uma breve introdução
Kubernetes
- Introdução Kubernetes
- Containers
- CFDN
- Fundamentos Kubernetes
- Arquitetura
- Componentes e diferenças
- Em prática (all-in-one)
- Instalação
- Comandos básicos
- Em prática (muilti-node)
- Instalação
- AWS EC2 (multi-node)
- Fechar um cluster



felipe f. rocha
Introdução
Kubernetes e containers
História
- Arquiteturas
-
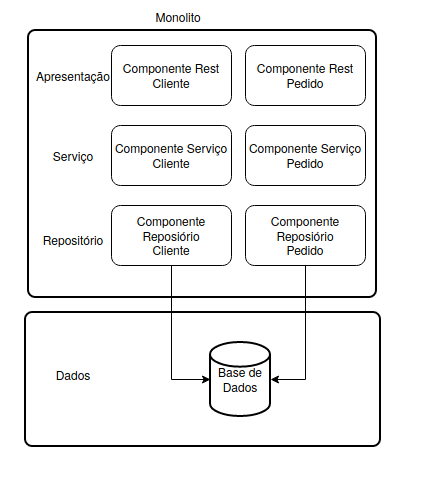
Monolítica
- Vertical
-
SOA
- Horizontal
-
EDA
- Assíncrona
-
Monolítica
- Computação em Núvem
- Gerência de container
- Borg (batch)¹
- Omega (schedulers)
- K8s (open source)
- κυβερνήτης ou k8s



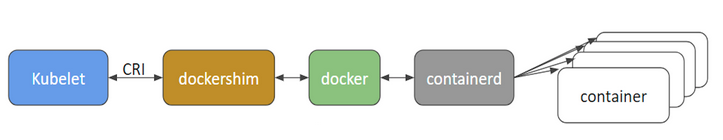
Container

- Isolamento
- Imagens
- código
- runtime
- dependências
- Runtime
- Multiplos containers
- Único host
- Exemplo de Runtime
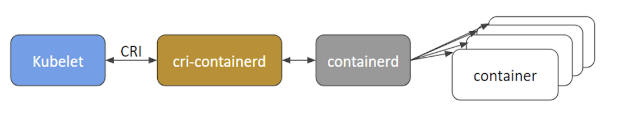
- runC
- Containerd
- CRI-O
Orquestrador
- Unidade de Gerenciamento/ Controle
-
1+ múltiplos nós (hosts)
- Cluster
-
1+ múltiplos nós (hosts)
- Requisitos
- Tolerância a falhas
- Escalabilidade (por demanda)
- Otimização de recursos
- Descoberta automática
- Acessibilidade
- Atualizações e restauração sem interrupção
- Política de acesso
CNCF
- Cloud Native Computing Foundation
- Graduated projects:
- Kubernetes
- Prometheus
- Envoy
- CoreDNS
- containerd
- Fluentd
- Incubating projects:
- rkt and CRI-O
- Linkerd
- etcd
- gRPC
- CNI
- Harbor
- Helm
- Rook and Vitess
- Notary
- TUF
- NATS
- Jaeger and OpenTracing
- Open Policy Agent
Kubernetes...
"... é um sistema Open source para deploy, escalabilidade, e gerenciamento automático de containers" - k8s site (+/- traduzido)
Arquitetura
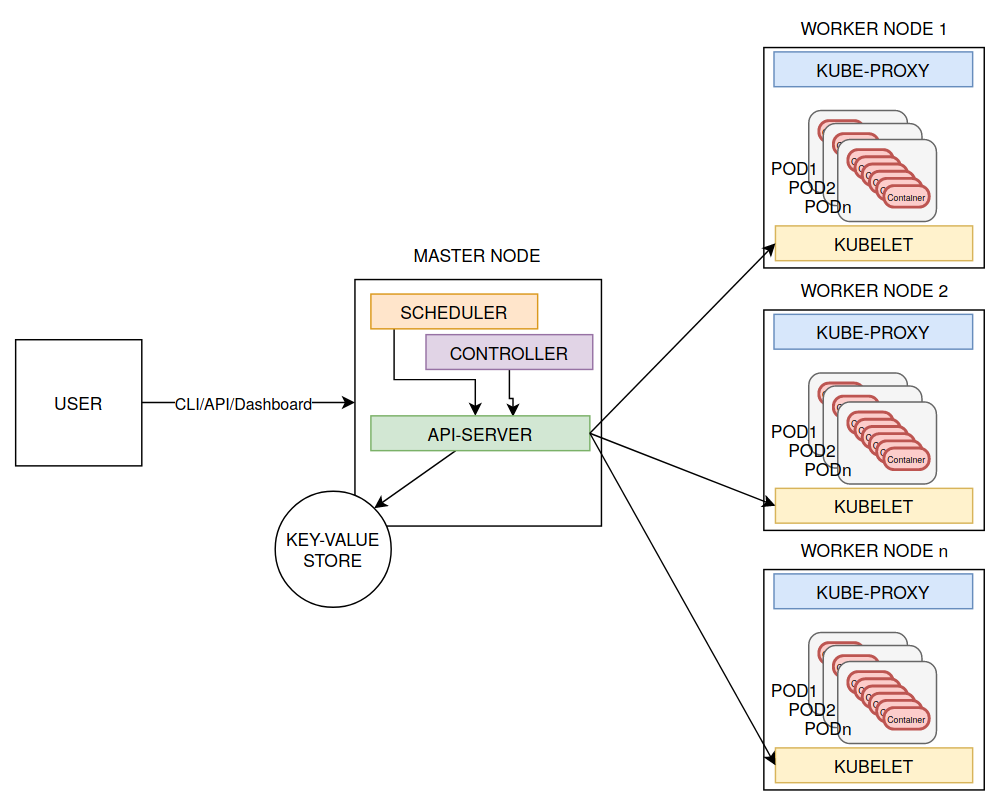
- Master Node (HA, multi sync)
- API-server
- Scheduler
-
Controller
- Kube
- Cloud
- etcd (stacked/external state)
- backup, snapshot, restore
- algoritimo raft consensus²
- Worker Nodes
- kube-proxy (external)
- kubelet (api-server)
- container runtime (pods)
- Addons
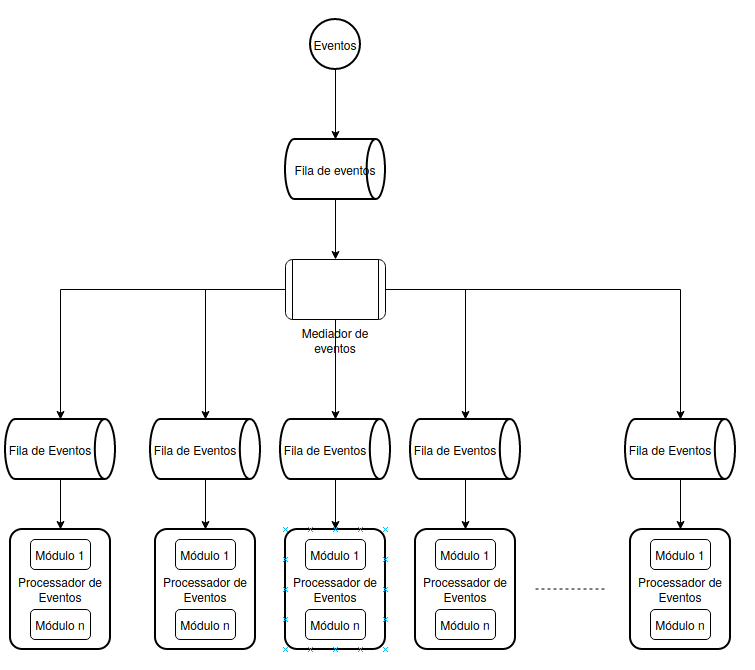
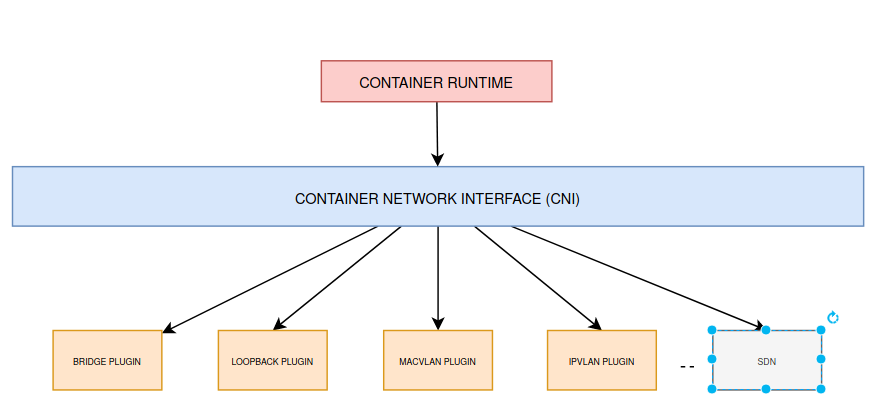
Desafio em rede
Kubernetes network
- Container - Container
- intra pods
- Pod - Pod
- inter pods
- Pod - Service
- namespaces
- cluster namespaces
- External - Service
Configurações
Organização de nós
- All-in-One-Node
- Sigle-Node etcd, Sigle-master, Multi-Worker
- Single-Node etcd, Multi-Master, Multi-worker
- Multi-Node etcd (HA), Multi-Master (HA), Multi-worker
Instalação
Distribuições e Integrações
- Sistema Operacional
- Distribuições Linux
- systemd, journald
- Microsoft (dev)
- Distribuições Linux
- Aprendizado e teste:
- minikube, kind, microk8s, docker desktop, minishift
- Containers
- On-premise VM
- On-premise Bare Metal
- minikube, kind, microk8s, docker desktop, minishift
Soluções
Tipos de soluções
-
Hosted
- EKS,
- GKE
- AKS
-
Turnkey Cloud
- EC2
- GCE
-
Turnkey On-premise
- GKE On-Prem
- IBM Cloud Private
- OpenShift Container Platf.



Componentes
Objetos
- Estrutura básica comum
- spec + status
- Tipo arquivo (json / yaml)
- Requisitos
- apiVersion
- kind
- metadata
- spec
-
Gerenciamento
- Comando imperativo
- Config. obj imperativo
- Config. obj declarativo
--
apiVersion: apps/v1 # for versions before 1.9.0 use apps/v1beta2
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 2 # tells deployment to run 2 pods matching the template
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80
#!/bin/bash
kubectl create deployment nginx --image nginx # Imperative Command
kubectl create -f nginx.yaml # Imperative Config
kubectl apply -f configs/ # Declarative ConfigComponentes
Objetos - Pod
- Container mais externo
- Menor objeto K8s
- Encapsula uma aplicação
- Unidade de deploy
- Tipos:
- One-container-per-pod
- Multi-container-per-pod
-
Workloads (controller)
- Deployment
- StatefulSet
- DeamonSet
--
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: configmap-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: test
image: busybox
volumeMounts:
- name: config-vol
mountPath: /etc/config
volumes:
- name: config-vol
configMap:
name: log-config
items:
- key: log_level
path: log_levelComponentes
Objetos - Service
- Conjunto lógico de Pods
- Políticas de acesso
- Endpoints
- Load Balance
- Service Descovery
- Variáveis de ambiente
- add-on DNS
- Selector
- targetPorts - names
--
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-service
spec:
selector:
app: MyApp
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 9376
Componentes
Objetos - Controllers
- Loop
- Tipo:
- Deployments
- DaemonSet
- StatefulSet
- ReplicaSet
- Job
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: fluentd-elasticsearch
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: fluentd-logging
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: fluentd-elasticsearch
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: fluentd-elasticsearch
spec:
tolerations:
# this toleration is to have the daemonset runnable on master nodes
# remove it if your masters can't run pods
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
effect: NoSchedule
containers:
- name: fluentd-elasticsearch
image: quay.io/fluentd_elasticsearch/fluentd:v2.5.2
resources:
limits:
memory: 200Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 200Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: varlog
mountPath: /var/log
- name: varlibdockercontainers
mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers
readOnly: true
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
volumes:
- name: varlog
hostPath:
path: /var/log
- name: varlibdockercontainers
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/docker/containers---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: ReplicaSet
metadata:
name: frontend
labels:
app: guestbook
tier: frontend
spec:
# modify replicas according to your case
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
tier: frontend
template:
metadata:
labels:
tier: frontend
spec:
containers:
- name: php-redis
image: gcr.io/google_samples/gb-frontend:v3
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: pi
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: pi
image: perl
command: ["perl", "-Mbignum=bpi", "-wle", "print bpi(2000)"]
restartPolicy: Never
backoffLimit: 4Tools
k... toolbox
- kubectl
- kubeadmin
- kubespray
- kops
- kube-aws
Em prática
all-in-one & k8s cli
minikube
#!/bin/bash
# Type 2 Hiper visor (os hosted)
sudo bash -c 'echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/debian $(lsb_release -a | grep Codename | cut -d":" --field 2 | xargs) contrib" >> /etc/apt/sources.list'
wget -q https://www.virtualbox.org/download/oracle_vbox_2016.asc -O- | sudo apt-key add -
wget -q https://www.virtualbox.org/download/oracle_vbox.asc -O- | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install virtualbox-6.1 -y
# Minikube
curl -Lo minikube https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64 \
&& chmod +x minikube
sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/bin/
sudo install minikube /usr/local/bin/
minikube config set driver virtualbox \
&& minikube delete \
&& minikube start
# kubectl
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl && chmod +x kubectl && sudo mv kubectl /usr/local/bin/
kubectl config view
kind
#!/bin/bash
# Docker
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com | bash -
# Kind
curl -Lo ./kind https://kind.sigs.k8s.io/dl/v0.8.1/kind-$(uname)-amd64
chmod +x ./kind
mv ./kind /usr/local/binEm prática
single-master multi-node & k8s cli
microk8s
#!/bin/bash
# Snap
sudo apt install snapd
# Microk8s
sudo snap install microk8s --classic --channel=1.18/stable
# Segurança
sudo usermod -a -G microk8s $USER
sudo chown -f -R $USER ~/.kube
su - $USER
# Check status
microk8s start
microk8s status --wait-ready
microk8s stop
# Teste
microk8s kubectl get nodeskind
#!/bin/bash
# Docker
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com | bash -
# Kind
curl -Lo ./kind https://kind.sigs.k8s.io/dl/v0.8.1/kind-$(uname)-amd64
chmod +x ./kind
mv ./kind /usr/local/bin
# seleciona e apaga todos os clusters
kind delete clusters $(kind get clusters)
# define uma arquivo de configuração para quantos nós no cluster e os tipos de nós
cat << EOF > kind-3nodes.yaml
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
nodes:
- role: control-plane
- role: worker
- role: worker
EOF
# Cria cluster com base nas especificações acima
kind create cluster --name wslkindmultinodes --config ./kind-3nodes.yaml
# Valida a criação do cluster (lembrando que a configuração e instalação do kind esta na primeira sessão)
kubectl get nodes