test-driven Infrastructure
with Ansible - docker - jenkins
Secrets to deliver gourmet automations...

@DambrineF

Florian Dambrine - DevOps Engineer - @ GumGum
> whoami
-
Florian Dambrine
-
DevOps Engineer @ GumGum
-
Joined GumGum 2 ½ years ago
-
Ansible fan!
> - Computer vision company


Offers innovative advertising and visual intelligence solutions for brands and publishers
Invented In-Image
advertising in 2008
> Agenda
-
Ansible 101 - Brief Introduction
-
Test-Driven Infrastructure :
- GumGum's main workflows
- How Ansible can ease testing
- Use of Ansible test modules
- Use of Docker to Mock AWS EC2
- Introducing test frameworks
-
Demo:
- Using Jenkins Pipelines in your workflows
-
Building a fully tested role from scratch
> test-driven infrastructure - The goal
- Make sure the automation worked as expected
- Detect breaking changes earlier
- Easily handle configuration management tool upgrades
- Test automation software upgrades
-
Test complex infrastructure configurations:
- Clusters depending on other ones (Zookeeper dependency)
- Opscenter / Cassandra / Maintenance operations / Rolling restarts
- Enforce Automation quality and best-practices
> Ansible 101 - What is ansible?
- Open source project started by Michael DeHaan in Feb. 2012
- Automation engine written in Python
- Used as :
- Configuration Management tool
- Orchestration tool
- Application deployment tool
- Push based and agent less (Can do pull too)
19K Stars
5.7K Forks
8.7 K Pull requests

> Ansible 101 - How does it look like?
### Playbook example: webserver.yaml
---
- name: Webservers configuration steps
hosts: webservers
become: yes
tasks:
- name: Install Nginx
apt:
name: nginx
- name: Removing Nginx default configuration
file:
state: absent
path: "/etc/nginx/{{ item }}/default"
with_items:
- sites-enabled
- sites-available
- name: Restart Nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: restarted### Inventory example: webapp.ini
[webservers]
00.webapp.tiad.com
01.webapp.tiad.com### Ansible execution example
$ sudo ansible-playbook webservers.yaml \
-i webapp.ini### Ansible execution example
PLAY [Webservers configuration steps] ******************************************
TASK [setup] *******************************************************************
ok: [00.webapp.tiad.com]
ok: [01.webapp.tiad.com]
TASK [Install Nginx] ***********************************************************
changed: [01.webapp.tiad.com]
changed: [00.webapp.tiad.com]
TASK [Removing Nginx default configuration] ************************************
changed: [01.webapp.tiad.com] => (item=sites-enabled)
changed: [00.webapp.tiad.com] => (item=sites-enabled)
changed: [01.webapp.tiad.com] => (item=sites-available)
changed: [00.webapp.tiad.com] => (item=sites-available)
TASK [Restart Nginx] ***********************************************************
changed: [00.webapp.tiad.com]
changed: [01.webapp.tiad.com]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
00.webapp.tiad.com : ok=4 changed=3 unreachable=0 failed=0
01.webapp.tiad.com : ok=4 changed=3 unreachable=0 failed=0 1
2
3
4
> gumgum's Automation workflow
Provision
Configure
Test


Provision
Configure
Test
Cleanup
Snapshot
Cluster Automation
Image creation
> Ansible playbook template
######################################################################
- name: EC2 instance provision
hosts: localhost
connection: local
become: yes
vars:
- instance: <SERVICE_NAME>
- configuration: "{{ lookup('env','<SERVICE_NAME>') }}"
# Explicit includes required
vars_files:
# Load EC2-001 role vars
- "{{ inventory_dir }}/group_vars/{{ instance }}/ec2-001/vars.yaml"
# Load EC2-001 instance vars
- "{{ inventory_dir }}/group_vars/{{ instance }}-{{ configuration }}/ec2-001/vars.yaml"
roles:
- { role: ec2-001, tags: ['provision'] }
######################################################################
######################################################################
- name: <SERVICE_NAME> installation and configuration
hosts: all
become: yes
roles:
# Playbook dependencies
- { role: common-001, tags: ['configure', 'test', 'cleanup', 'create-ami', 'test-ami', 'common'] }
- { role: aws-cli-001, tags: ['configure', 'test', 'cleanup', 'create-ami', 'test-ami', 'aws-cli'] }
- { role: user-001, tags: ['configure', 'test', 'cleanup', 'create-ami', 'test-ami', 'user'] }
# Main Role that can be called with 'configure', 'test' and 'cleanup'
- { role: YOUR_MAIN_ROLE, tags: ['create-ami', 'test-ami', 'YOUR_MAIN_ROLE_TAG'] }
# These two following roles allow you to create and test an AMI of the automated system
- { role: ec2-ami-001, tags: ['create-ami', 'test-ami', 'ec2-ami'] }
- { role: ec2-001, tags: ['test-ami'] }
######################################################################
> How ansible can help testing ?
Ansible modules can help you testing:
Ansible is actually designed to be a “fail-fast” and ordered system.
-- docs.ansible.com/ansible/test_strategies.html
- service
- wait_for
- uri and shell
- register and fail
- assert
- stat
### tasks/test.yaml
---
- name: Test - Make sure the application is listening
wait_for:
host: "localhost"
port: "{{ item }}"
delay: 0
timeout: 60
with_items:
- 80
- 1717
- name: Test - Check multiple application endpoints
uri:
url: "http://localhost/{{ item.endpoint }}?{{ item.body | default(omit) }}"
method: "{{ item.method | default('GET') }}"
with_items: "{{ app_endpoints }}"
##########################################################################
### vars/main.yaml
app_endpoints:
- endpoint: 'heartbeat'
- endpoint: 'sentiment'
method: POST
body: "text='I have a good feeling'"
> introducing docker to mock aws ec2 servers


Connection plugins

SSH
Docker-Cli
$ ansible-playbook elasticsearch.yaml \
--tags configure \
--limit <EC2_INSTANCE_ID>
$ ansible-playbook elasticsearch.yaml \
--tags configure \
--limit <DOCKER_CONTAINER_ID> \
--connection docker> why docker?
-
Container launch times are really fast, they start instantly!
-
We could not test all our modules if we had to wait for EC2 instances.
-
More efficient resource utilization.
-
Containers are disposable and cheap!
Because testing is now a requirement !
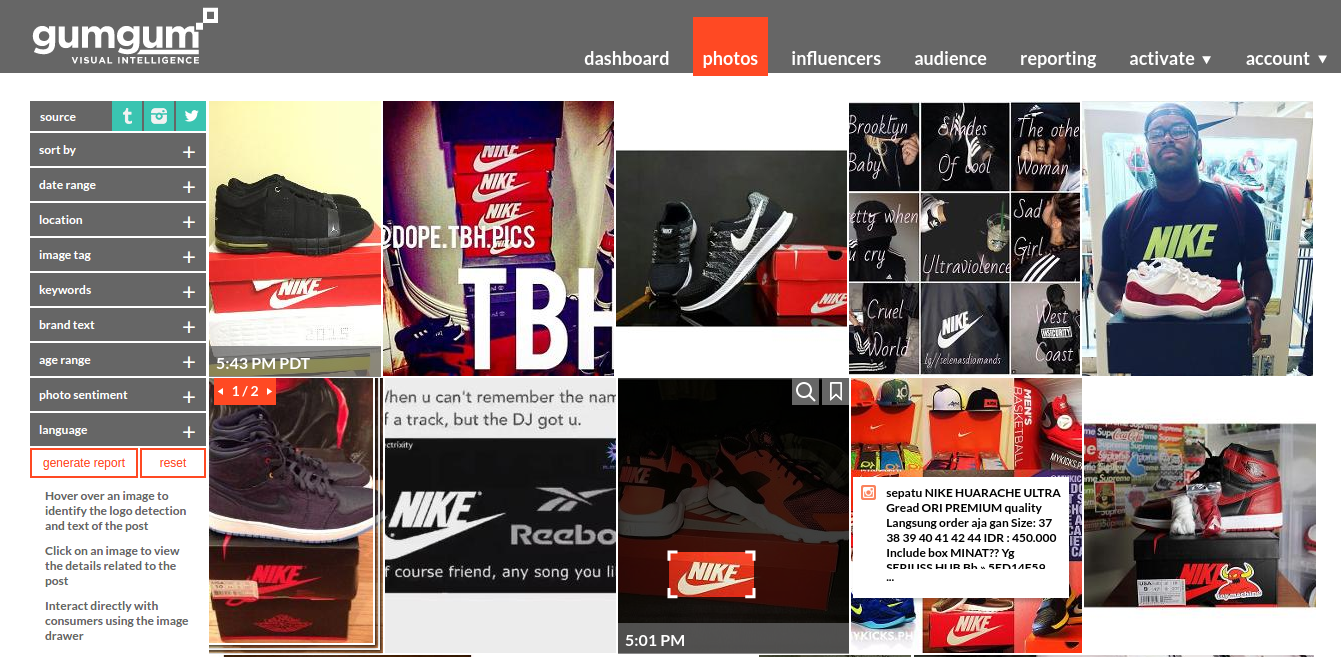
activemq ad-server ansible
ansible-metadata apt-cacher-ng asset-queue-processor
aws-api-server aws-cli aws-mon-linux
bid-predictor bower cache-flush-queue-processor
cassandra cassandra-cleanup cassandra-compaction
cassandra-firewall cassandra-repair cassandra-rolling-restart
cloudfront-origin codedeploy common
cron cserver deploy-ad-server
deploy-fluentd-aggregator deploy-fluentd-forwarder deploy-mantii-api
deploy-reporting-server design-prototypes development
docker docker-container druid
druid-pivot ec2 ec2-ami
ec2-ami-find ec2-metadata elasticsearch
elasticsearch-rolling-restart esa-categorizer flask-example
fluentd fluentd-aggregator fluentd-forwarder
forecasting-server ganglia ganglia-server
geoserver gnip-consumer gradle
graphite groovy grunt
gumgum-adbuilder gumgum-ad-unit-test gumgum-dashboard
gumgum-vi-web gumgum-web-api gumgum-webapp
gumgum-wrapdeck icinga2 image-queue-processor
java jenkins kafka
kafka-firewall kafka-manager kafka-monitoring
kafka-offset-monitor kafka-rolling-restart logoserver
logstash-client manage-user mantii-api
mantii-web memcached mysql-server
nagios new-relic nginx
nodejs opscenter page-queue-processor
payments-server php PHPCi
phpmemcachedadmin postfix-client postfix-relay
queue-processor raid0 redis
reload-icinga2 reporting-server role
ruby rvm s3s3mirror
sails sbt security-aws-public-range
spark spiderami squid
storm sumologic taskrunner
text-web-services tomcat tws
user uwsgi vertex-api
vertex-logo vertex-visage zookeeper 10 automations
60 automations
120 automations
> ec2 vs docker provision with ansible
---
######################################################################
- name: Docker container provision
hosts: localhost
connection: local
become: yes
vars:
- instance: <SERVICE_NAME>
- configuration: "{{ lookup('env','<SERVICE_NAME>') }}"
# Explicit includes required
vars_files:
# Load Docker container vars, fallback to default if no specific configuration provided
- [
"{{ inventory_dir }}/group_vars/{{ instance }}-{{ configuration }}/docker-container-001/vars.yaml",
"{{ inventory_dir }}/group_vars/{{ instance }}/docker-container-001/vars.yaml",
"{{ inventory_dir }}/group_vars/all/docker-container-001/vars.yaml"
]
roles:
- { role: docker-container-001, tags: ['docker'] }
######################################################################
######################################################################
- name: EC2 instance provision
hosts: localhost
connection: local
become: yes
vars:
- instance: <SERVICE_NAME>
- configuration: "{{ lookup('env','<SERVICE_NAME>') }}"
# Explicit includes required
vars_files:
# Load EC2-001 role vars
- "{{ inventory_dir }}/group_vars/{{ instance }}/ec2-001/vars.yaml"
# Load EC2-001 instance vars
- "{{ inventory_dir }}/group_vars/{{ instance }}-{{ configuration }}/ec2-001/vars.yaml"
roles:
- { role: ec2-001, tags: ['provision'] }
######################################################################ansible-playbook <automation>.yaml \
--tags docker
ansible-playbook <automation>.yaml \
--tags provision
> ec2 vs docker provision with ansible
production
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
├── ec2.ini # Inventory script configuration file
├── ec2.py # Inventory script returning the list of EC2 servers as JSON
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
└─── group_vars # Define variable overrides to change default roles behavior
├── <service> # Overrides role variables at the service level
├── <service>-<cluster_id> # Overrides role variables at the cluster level
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
├── cassandra # Scope to override vars for all cassandra clusters
│ └── java
│ └── vars.yaml # Provides the Java version (1.8)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
├── cassandra-analytics # Scope to override vars for cassandra-analytics cluster
│ └── cassandra
│ └── vars.yaml # Defines cassandra.yml configuration
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
└── cassandra-realtime # Scope to override vars for cassandra-realtime cluster
└── cassandra
└── vars.yaml # Defines cassandra.yml configuration
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
docker
├── docker.cfg # Inventory script configuration file
├── docker.py # Inventory script returning docker containers as JSON
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
└─── group_vars # Define variable overrides to change default roles behavior
├── <service> # Overrides role variables at the service level
└── <service>-test # Overrides role variables at the container group level
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
├── cassandra # Scope to override vars for all cassandra clusters
│ └── java
│ └── vars.yaml # Provides the Java version (1.8)
...The Docker inventory can either be:
- Really close to the production one
- Different from production to test upgrades
> Seems like we could do even better...
Docker provision
Ansible Configuration
Ansible Tests
Syntax check
Check idempotency
Run extra playbooks
Run ServerSpec
Run Ansible-Lint
Run extra scripts
Automation
100% accurate

@willthames



> Introducing jenkins Pipelines
In contrast to freestyle jobs, pipelines enable you to define the whole application lifecycle. Pipeline functionality helps Jenkins to support continuous delivery (CD). The Pipeline plugin was built with requirements for a flexible, extensible, and script-based CD workflow capability in mind.
-- jenkins.io/doc/pipeline/
Requirements:
-
Jenkins 1.642.3 or later (Jenkins 2 is recommended)
-
The Pipeline plugin
-
A bit of Groovy learning (scripting language on top of Java)
Why using Jenkins as an Orchestrator ?
-
Trigger corresponding pipelines based on changes
-
Multibranch pipelines can help you to test new features
> Jenkins Pipeline Skeleton
node {
//--- (0) Preliminary steps
stage 'Checkout Ops repo'
git url: 'git@<url_to_git_repo>'
def testedAnsiblePlaybooks = [...]
//--- Print colored Ansible logs
wrap([$class: 'AnsiColorBuildWrapper', 'colorMapName': 'xterm']) {
for (testedAnsiblePlaybook in testedAnsiblePlaybooks) {
//--- (1) - Run a simple ansible syntax-check
stage "Check ${testedAnsiblePlaybook} playbook syntax"
// TODO
//--- (2) - Provision docker containers
stage "Run ${testedAnsiblePlaybook} to start docker containers"
// TODO
//--- (3) - Automate docker containers
stage "Run ${testedAnsiblePlaybook} against docker containers"
// TODO
//--- (4) - Extra playbooks / commands to run once the service is up
stage "Run extra playbook ${testedAnsiblePlaybook}"
// TODO
//--- (5) - Run extra tests (Ansible Commands, ServerSpec or others)
stage "Run serverspec to test ${testedAnsiblePlaybook}"
// TODO
stage "Run ansible-lint on ${testedAnsiblePlaybook}"
// TODO
stage "Run extra automation tests"
// TODO
}
//--- (6) - Destroy all previously started docker containers
for (testedAnsiblePlaybook in testedAnsiblePlaybooks) {
stage "Run ${testedAnsiblePlaybook} to destroy docker containers"
// TODO
}
}
}> Why Jenkins pipelines?
[H] - The example above is 45 lines (19 useful ones)
[Q] - How many clicks would you have done if you were not using Jenkins Pipelines?
[A] - Too many...
- Pipelines are part of your code repository
- Configure Jenkins to run a script from the SCM
- Share / Import code between pipelines (DRY!)
- Jenkins provides an Ansible plugin

_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
> DEMO - Jenkins Pipeline overview
> DEMO - Building a fully tested role from scratch!


- Ansible configure.yaml
- Ansible test.yaml
- Jenkins Pipeline
- ServerSpec tests
- Ansible-Lint
Flask HelloWorld Webapp


Automation
100% accurate
> DEMO - STEP 1 & 2 - ANSIBLE ROLE

1. Ansible configure.yaml

2. Ansible test.yaml
---
### Make the application folder, clone from GitHub,
### install pip requirements
- name: Make the application folder
file:
...
- name: Pull flask-helloworld from GitHub
git:
...
- name: Install requirements into virtualenv
pip:
...
### Configure UWSGI
- name: Create the apps-available configuration file
template:
...
- name: Create the apps-enabled symlink
file:
...---
### Start the webapp and make sure it's healthy
- name: Test - Start Uwsgi Emperor
service:
name: emperor
state: started
pattern: 'uwsgi --emperor'
- name: Test - Wait for the application
wait_for:
host: localhost
port: 5000
delay: 0
timeout: 30
- name: Test - Check the application endpoint
uri:
url: http://localhost:5000
method: GET
> DEMO - STEP 3 - JENKINS PIPELINE

3. Jenkins Pipeline
### /opt/ops/ansible/tests/pipelines/flask-webapp-pipeline/Strategy.groovy
# File used by the pipeline skeleton to configure it
utils = load('ansible/tests/pipelines/utils/Utils.groovy')
def getPipelineStrategy() {
strategy = [
runWithAnsibleVersion: 'ansible-2.1.1.0', // Which ansible version ?
runDestroyWithinTheLoop: true, // Which destruction policy ?
runAnsibleLint: true, // Should it run Ansible-Lint ?
runServerSpec: true // Should it run ServerSpec ?
]
strategy ? strategy : null
}
def getPlaybookList() {
playbooks = [
"flask-example-001.yaml" // Which playbooks should be tested in the pipeline ?
]
playbooks ? playbooks : null
}
this> DEMO - Flask WebApp
> DEMO - STEP 4 - ServerSpec
4. ServerSpec tests
### spec/flask-example/flask-example_spec.rb
require 'spec_helper'
role = 'flask-example'
describe "#{role}" do
### - 1 - Apply universal ansible role
### tests based on properties.yml
it_should_behave_like "an ansible role",
property["#{role}"]
### - 2 - Any extra other tests you need
### to perform on this service goes here
# TODO if needed
end### properties.yml
flask-example:
:dependencies:
- common
- uwsgi
:packages:
:folders:
- :path: /opt/flask-helloworld
:owner: ggdeploy
:group: ggapp
:mode: 755
:files:
- :path: /opt/flask-helloworld/hello.py
:owner: ggdeploy
:group: ggapp
- :path: /etc/uwsgi/apps-available/flask-helloworld.ini
:owner: root
:group: root
:mode: 644
- :path: /etc/uwsgi/apps-enabled/flask-helloworld.ini
:owner: root
:group: root
:type: symlink
:ports:
- :port: 5000
:type: tcp
:commands:
- :cmd: "curl -s localhost:5000"
:match: "Hello World!"
:services:
- :name: emperor
:enabled: yes
:running: yes$ tree /opt/ops/ansible/tests/serverspec/spec/
spec/
├── flask-example
│ └── flask-example_spec.rb
│
└── shared
└── universal
└── init.rb
> DEMO - STEP 5 - Ansible-lint

5. Ansible-Lint tests
### roles/flask-example-001/configure.yaml
---
- name: Make the application folder
file:
state: directory
path: "{{ flask_example_root_folder }}"
owner: "{{ gg_deploy }}"
group: "{{ gg_app }}"
mode: 755
- name: Pull flask-helloworld from GitHub
git:
repo: https://github.com/Lowess/flask-helloworld.git
dest: "{{ flask_example_root_folder }}"
accept_hostkey: yes
become_user: "{{ gg_deploy }}"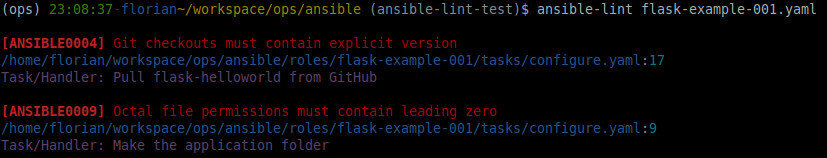
> Thanks !
IT's time for
Q&A !
Slides: http://bit.ly/2cg2wBd
florian@gumgum.com
> APPENDIX
Ansible 101
> Ansible 101 - What is ansible?
- Open source project started by Michael DeHaan in Feb. 2012
- Automation engine written in Python
- Used as :
- Configuration Management tool
- Orchestration tool
- Application deployment tool
- Push based (Can do pull too)
18K Stars
5440 Forks
8.5 K Pull requests

> Ansible 101 - Terminology
- Inventory : Against what you are running your automations?
### INI file format
[dbservers]
db-prod.tiad.com
db-test.tiad.com
[webservers]
foo.tiad.com
bar.tiad.com
...
Static Inventory
Dynamic Inventory





> Ansible 101 - Terminology
- Fact : System information that can be discovered from a system
{
...
"ansible_eth0": {
"active": true,
"device": "eth0",
"ipv4": {
"address": "REDACTED",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0",
"network": "REDACTED"
},
...
},
"ansible_kernel": "3.5.0-23-generic",
"ansible_lsb": {
"codename": "precise",
"description": "Ubuntu 12.04.2 LTS",
"id": "Ubuntu",
"major_release": "12",
"release": "12.04"
},
"ansible_machine": "x86_64",
...
}> Ansible 101 - Terminology
- Module : Abstraction of a task
Linux commands
Ansible modules
apt
ln
mkdir
touch
apt
file
> Ansible 101 - Terminology
- Task : Run an action from a module with specified arguments
ok - changed - skipped - failed
Return codes of a task:
---
- name: Install Nginx
apt:
name: nginx
update_cache: yes
state: present---
- name: Start an EC2 instance
local_action:
module: ec2
aws_access_key: 'AKIAXXXXXXXXX'
aws_secret_key: 'XXXXXXXXXXXXX'
key_name: 'mykeypair.pem'
instance_type: 'c3.large'
wait: yes
image: 'ami-XXXXXX'
count: 1
region: 'us-east-1'
zone: 'us-east-1b'
monitoring: yes
group: ['sshonly', 'webapp']
instance_tags:
Name: demo
Owner: 'Florian Dambrine'
volumes:
- device_name: /dev/sda1
volume_size: 30
---
- name: Create the scripts log folder
file:
state: directory
path: /var/log/gumgum-scripts
owner: gumgum
group: gumgum
mode: 644> Ansible 101 - Terminology
- Play : What tasks to play on what servers (a Task + Inventory)
$ ansible webservers -s -m apt -a "name=nginx state=latest update_cache=yes"
foo.tiad.com | success >> {
"changed": true,
"stderr": "",
"stdout": "Reading package lists...\nBuilding dependency tree...\nReading state......"
}
bar.tiad.com | success >> { ...### nginx-play.yaml
---
- hosts: webservers
sudo: yes
tasks:
- name: Install Nginx
apt:
name: nginx
update_cache: yes
state: present$ ansible-playbook nginx-play.yaml
PLAY [webserver] *************************************
TASK: [Install Nginx] ********************************
changed: [foo.tiad.com]
changed: [bar.tiad.com]
PLAY RECAP *******************************************
foo.tiad.com : ok=0 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
bar.tiad.com : ok=0 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
Example with the ansible-playbook command
Example with an ad-hoc command
> Ansible 101 - Terminology
- Playbook : A list of plays
### nginx-playbook.yaml
---
- hosts: webservers
sudo: yes
tasks:
- name: Install Nginx
apt:
name: nginx
state: latest
update_cache: yes
- name: Cleaning apps-enabled
file:
state: absent
path: /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
- name: Cleaning apps-available
file:
state: absent
path: /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
- name: Restart Nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: restarted

receipe
manifest
> Ansible 101 - Terminology
- Role : Reusable self-contained entity


cookbook
module
rolename/
├── defaults/ ---> Lowest priority variables.
│ └── main.yaml
├── files/ ---> Contains static files that need to be deployed on remote server.
│ └── ...
├── handlers/ ---> Contains tasks that can be triggered by a notification event.
│ └── main.yaml
├── meta/ ---> Contains dependencies between roles.
│ └── main.yaml
├── tasks/ ---> Contains your soup.
│ ├── ...
│ └── main.yaml
├── templates/ ---> Contains templates that will be fed with variables (facts, or role vars).
│ ├── ....j2
└── vars/ ---> Higher level of priority where default variables will be overiden.
├── ...
└── main.yaml> APPENDIX
Jenkins Pipeline
> Current pipeline structure
$ tree ops/ansible/tests/pipelines/
├── ansible-installer.sh ### Shell script run by Jenkins to install ansible
├── ansible-version.txt ### Defines the Ansible version with which all pipelines will run
│
├── big-data-pipeline
│ ├── Pipeline.groovy -> ../utils/LinearPipeline.groovy ### Symlink to pipeline skeleton
│ ├── SpecificSteps.groovy ### Runs specific commands
│ └── Strategy.groovy ### Determines what sould run
│
├── cluster-pipeline
│ ├── Pipeline.groovy -> ../utils/LinearPipeline.groovy
│ ├── SpecificSteps.groovy
│ └── Strategy.groovy
│
├── main-roles-pipeline
│ ├── Pipeline.groovy -> ../utils/LinearPipeline.groovy
│ ├── SpecificSteps.groovy
│ └── Strategy.groovy
...
├── ...
│ ├── Pipeline.groovy -> ../utils/LinearPipeline.groovy
│ ├── SpecificSteps.groovy
│ └── Strategy.groovy
...
└── utils ### Files shared across pipelines
├── AnsibleHelpers.groovy ### Calls with ansiblePlaybook plugin
├── Hitman.groovy ### Independent script checking for best-practices
├── LinearPipeline.groovy ### Pipeline template shown in this presentation
├── ServerSpecHelpers.groovy ### Calls with ServerSpec
└── Utils.groovy ### All kind of utilities (Email notifications, ...)
> Jenkins Pipelines - tips & tricks
- Test a configuration management version upgrade
### utils/Utils.groovy
def grabAnsibleRunner(ansibleRunnerName=null) {
/***************************************************************************
* If @ansibleRunnerName is not set, get the Ansible executable based on
* the version listed ansible-version.txt. Otherwise uses the runner provided.
* @ansibleRunner: Valid ansible version registered on the Jenkins server
***************************************************************************/
def ansibleRunner = null
if (ansibleRunnerName==null) {
def ansibleVersion = readFile('ansible/tests/pipelines/ansible-version.txt')
ansibleRunner = "ansible-${ansibleVersion}"
} else {
ansibleRunner = "${ansibleRunnerName}"
}
echo "Running pipeline using Ansible runner ${ansibleRunner}"
def ansibleTool = tool "${ansibleRunner}"
sh "${ansibleTool}/ansible --version"
ansibleRunner ? ansibleRunner : null
}
Manage Jenkins > Global Tool Configuration > Ansible Installations