Subsytem Map2
Adrian Crespo
Kacper Kendi Kędziera
Map2
Map2 is a subsystem to take the user from the current position to the Level Start Point and dynamically showing navigation hints. The user can choose the preferred mode of transport (for example: car, bike, bus, train, etc).
Generally, it works as standard GPS system.
functional requirements
- A user should be able to the check the status of his/her quest based on the route defined by the map.
- The graphical layout should be able to ask for hints, based on the information provided by the route.
- The hints should be generated dynamically, this means that it won't be a static text.
- The subsystem will retrieve the map and the transport method from the database.
- It can display the start point if the player is lost.
- The user can list all the hints until that moment.
Non-functional requirements
- The range of the GPS position can introduce error in the distance measurement (>50 m).[i]
- Also, it should work only for outdoor.
- The algorithm will depend on the language used by the whole system (Java).
- It needs a database to retrieve the preferences of the player, for example the preferred way to go to the start point (driiving, walking, running).
[i] How accurate is Android GPS? http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1567443/how-accurate-is-android-gps
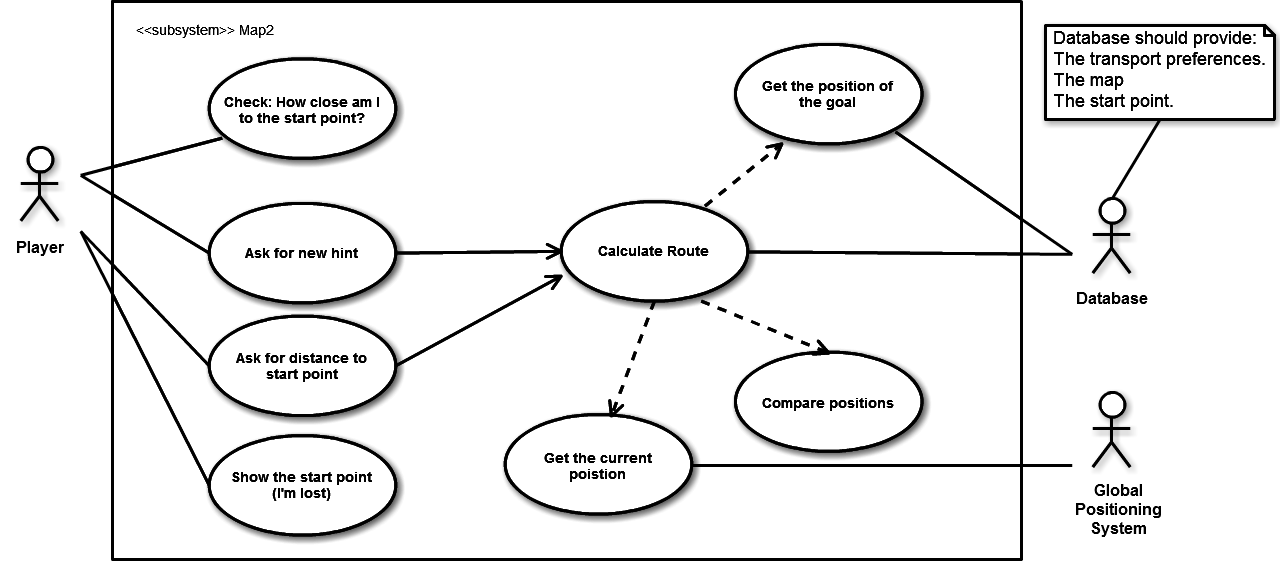
Use Case
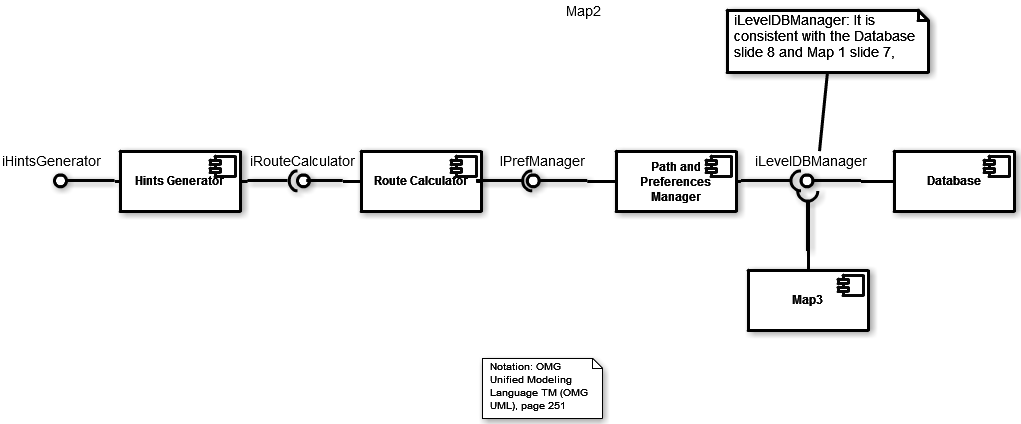
Components Diagram
We will have three main components:
- Hints Generator: this component is responsible to retrieve the distance to the start point provided by Route Calculator and using it to create and sending new hints.
- Route Calculator: this component analyzes the path and calculates the distance to the start point.
- Paths and Preferences Manager: It acts "as a proxy", it retrieves the needed preferences from the database and saves them. Why should it do it? Because it could process the preferences before saving them, for example to parse the map and generate a route.
Components Diagram
Classes Diagram
There will be four classes and they will implement three classes.
-
The classes will be: HintsManager, RouteCalculator, Path, PrefManager.
-
HintsManager will implement iHintsGenerator, RouteCalculator will implement iRouteCalculator and PrefManager will implement iPrefManager.
Classes Diagram
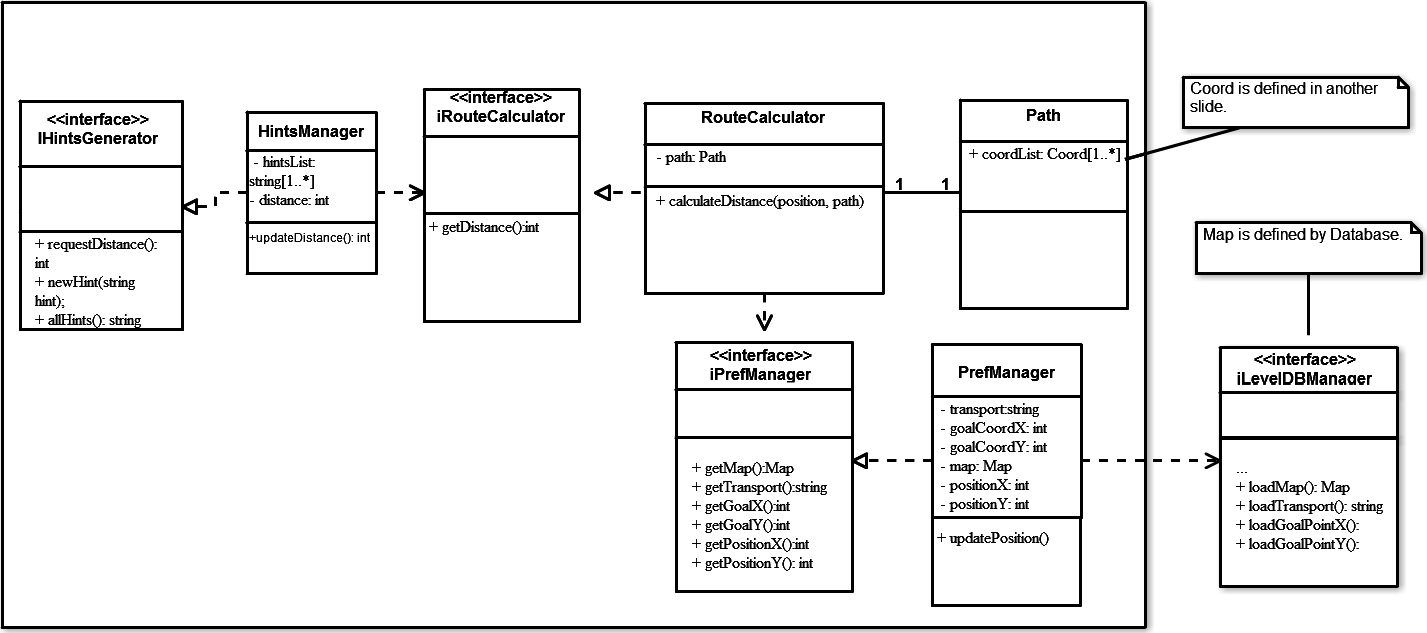
Classes Diagram
We will need a specific type of data used by RouteCalculator. Because of that, we will use two additional classes:
- We will a type named Coord. It will represent a coordinate, so it will be composed of two values, X and Y, that may be relative to the map.
- A set of coordinates will create a path that will be used by RouteCalculator to measure distances.
Classes Diagram

Sequence Diagram
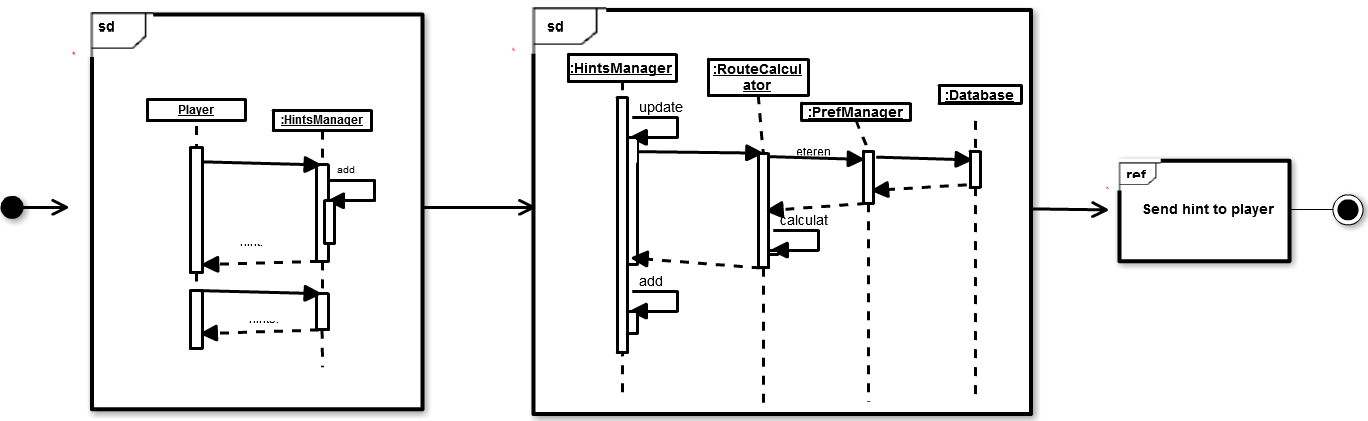
The following sequence diagram display the following use cases.
- The player asks for a new hint. Then HintsManager asks RouteCalculator for the current distance and HitsManager updates it. Then, accordingly to the distance, it add a new hint.
- The player asks for all the hints. HintsManager returns all the hints saved until that moment.
Sequence Diagram
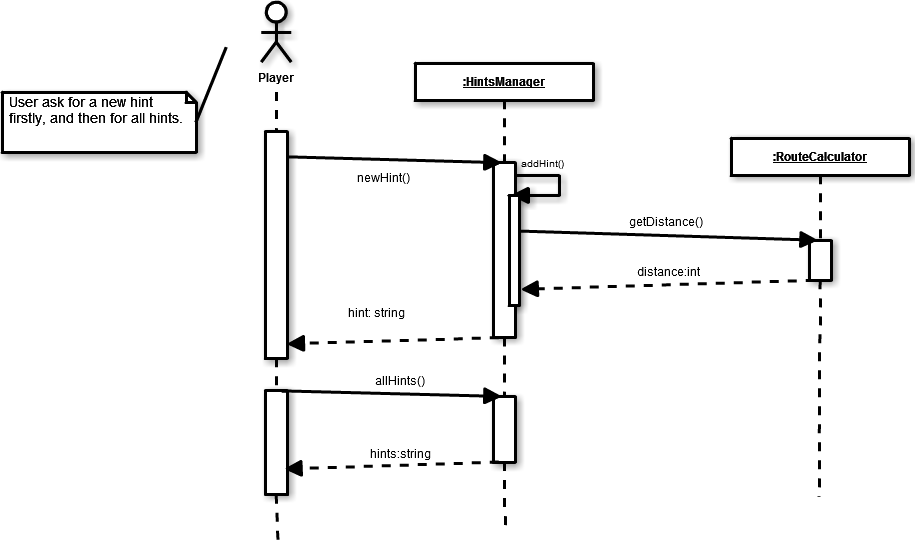
Sequence Diagram
There is another sequence diagram:
- In this case, it is shown how is calculated the distance to the start point and how is generated the hint accordingly to that distance.
-
getPreferences has been simplified in this diagram, but it involves the following methods:
- getMap()
- getTransport()
- getGoalX()
- getGoalY()
- getPositionX()
- getPositionY()
Sequence Diagram
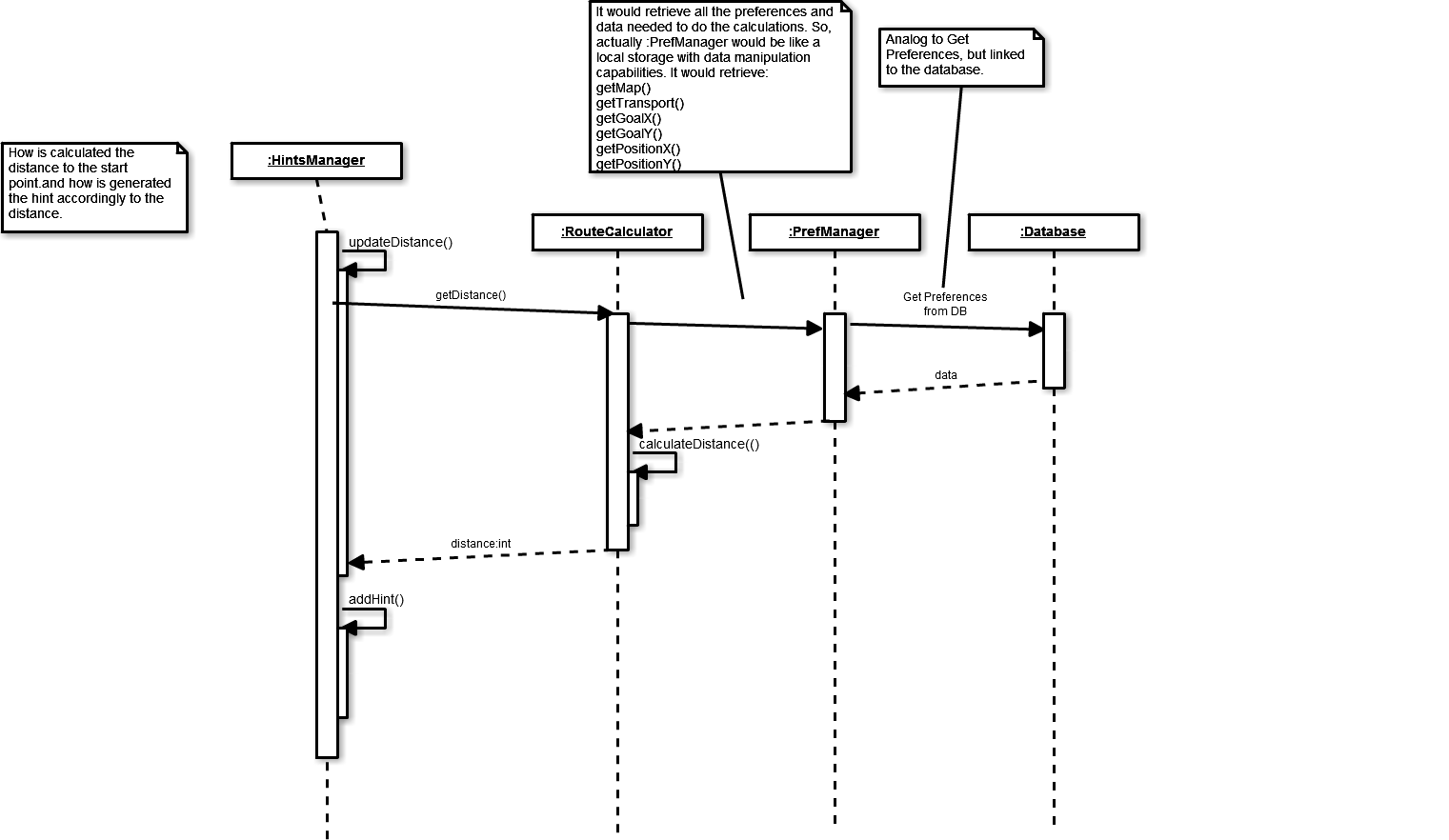
States Diagram
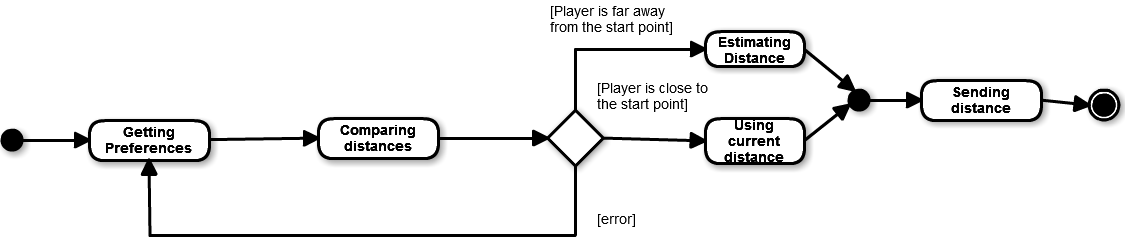
The following diagram shows the lifecycle of RouteCalculator.
- When it is asked to get the distance to the start point, it needs to gather the preferences from PrefManager.
- Once they are received, he gets the current position and compare the distance to the start point.
- If the player is too far away, there may be a huge error introduced to the GPS, so it needs to estimate the real distance.
- If the player is too close, there is no need to estimate the distance.
- But if there were any other error, for example not being able to estimate it, it will calculate the distances again.
States Diagram
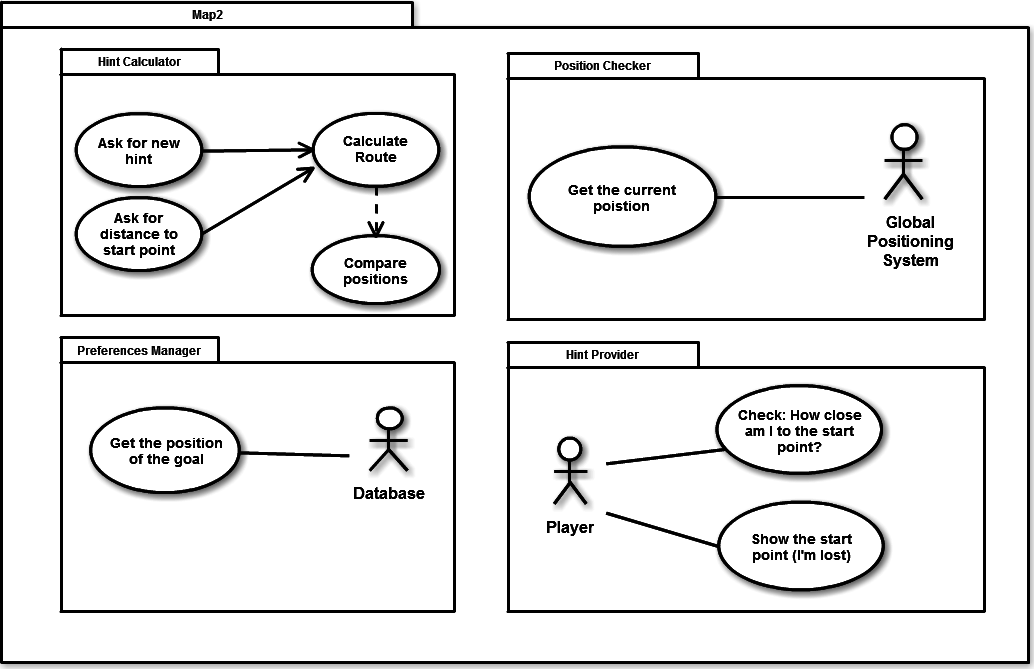
Package Diagram
This package diagram is used to reflect the organization of packages and provide a visualization of the namespaces.
This Package diagram will use packages containing use cases to illustrate the functionality of the software system.
Package Diagram
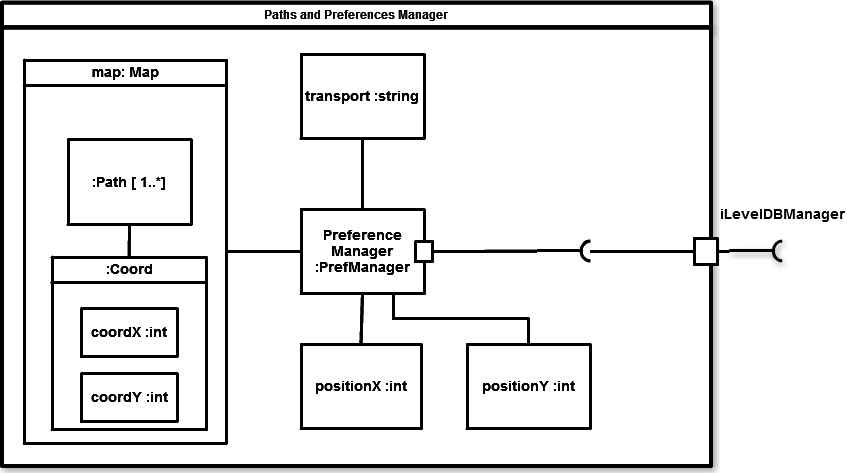
Structural Diagram
This structural diagram will show the internal structure of the preferences manager. It will show the configuration and relationship of its parts.
Structural Diagram
Interaction Overview Diagram
This interaction overview diagram will show the communication between interaction diagrams.
In will focus on the overview of requesting a hint, calculating the distances and returning the hint to the player.
Interaction Overview Diagram