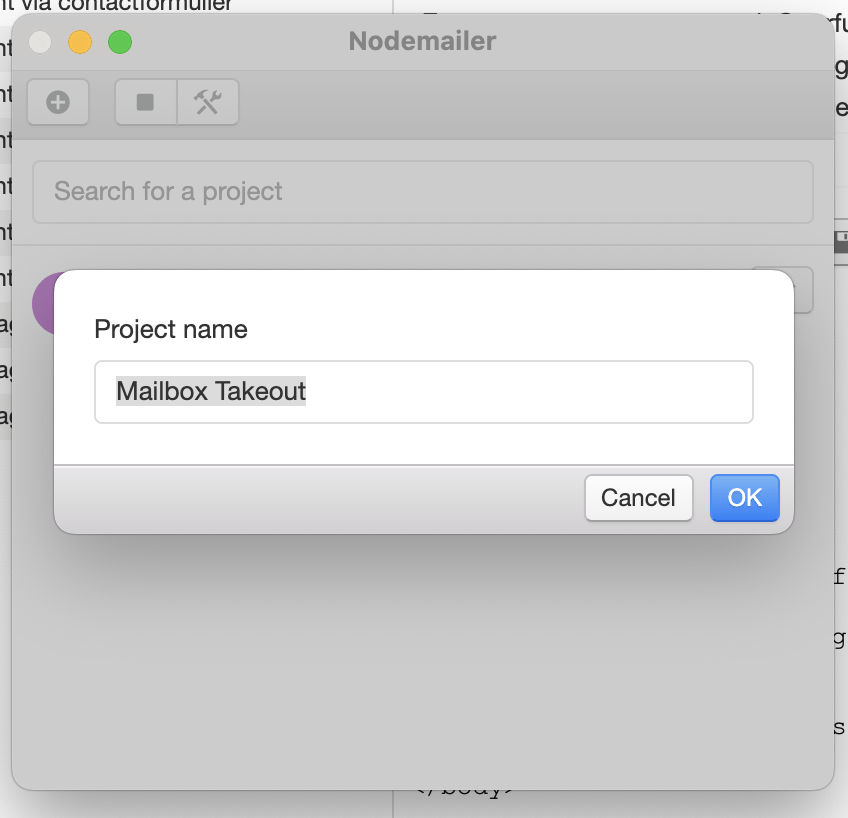

Configuratie Nodemailer App
Ga naar het tabblad "Local Server" en stel zo nodig port, username en password in
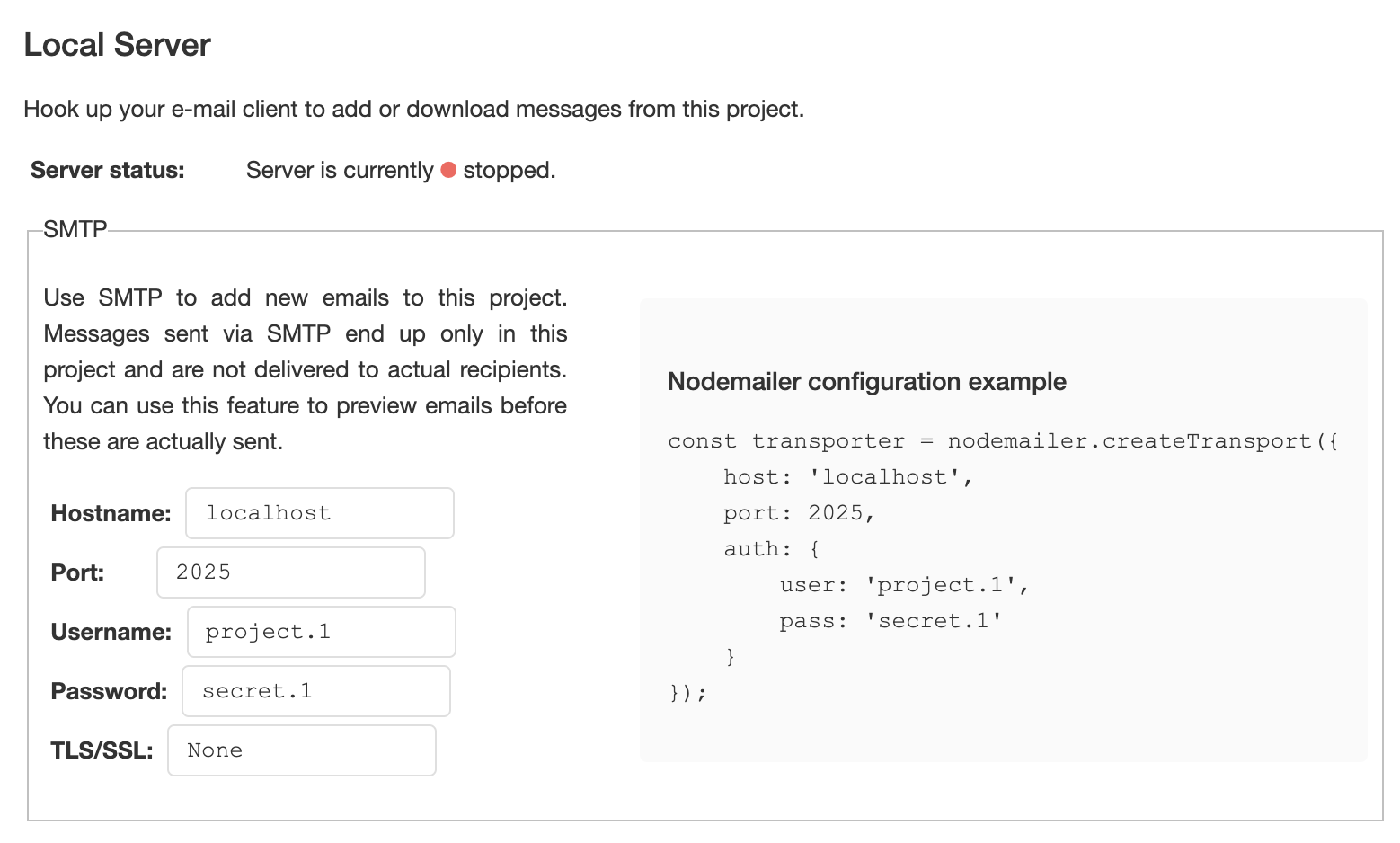
Kopieer
het transporter
script

Configuratie Nodemailer App
Start de server
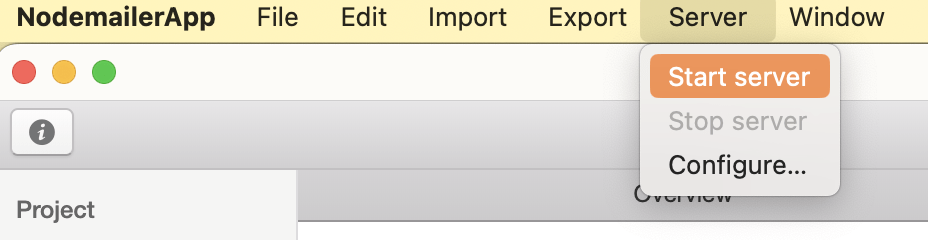
Via het tabblad zou Server Status nu op running moeten staan


Module configuratie
- Maak een configuratie-bestand aan in je project
src/lib/MailTransporter.js - Plak daar de code uit de app
- Vergeet niet nodemailer import en transporter export
import nodemailer from "nodemailer";
const transporter = nodemailer.createTransport({
host: "localhost",
port: 1025,
auth: {
user: "project.1",
pass: "secret.1",
},
});
export default transporter;

Een eerste testmail
- Beschrijf een route die een testmail verzendt
import transporter from "./lib/MailTransporter.js";
// ...
app.get("/testmail", async (req, res) => {
try {
const mailInfo = await transporter.sendMail({
from: "noreply@parfumeriegeorgettemadelein.be",
to: "foobar@example.com",
subject: "Test mail",
text: "This is a test mail",
});
res.send(mailInfo);
} catch (error) {
res.send(error);
}
});
Een eerste testmail
- Als je de route bezoekt, ontvang je normaal de e-mail
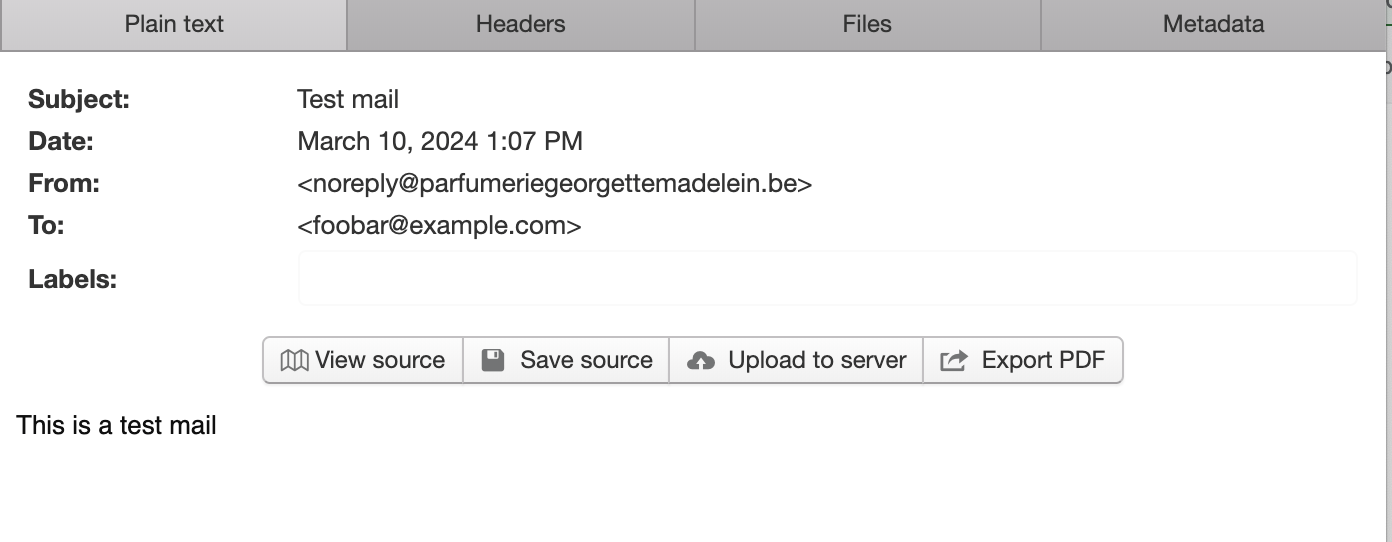

HTML mail
- Je kan ook mails sturen met (opgemaakte) HTML
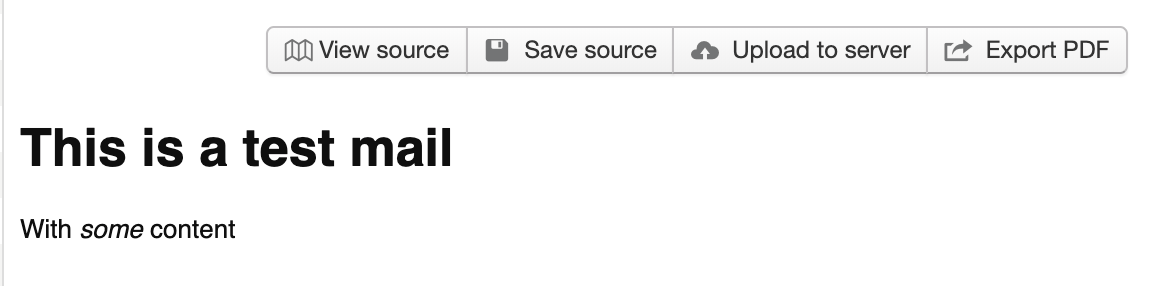
const mailInfo = await transporter.sendMail({
from: "noreply@parfumeriegeorgettemadelein.be",
to: "foobar@example.com",
subject: "Test mail",
// text: "This is a test mail",
html: `
<h1>This is a test mail</h1>
<p>With <em>some</em> content</p>
`,
});