Functions in C/C++
C/C++中的函数
by 方泓睿
With reveal.js and plantUML
What's Function in Programming Language?
编程语言中的函数是啥
In programming, a named section of a program that performs a specific task is called function . In this sense, a function is a type of procedure or routine. Some programming languages make a distinction between a function, which returns a value, and a procedure, which performs some operation but does not return a value.
在编程中,执行特定任务的程序的命名部分称为函数。 从这个意义上讲,函数是一种过程或例程。 一些编程语言区分了一个返回值的函数和一个执行某些操作但不返回值的过程。
Functions in C/C++
C/C++中的函数
Every C/C++ program has at least one function, which is main(), and all the most trivial programs can define additional functions.
每个C/C++程序至少有一个函数,即main()。所有C++程序都可以定义其他函数。
You can divide up your code into separate functions. How you divide up your code among different functions is up to you, but logically the division usually is such that each function performs a specific task.
您可以将代码划分为单独的函数。 如何划分代码到不同的函数取决于您,但从逻辑上讲,通常做法是让每个函数执行某一项特定任务。
Functions in C/C++
C/C++中的函数
In C/C++, a complete function consists of two parts: declaration and definition.
在C / C ++中,一个完整的函数由两部分组成:声明和定义。
A function declaration tells the compiler about a function's name, return type, and parameters. A function definition provides the actual body of the function.
函数声明告诉编译器函数的名称,返回类型和参数。 函数定义提供函数的实际主体。
Defining a Function
函数定义
The general form of a C/C++ function definition is as follows:
C/C ++函数定义的一般形式如下:
// In C/C++
return_type function_name( parameter list ) {
//body of the function
}
// In C++11 and above:
auto function_name( parameter list ) -> return_type {
//body of the function
}Defining a Function
函数定义
- Return Type - A function may return a value. The return_type is the data type of the value the function returns. Some functions perform the desired operations without returning a value. In this case, the return_type is the keyword void.
- 返回类型 - 函数可以返回值。 return_type是函数返回的值的数据类型。 某些函数执行所需的操作而不返回值。 在这种情况下,return_type是关键字void。
Defining a Function
函数定义
- Parameters − A parameter is like a placeholder. When a function is invoked, you pass a value to the parameter. This value is referred to as actual parameter or argument. The parameter list refers to the type, order, and number of the parameters of a function. Parameters are optional; that is, a function may contain no parameters.
- 参数 - 参数类似于占位符。 调用函数时,将值传递给参数。 该值称为实际参数或参数。 参数列表是指函数参数的类型,顺序和数量。 参数是可选的; 也就是说,函数可能不包含任何参数。
Defining a Function
函数定义
- Function Body − The function body contains a collection of statements that define what the function does.
- 函数体 - 函数体包含一组语句,用于实现函数的功能
Let's see an example.....
Defining a Function
函数定义
we can imagine that there is a function named max which finds the biggest number among two number:
我们可以想象有一个名为max的函数可以找到两个数中最大的数字:
// max returns the max between two numbers
int max(int num1, int num2) {
// local variable declaration
int result;
if (num1 > num2)
result = num1;
else
result = num2;
return result;
}// or
auto max(int num1, int num2) -> int {
// local variable declaration
int result;
if (num1 > num2)
result = num1;
else
result = num2;
return result;
}Function Declarations
函数声明
A function declaration tells the compiler about a function name and how to call the function. The actual body of the function can be defined separately.
函数声明告诉编译器函数名称以及如何调用函数。 函数的实际主体可以单独定义。
Function Declarations
函数声明
A function declaration has the following parts :
函数的声明由这几个部分构成:
// in C and C++
return_type function_name( parameter list );
// in C++11 and above:
auto function_name( parameter list ) -> return_type;Function Declarations
函数声明
For the above defined function max(), following is the function declaration:
对于之前定义的函数max(),以下是函数声明:
int max(int num1,int num2);
//or
auto max(int num1,int num2) -> int;Function Declarations
函数声明
Parameter names are not important in function declaration only their type is required, so following is also valid declaration :
参数名称在函数声明中并不重要,只需要它们的类型,因此以下也是有效的声明:
int max(int,int);
//or
auto max(int,int) -> int;Function defination can be considered as the combination of function declaration and function body
函数定义可以被看做函数声明+函数体
Calling a Function
函数调用
While creating a function, you give a definition of what the function has to do. To use a function, you will have to call or invoke that function.
在创建函数时,您可以定义函数必须执行的操作。 要使用函数,您必须调用该函数。
When a program calls a function, program control is transferred to the called function. A called function performs defined task and when it’s return statement is executed or when its function-ending closing brace is reached, it returns program control back to the main program.
当程序调用一个函数时,程序控制流被转移到被调用的函数。 被调用的函数执行已定义的任务,当执行return语句或达到其函数结束右括号时,它将程序控制返回给调用者。
Calling a Function
函数调用
To call a function, you simply need to pass the required parameters along with function name, and if function returns a value, then you can store returned value.
要调用函数,只需要传递必需的参数和函数名称,如果函数返回一个值,那么您可以存储返回的值。
Calling a Function
函数调用
To call a function, you simply need to pass the required parameters along with function name, and if function returns a value, then you can store returned value.
要调用函数,只需要传递必需的参数和函数名称,如果函数返回一个值,那么您可以存储返回的值。
For example...
Calling a Function
函数调用
#include <iostream>
using std::cout, std::endl;
// function declaration
auto max(int num1, int num2) -> int;
auto main() -> int {
// local variable declaration:
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
int ret;
// calling a function to get max value.
ret = max(a, b);
cout << "Max value is : " << ret << endl;
return 0;
}
// function returning the max between two numbers
auto max(int num1, int num2) -> int {
// local variable declaration
int result;
if (num1 > num2)
result = num1;
else
result = num2;
return result;
}Tell me what's the output of the code on the right:
告诉我右边这段代码的输出是啥
Function declaration is required when you define a function in one source file and you call that function in another file. In such case, you should declare the function at the top of the file calling the function.
在一个源文件(.cpp/.cc)中定义函数并在另一个文件中调用该函数时,需要函数声明。 在这种情况下,您应该在调用该函数的文件顶部声明该函数。
For example...
auto max(int a, int b)->int{
return a>b?a:b
}In max.cc:
In main.cc:
#include <iostream>
using std::cout,std::endl;
auto max(int,int) -> int;
auto main()->int{
cout << max(1,2) << endl;
}Compile the program with:
c++ -std=c++17 main.cc max.cc -o maxThen run it:
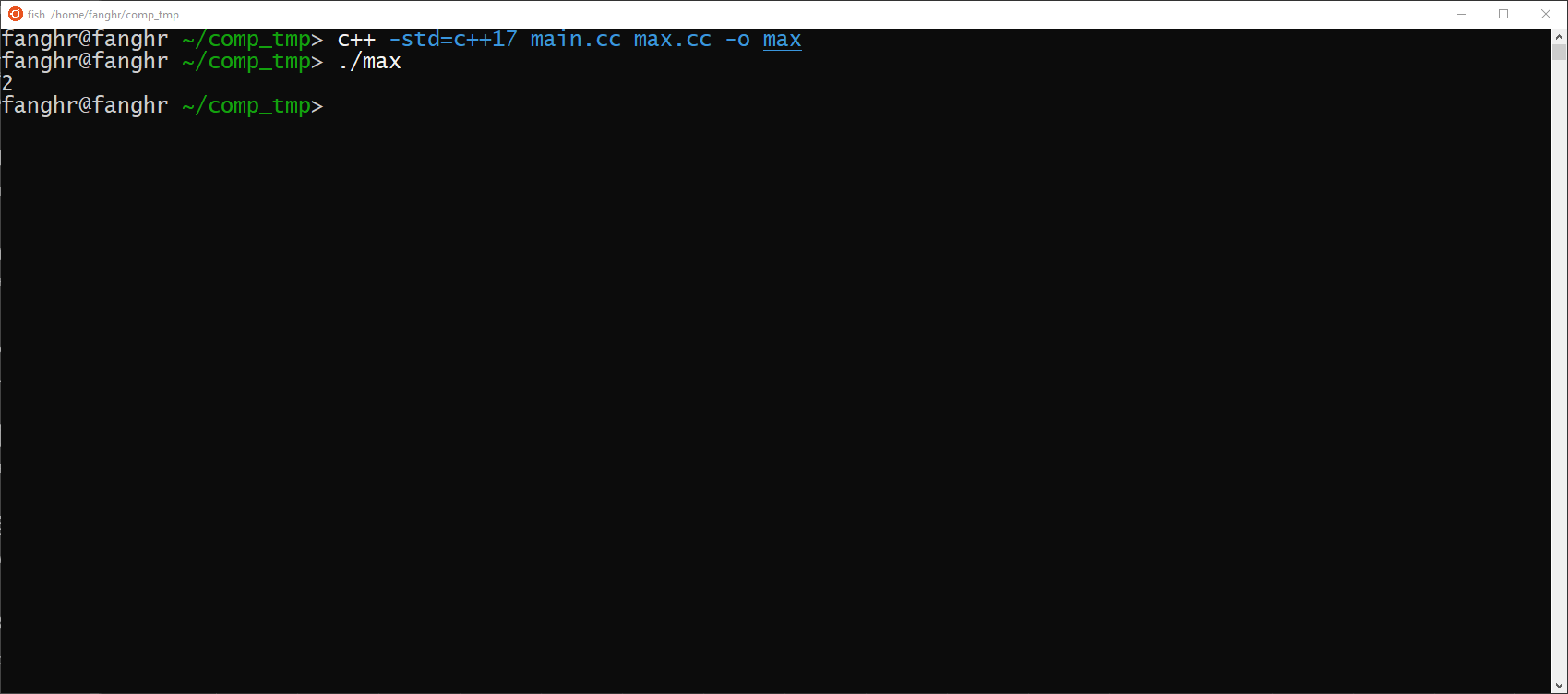
Actually,to call a function you just need function's return type ,function name and types of parameters
事实上,只要你知道函数的返回值,函数的名字以及参数的类型,你就可以调用这个函数。
Function Arguments
函数参数
If a function is to use arguments, it must declare variables that accept the values of the arguments. These variables are called the formal parameters of the function.
如果函数使用参数,它必须声明接受参数值的变量。 这些变量称为函数的形式参数。
The formal parameters behave like other local variables inside the function and are created upon entry into the function and destroyed upon exit.
形式参数的行为与函数内部的其他局部变量相似,并在进入函数时创建,并在退出时销毁。
Function Arguments
函数参数
While calling a function, there are three ways that arguments can be passed to a function:
在调用函数时,有三种方法可以将参数传递给函数:
Function Arguments
函数参数
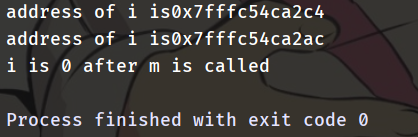
1. Call by Value 传值调用
This method copies the actual value of an argument into the formal parameter of the function. In this case, changes made to the parameter inside the function have no effect on the argument.
此方法将参数的实际值复制到函数的形式参数中。 在这种情况下,对函数内部参数所做的更改对参数没有影响。
Function Arguments
函数参数
#include <iostream>
using std::cout, std::endl;
auto m(int i) -> void {
cout << "address of i is" << &i << endl;
i += 10;
}
auto main() -> int {
auto i = 0;
cout << "address of i is" << &i << endl;
m(i);
cout << "i is " << i << " after m is called" << endl;
}
Function Arguments
函数参数
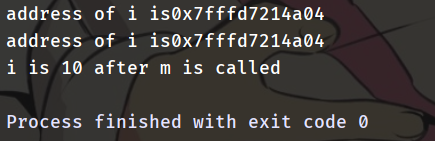
2. Call by Pointer 传指针调用(开始不会翻译)
This method copies the address of an argument into the formal parameter. Inside the function, the address is used to access the actual argument used in the call. This means that changes made to the parameter affect the argument.
此方法将参数的地址复制到形式参数中。 在函数内部,该地址用于访问调用中使用的实际参数。 这意味着对参数所做的更改会影响参数。
Function Arguments
函数参数
#include <iostream>
using std::cout, std::endl;
auto m(int *i) -> void {
cout << "address of i is" << i << endl;
*i += 10;
}
auto main() -> int {
auto i = 0;
cout << "address of i is" << &i << endl;
m(&i);
cout << "i is " << i << " after m is called" << endl;
}
Function Arguments
函数参数
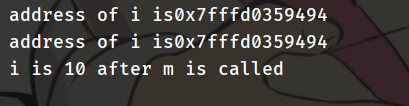
2. Call by Reference(C++ only) 传引用调用(仅限C++)
This method copies the reference of an argument into the formal parameter. Inside the function, the reference is used to access the actual argument used in the call. This means that changes made to the parameter affect the argument.
此方法将参数的引用复制到形式参数中。 在函数内部,引用用于访问调用中使用的实际参数。 这意味着对参数所做的更改会影响参数。
Function Arguments
函数参数
#include <iostream>
using std::cout, std::endl;
auto m(int &i) -> void {
cout << "address of i is" << &i << endl;
i += 10;
}
auto main() -> int {
auto i = 0;
cout << "address of i is" << &i << endl;
m(i);
cout << "i is " << i << " after m is called" << endl;
}
Function Arguments
函数参数
By default, C++ uses call by value to pass arguments. In general, this means that code within a function cannot alter the arguments used to call the function
默认情况下,C ++使用复制(call by value)来传递参数。 通常,这意味着函数内的代码不能改变用于调用函数的参数
Default Values for Parameters(C++)
参数默认值(C++)
When you define a function, you can specify a default value for each of the last parameters. This value will be used if the corresponding argument is left blank when calling to the function.
定义函数时,可以为每个最后一个或几个参数指定默认值。 如果在调用函数时相应的参数保留为空,则将使用此值。
Default Values for Parameters(C++)
参数默认值(C++)
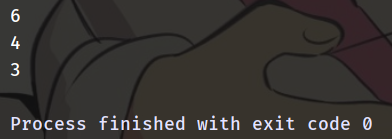
#include <iostream>
using std::cout, std::endl;
auto SumThreeNumber(int a, int b = 1, int c = 1) -> int {
return a + b + c;
}
auto main() -> int {
cout << SumThreeNumber(1, 2, 3) << endl;
cout << SumThreeNumber(1, 2) << endl;
cout << SumThreeNumber(1) << endl;
}
Thanks for listening
and special thanks to google translate.....