The Magic Wand of Web Design
{Mastering CSS}
1
What is CSS?
3
Selectors
5
Typography
Summary
2
Basic Structure
4
The Box Model
6
Units
7
Backgrounds
8
Variables
# What is HTML?
1. What
is CSS?
Cascading Style Sheets
CSS is a stylesheet language used to style and layout web pages. It controls the appearance of HTML elements by defining colors, fonts, spacing, and positioning. CSS also enables responsive designs, animations, and custom themes, making websites visually appealing and user-friendly. In short, it’s what turns your web pages from plain text to works of art!
# What is HTML?

Think of HTML as the skeleton of a webpage and CSS as the skin and clothes.
# What is HTML?

Or you can see CSS as the makeup artist of the web!
# What is HTML?
# Basic Structure
2. Anatomy of a CSS Document
The CSS document structure defines how CSS is written, organized, and applied to a web page.
Notes
- Every Css file has '.CSS’ extention.
- We can include the CSS file in three main ways
# Basic Structure
-
Inline CSS: Written directly in the HTML element using the
styleattribute.
<p style="color: blue; font-size: 20px;">This is styled text.</p>2. Internal CSS: Defined within a <style> tag inside the <head> of the HTML document.
3. External CSS: Written in a separate .css file and linked to the HTML document.
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css" />Notes
-
CSS file mainly contain a set of elements called rules
-
The rules consists of selectors and declaration blocks
-
Selector: Specifies the HTML elements to style
-
Declaration Block: Contains one or more style declarations in
{} - A style declaration comes with a key and a value.
# Basic Structure
selector {
property: value;
}
h1 {
color: red;
}
# VSC Interface Overview
3. Selectors:
Targeting Elements
# VSC Interface Overview
CSS Selectors Cheat Sheet!
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
} /* Useful for resetting default styles. */
1. Universal Selector
- Targets all elements on the page.
p {
font-size: 16px;
color: #333;
} /* usefull To style all instances of an element similarly. */2. Type Selector
- Targets all elements of a specific HTML tag.
# VSC Interface Overview
CSS Selectors Cheat Sheet!
.button {
background-color: blue;
color: white;
} /* usefull For styling multiple elements with the same class. */3. Class Selector
- Targets elements with a specific
classattribute: .classname
#header {
background-color: gray;
} /* usefull For unique elements like a header or footer. */4. ID Selector
- Targets a single element with a specific
id: #idname
# VSC Interface Overview
h1, h2, h3 {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
}/* usefull To reduce repetitive code */5. Group Selector
- Applies the same styles to multiple elements
: selector1, selector2, selector3
CSS Selectors Cheat Sheet!
.container p {
color: green;
} /*To style elements within a specific section. */6. Descendant Selector
- Targets elements inside a specific parent.
ancestor descendant
# VSC Interface Overview
.menu > li {
list-style: none;
}
/* To avoid affecting nested elements.*/7. Child Selector
- Targets direct child elements of a specific parent.
parent > child
CSS Selectors Cheat Sheet!
h1 + p {
margin-top: 10px;
} /* To style the first paragraph after a header.*/8. Adjacent Sibling Selector
- Styles an element that immediately follows another.
element1 + element2
# VSC Interface Overview
h1 ~ p {
color: blue;
}
/* For styling all siblings of a specific element.*/9. General Sibling Selector
- Styles all elements that share the same parent and follow another element.
element1 ~ element2
CSS Selectors Cheat Sheet!
# VSC Interface Overview
input[type="text"] {
border: 1px solid black;
}
/* For forms and specific attributes.*/10. Attribute Selector
- Targets elements based on their attributes or attribute values.
-
[attribute]– Elements with a specific attribute. -
[attribute=value]– Elements with an attribute of a specific value. -
[attribute^=value]– Starts with a value. -
[attribute$=value]– Ends with a value. -
[attribute*=value]– Contains a value.
CSS Selectors Cheat Sheet!
# VSC Interface Overview
a:hover {
color: red;
}
11. Pseudo-classes
- Targets elements in a specific state.
selector:pseudo-class- Common examples:
-
:hover– When the user hovers over an element. -
:nth-child(n)– Targets the nth child of a parent.
CSS Selectors Cheat Sheet!
# VSC Interface Overview
p::first-line {
font-weight: bold;
}
12. Pseudo-elements
- Targets specific parts of an element.
selector::pseudo-element- Common examples:
-
::before– Adds content before an element. -
::after– Adds content after an element.
CSS Selectors Cheat Sheet!
# VSC Interface Overview
inline > ID > Class > selectors13. Cascading and Specificity
- When multiple selectors apply, specificity determines which style wins:
- Inline styles: Highest specificity.
- ID selectors: More specific than class or type selectors.
- Class selectors: More specific than type selectors.
- Universal selector: Lowest specificity.
CSS Selectors Cheat Sheet!
# VSC Interface Overview
# Essential Extensions
4. The Box Model
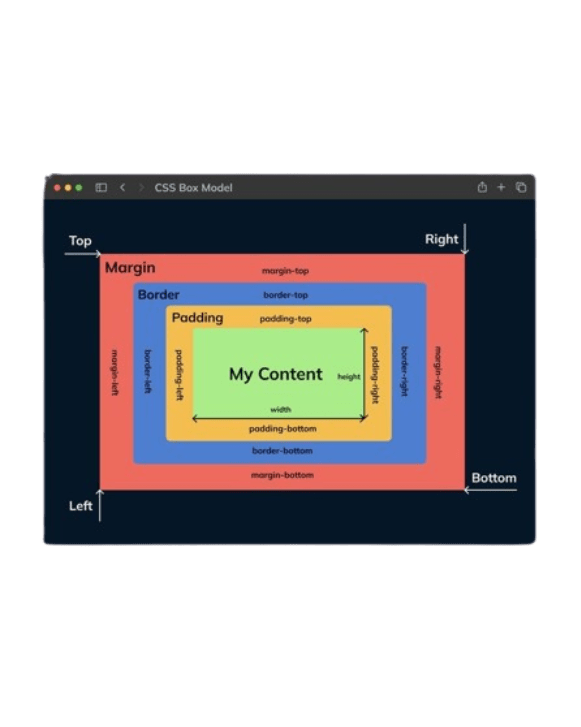
# Attributes
5. CSS Typography
# VSC Interface Overview
CSS Typography: Making Text Look Amazing
body {
font-family: "Arial", sans-serif;
}
1. Font Family
- Specifies the font for text.
font-family: "Font Name", fallback-font;
p {
font-size: 16px;
}
2. Font Size
- Sets the size of the text.
# VSC Interface Overview
CSS Typography: Making Text Look Amazing
h1 {
font-weight: bold; /* Or numeric values: 100 to 900 */
}
3. Font Weight
- Controls the boldness of text.
- Common values:
normal(default)boldlighterbolder
# VSC Interface Overview
CSS Typography: Making Text Look Amazing
em {
font-style: italic;
}
4. Font Style
- Defines whether text is normal, italicized, or oblique.
font-style: style;
p {
line-height: 1.5; /* Relative to the font size */
}
5. Line Height
- Controls the space between lines of text.
# VSC Interface Overview
CSS Typography: Making Text Look Amazing
h1 {
text-align: center;
}
6. Text Alignment
- Aligns text horizontally within its container
text-align: alignment;- Values:
-
left(default) centerrightjustify
-
# VSC Interface Overview
CSS Typography: Making Text Look Amazing
a {
text-decoration: none;
}
7. Text Decoration
- Adds or removes text decorations.
text-decoration: value;- Values:
-
none(removes decoration) underlineoverline-
line-through(strikethrough)
-
# VSC Interface Overview
CSS Typography: Making Text Look Amazing
h2 {
text-transform: uppercase;
}
8. Text Transform
- Changes the text’s casing.
text-transform: value;- Values:
-
capitalize(first letter of each word) uppercaselowercase
-
# VSC Interface Overview
CSS Typography: Making Text Look Amazing
h1 {
letter-spacing: 2px;
}9. Letter Spacing
- Controls the space between characters.
p {
word-spacing: 5px;
}
10. Word Spacing
- Adjusts the space between words.
# VSC Interface Overview
CSS Typography: Making Text Look Amazing
h1 {
text-shadow: 2px 2px 5px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
}
12. Text Shadow
- Adds shadow effects to text.
text-shadow: x-offset y-offset blur-radius color;
p {
color: #333;
}
11. Color
- Changes the text color.
# Customize Your VSCode
6. CSS Units
# Customize Your VSCode
CSS Units
CSS units define the size of elements, spacing, and other dimensions on a web page. Choosing the right unit is crucial for creating responsive, scalable, and visually appealing designs.
# VSC Interface Overview
p {
font-size: 16px;
}
div {
width: 5cm;
height: 2in;
}
p {
font-size: 12pt;
}1. Absolute Units
-
Absolute units are fixed and do not scale based on other elements. They are ideal for print designs but less flexible for responsive web designs
-
px (pixels), cm / mm, in (inches), pt (points)
# VSC Interface Overview
p {
font-size: 1.5em; /* 1.5 times the parent font size */
}2. Relative Units
-
Relative units are flexible and adapt to the size of their context, making them ideal for responsive designs.
-
em: Relative to the font size of the parent element.
# VSC Interface Overview
html {
font-size: 16px; /* Default */
}
h1 {
font-size: 2rem; /* 32px */
}2. Relative Units
-
rem: Relative to the root element's font size.
div {
width: 50%; /* Half of the parent container */
}-
%: Relative to the parent element.
Absolute vs. Relative Units: When to Use
| Use Case | Best Unit |
|---|---|
| Fixed designs | px |
| Scalable text | rem, em |
| Responsive layouts | % |
| Typography (print) | pt |
# Customize Your VSCode
7. CSS Backgrounds
# Customize Your VSCode
CSS Backgrounds: Making Your Web Pages Pop!
The background property in CSS is used to control the visual appearance of the area behind elements. From simple colors to stunning images and patterns, backgrounds can add depth and personality to your designs.
# VSC Interface Overview
body {
background-color: lightblue;
}1. Background Color
- Sets the background color of an element.
- background-color: value;
-
Values:
- Named colors:
red,blue,green, etc. - Hexadecimal:
#ff5733 - RGB:
rgb(255, 87, 51) - HSL:
hsl(10, 100%, 50%)
- Named colors:
# VSC Interface Overview
body {
background-image: url('background.jpg');
}2. Background Image
- Adds an image as the background.
- background-image: url('path-to-image');
# VSC Interface Overview
div {
background-image: url('pattern.png');
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}3. Background Repeat
- Controls whether the background image repeats and how.
- background-repeat: value;
-
Values:
-
repeat(default): Repeats both horizontally and vertically. -
repeat-x: Repeats horizontally only. -
repeat-y: Repeats vertically only. -
no-repeat: Stops repetition.
-
# VSC Interface Overview
div {
background-image: url('hero.jpg');
background-size: cover;
}4. Background Size
- Sets the size of the background image.
- background-size: value;
-
Values:
-
auto(default): Keeps the image's original size. -
cover: Scales the image to cover the element, maintaining aspect ratio. -
contain: Scales the image to fit within the element. - Specific sizes:
100px,50%, etc.
-
# VSC Interface Overview
div {
background-image: url('logo.png');
background-position: center center;
}5. Background Position
- Determines the starting position of the background image.
- background-position: x y;
- Values:
-
- Keywords:
top,center,bottom,left,right(or combinations liketop left). - Specific values:
50px 100px,50% 50%.
- Keywords:
# VSC Interface Overview
body {
background-image: url('parallax.jpg');
background-attachment: fixed;
}6. Background Attachment
- Controls whether the background scrolls with the content.
- background-attachment: value;
-
Values:
-
scroll(default): Background scrolls with the page. -
fixed: Background stays fixed in place. -
local: Background scrolls with the element's content
-
# VSC Interface Overview
div {
background-color: yellow;
background-clip: padding-box;
}7. Background Clip
- Specifies how far the background extends within the element.
- background-clip: value;
-
Values:
-
border-box: Extends to the border (default). -
padding-box: Clips to the padding. -
content-box: Clips to the content area.
-
# VSC Interface Overview
div {
background: linear-gradient(to right, red, blue);
}
div {
background: radial-gradient(circle, red, yellow, green);
}
8. Background Gradient
- Creates smooth transitions between colors.
- background: gradient-type(color1, color2, ...);
-
Types:
- Linear Gradient
- Radial Gradient
# VSC Interface Overview
div {
background: #ff5733 url('pattern.png') no-repeat center/contain fixed;
}9. Background Shorthand
- Combines all background properties into one.
- background: color image repeat position/size attachment;
# Customize Your VSCode
8. CSS Variables
# Customize Your VSCode
CSS Variables
CSS variables (or Custom Properties) are a powerful CSS feature that allow you to store reusable values, such as colors, sizes or spacing. They make styles more modular, maintainable and dynamic.
# VSC Interface Overview
body {
background-color: lightblue;
}1. Basic CSS variable syntax
- Sets the background color of an element.
- background-color: value;
-
Values:
- Named colors:
red,blue,green, etc. - Hexadecimal:
#ff5733 - RGB:
rgb(255, 87, 51) - HSL:
hsl(10, 100%, 50%)
- Named colors:
# Customize Your VSCode
9. Styling Lists
# VSC Interface Overview
ul {
list-style-type: square;
}
ol {
list-style-type: upper-roman;
}1. list-style-type
- Defines the marker type:
-
disc(default for<ul>) -
circle,square -
decimal(default for<ol>) -
upper-roman,lower-roman none
-
Main CSS Properties for Styling Lists
# VSC Interface Overview
ul {
list-style-position: inside;
}
2. list-style-position
-
outside(default): Marker outside content -
inside: Marker aligned with text
ul {
list-style-image: url('custom-bullet.png');
}
3. list-style-image
- Use a custom image as a marker.
# VSC Interface Overview
ul {
list-style: square inside;
}
4. list-style (Shorthand)
- Combines all three properties:
# VSC Interface Overview
li {
color: #3498db;
font-size: 18px;
margin: 5px 0;
padding-left: 10px;
}
You can style individual list items:
Customizing <li> Elements
ul, ol {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
You can style individual list items:
Removing Bullets or Numbers
# VSC Interface Overview
ul ul {
list-style-type: circle;
padding-left: 20px;
}
ol ol {
list-style-type: lower-alpha;
padding-left: 20px;
}
Apply specific styles to nested lists:
Nested Lists Styling
ul li::before {
content: "✓";
color: green;
margin-right: 10px;
}
Use pseudo-elements:
Adding Icons to Lists
# Customize Your VSCode
12. Display & Visibility
# VSC Interface Overview
div { display: block; }
span { display: inline; }
button { display: inline-block; }
.hidden { display: none; }
.container { display: flex; }
.grid-container { display: grid; }1. Common Values
-
block: Full width, new line (e.g.,<div>,<p>) -
inline: Only takes content width (e.g.,<span>) -
inline-block: Inline but supports width/height -
none: Hides the element completely -
flex: Enables Flexbox layout -
grid: Enables CSS Grid layout
Display Property
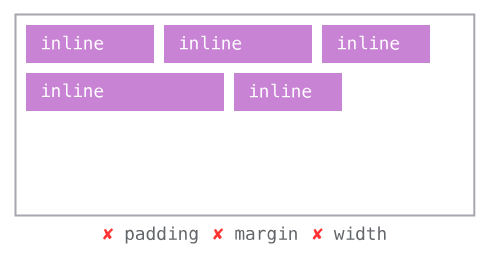
The display property controls how an element is rendered in the layout.
# VSC Interface Overview
display: inline
display: block

Allows other elements beside; margin, padding & width don’t work.
Takes up an entire line; margin, padding & width work.
# VSC Interface Overview
display: inline-block
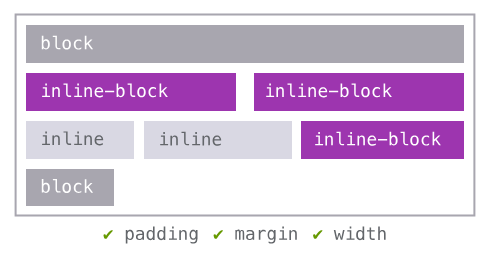
Allows other elements beside; margin, padding & width work. Can create columns, but will force a space between boxes.
# VSC Interface Overview
.visible { visibility: visible; }
.hidden-layout { visibility: hidden; }
1. Values
-
visible: Default -
hidden: Invisible but still occupies space -
collapse: Used for table rows/columns
Visibility Property
Controls whether an element is visible without affecting layout.
# VSC Interface Overview
visibility: hidden vs display: none
Controls whether an element is visible without affecting layout.
| Feature | display: none | visibility: hidden |
|---|---|---|
| Space occupied | No | Yes |
| Interactivity | Not possible | Not possible |
| Performance | Slower on frequent change | Faster |
# Customize Your VSCode
10. Positioning
# VSC Interface Overview
.relative {
position: relative;
top: 10px;
left: 20px;
}
.absolute {
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
right: 20px;
}
.fixed {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
}
.sticky {
position: sticky;
top: 10px;
}1. Types
-
static(default): Normal flow -
relative: Relative to its normal position -
absolute: Positioned relative to nearest positioned ancestor -
fixed: Relative to viewport (doesn't scroll) -
sticky: Hybrid of relative and fixed
Positioning
Control the placement of elements using the position property.
# VSC Interface Overview
position: absolute
position: relative


Move an element around based on coordinates.
Added to a parent element to reset absolute child’s coordinates.
# VSC Interface Overview
position: fixed

z-index
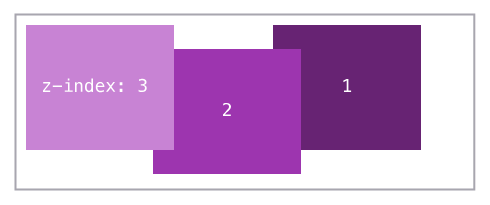
Forces an element to not move when the page is scrolled.
Control the stacking order of elements, higher number is closer.
# Customize Your VSCode
11. Overflow
# VSC Interface Overview
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
overflow: auto;
border: 1px solid black;
}1. Values
-
visible(default): Content overflows -
hidden: Clipped without scrollbars -
scroll: Always show scrollbars -
auto: Show only if needed -
clip: Similar tohidden, but no access to overflow
Overflow Property
Controls what happens when content overflows its container.
# VSC Interface Overview
div {
overflow-x: scroll;
overflow-y: hidden;
}
2. Separate Axes
- Use overflow-x and overflow-y independently:
Overflow Property
# Customize Your VSCode