The hidden treasure of the web!
{ Discovering the DOM }
1
What is the DOM ?
3
DOM Manipulation
Summary
2
DOM Elements
4
DOM Events
# What is the DOM ?
1. What is the DOM ?
Document Object Model
The Javascript DOM (Document Object Model) is tree-like representation of the contents of a webpage, that allows developers to manipulate the content, structure, and style of a website. It's a structured representation of an HTML document that can be manipulated
# What is HTML?

# What is HTML?
This is how your browser sees the web. Welcome to the DOMatrix!
# What is HTML?
The DOM is the bridge between your HTML (structure of a webpage) and the interactivity provided by JavaScript.
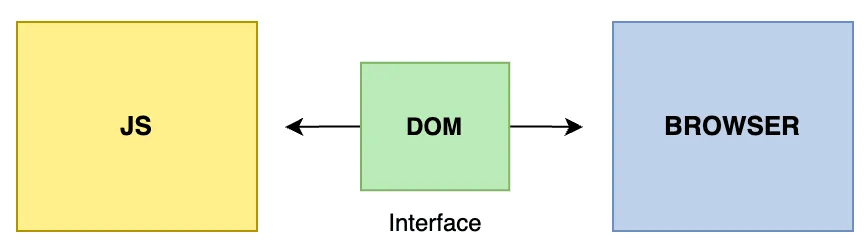
it’s a programming interface that transforms a web page into an object model that the browser can understand.
# What is HTML?
DOM Representation
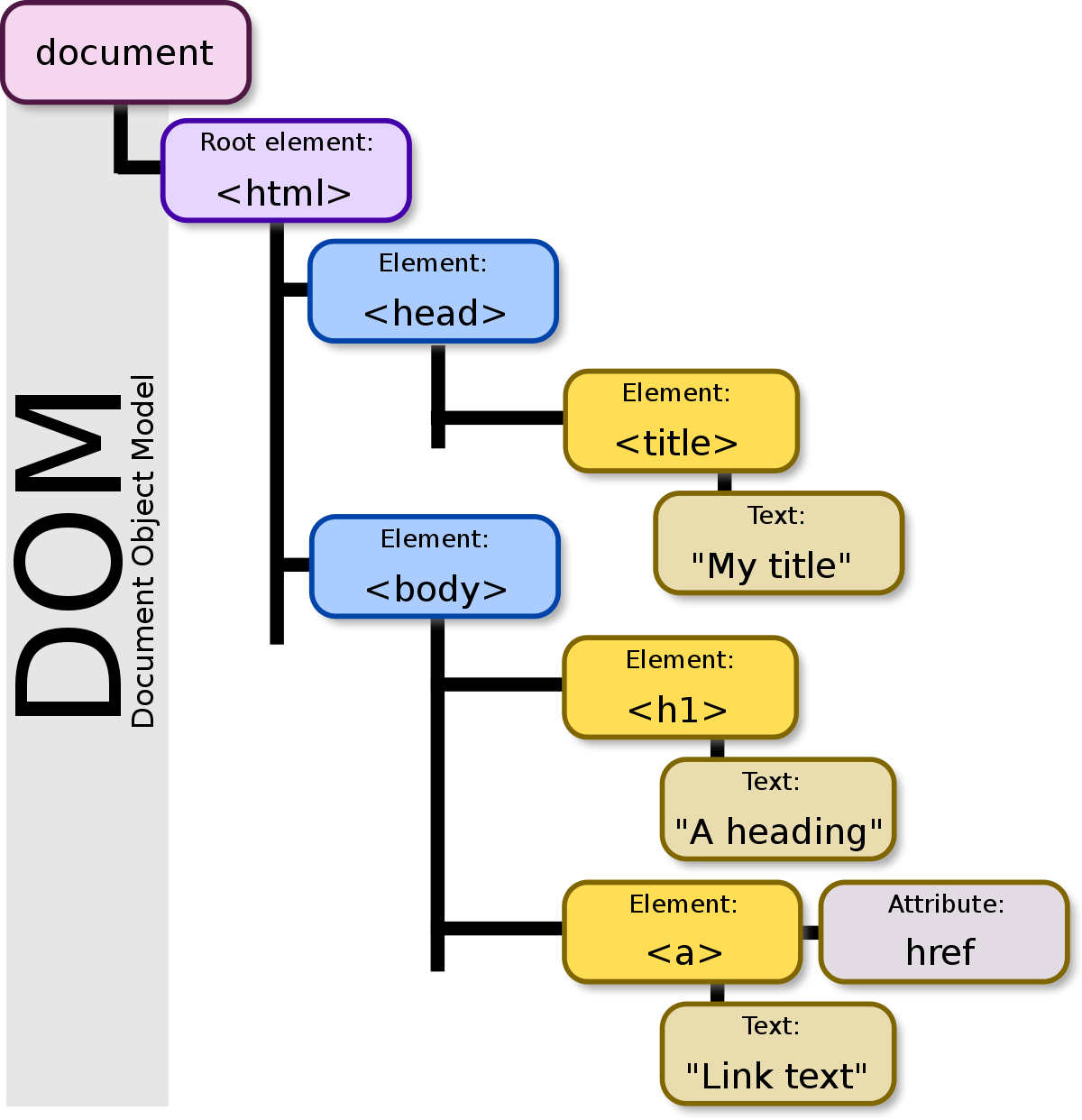
The DOM represents a webpage as a tree structure where:
- The ROOT: is the HTML document.
- Nodes: HTML element (<div>, <p>...).
- Leaves : Text and attributes (id, class...).
These nodes can be accessed, modified, added, or removed using JavaScript.
# What is HTML?

VS
Without DOM
With DOM ✨
Why is the DOM Important?
- Without the DOM, your webpage is just a static photo 📷.
- The DOM allows your page to:
- React to user input (clicks, typing, etc.).
- Dynamically change its content.
# Essential Extensions
2. DOM Elements
# VSC Interface Overview
Accessing Elements in the DOM
const header = document.getElementById('header');
console.log(header.textContent); // Outputs: "Welcome to the DOM"- Selecting Elements
When working with the DOM, you use “selectors” to target the nodes you want to work with.
You can use a combination of CSS-style selectors and relationship properties to target the nodes you want.
JavaScript provides several ways to select and work with elements in the DOM.
- getElementById(id)
Selects an element by its unique id.
# VSC Interface Overview
Accessing Elements in the DOM
const descriptions = document.getElementsByClassName('description');
console.log(descriptions[0].textContent); // "Learn DOM manipulation step by step."2. getElementsByClassName(className)
Selects all elements with a specific class name.
const header = document.querySelector('#header');
console.log(header); // "Learn DOM manipulation step by step."3. querySelector(selector)
Selects the first element that matches a CSS selector.
# VSC Interface Overview
Accessing Elements in the DOM
const paragraphs = document.querySelectorAll('p');
paragraphs.forEach(p => console.log(p.textContent));4. querySelectorAll(selector)
Selects all elements matching a CSS selector and returns a NodeList.
Important ! the return value is not an array. It looks like an array, and it somewhat acts like an array, but it’s really a “NodeList”. The big distinction is that several array methods are missing from NodeLists. One solution, if problems arise, is to convert the NodeList into an array. You can do this with Array.from() or the spread operator.
# VSC Interface Overview
Accessing Elements in the DOM
const body = header.parentNode;- Traversing the DOM
1. Parent Node
Access the parent of an element.
const children = body.childNodes;2. Child Nodes
Access all child nodes of an element.
# VSC Interface Overview
Accessing Elements in the DOM
const nextElement = header.nextElementSibling;- Traversing the DOM
3. Sibling Nodes
Navigate between elements on the same level.
# Attributes
3. DOM Manipulation
# VSC Interface Overview
Modifying the DOM
header.textContent = "Welcome to Advanced DOM Manipulation!";- Changing Content
- textContent
Modifies only the text inside an element (inner text) .
header.innerHTML = "<span>Welcome to <strong>DOM</strong>!</span>";2. innerHTML
Modifies the HTML content inside an element (inner HTML). Dangerous !
# VSC Interface Overview
Modifying the DOM
document.createElement(tagName, [options])
const newElement = document.createElement('button');
newElement.textContent = "Click Me!";
- Adding Elements
- Create an Element ()
document.body.appendChild(newElement); //appends childNode as the last child of parentNode.
parentNode.insertBefore(newNode, referenceNode)// inserts newNode into parentNode before referenceNode.
This function does NOT put your new element into the DOM, it creates it in memory. This is so that you can manipulate the element (by adding styles, classes, ids, text, etc.) before placing it on the page
# VSC Interface Overview
Modifying the DOM
- Removing Elements
document.body.removeChild(newElement);# VSC Interface Overview
Modifying the DOM
header.classList.add('highlight');- Adding and Removing Classes
- Add a Class
header.classList.remove('highlight');2. Remove a Class
header.classList.toggle('highlight'); 3. Toggle a Class
# VSC Interface Overview
Example
<body>
<h1>THE TITLE OF YOUR WEBPAGE</h1>
<div id="container"></div>
</body>
- HTML File
const container = document.querySelector("#container");
const content = document.createElement("div");
content.classList.add("content");
content.textContent = "This is the glorious text-content!";
container.appendChild(content);
2. JS File
# VSC Interface Overview
Note
Keep in mind that the JavaScript does not alter your HTML, but the DOM - your HTML file will look the same, but the JavaScript changes what the browser renders.
4. DOM Events
# What is HTML?
Events in the DOM
Events are actions that occur when a user interacts with a webpage (e.g., clicks, keystrokes, mouse movements), which JavaScript can "listen to" and respond to.
Examples of Events:
- Clicking a button.
- Typing in a form field.
- Scrolling the page.
- Moving the mouse over an image.
Imagine ringing a doorbell (the event). JavaScript is the person inside who hears the bell and decides what to do next (the event handler).
Real-World Analogy !
# VSC Interface Overview
Adding Event Listeners
const button = document.querySelector('button');
button.addEventListener('click', () => {
alert('Button clicked!');
});Steps:
- Select the element.
- Specify the event type (e.g.,
'click'). - Define the function to run when the event occurs.
element.addEventListener('event', callbackFunction);# VSC Interface Overview
Types of DOM Events
const image = document.querySelector('img');
image.addEventListener('mouseover', () => {
console.log('Mouse hovered over the image!');
});1. Mouse Event
-
click: When the user clicks on an element. -
dblclick: Double-clicking an element. -
mouseover: Hovering over an element. -
mouseout: Moving the mouse away from an element. -
mousedown: When the mouse button is pressed down. -
mouseup: When the mouse button is released.
# VSC Interface Overview
Types of DOM Events
document.addEventListener('keydown', (event) => {
console.log(`Key pressed: ${event.key}`);
});2. Keyboard Events
-
keydown: When a key is pressed. -
keyup: When a key is released. -
keypress(deprecated): When a key is pressed down (excluding special keys).
The event object gives details about the key, like event.key (e.g., 'Enter') and event.code (e.g., 'KeyA').
# VSC Interface Overview
Types of DOM Events
const inputField = document.querySelector('input');
inputField.addEventListener('input', () => {
console.log('Input value changed!');
});3. Form Events
-
submit: When a form is submitted. -
input: When the user types in an input field. -
change: When the value of an input, select, or textarea changes. -
focus/blur: When an element gains or loses focus.
# VSC Interface Overview
Types of DOM Events
window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
console.log('You are scrolling!');
});4. Window Events
-
load: When the entire page (including images and styles) has loaded. -
resize: When the browser window is resized. -
scroll: When the user scrolls the page.
# VSC Interface Overview
The Event Object
const inputField = document.querySelector('input');
inputField.addEventListener('input', () => {
console.log('Input value changed!');
});Properties of the Event Object:
-
type: The type of event (e.g.,'click','keydown'). -
target: The element that triggered the event. -
key: The key pressed during a keyboard event. -
clientX/clientY: The x and y coordinates of the mouse. -
defaultPrevented: Whether the default action was prevented.
Whenever an event occurs, JavaScript creates an Event Object that provides details about the event.
# VSC Interface Overview
Preventing Default Behavior
form.addEventListener('submit', (event) => {
event.preventDefault();
console.log('Form submission prevented!');
});Example: Preventing Form Submission
Sometimes, you want to stop the browser's default action for an event.
# VSC Interface Overview
Advanced: Event Delegation
document.querySelector('ul').addEventListener('click', (event) => {
if (event.target.tagName === 'LI') {
console.log(`You clicked on: ${event.target.textContent}`);
}
});Instead of adding listeners to multiple elements, add one listener to a parent element and use the target property.