Lecture → (7.5, Lecture)
Parser combinators
What is parsing?
Parsing is the process of converting poorly structured data (e.g. text, bytes) into strongly structured data (e.g. abstract syntax trees w/ meta information, custom data types, etc.).
How do people usually employ parsing?
1. Somehow
2. With parser generators: ANTLR, Yacc/Bison, Happy
3. With parser combinators (for example, the Haskell-written ones)
Idea of parser combinators
We want to combine parsers easily.
We want to build bigger parsers from smaller ones.

Type of parser
What is a type of function which parses integer number?
parseInteger :: String -> BoolNo. We want to get actual Integer.
parseInteger :: String -> IntegerNo. Parsers can fail.
parseInteger :: String -> Maybe Integer -- Either for more descriptive errorNow. How do you parse two integers separated by space? Or by any number of spaces? Or comma-separated list of integers? Or the same list inside square brackets [] with any number of spaces between elements?
parseInteger :: String -> Maybe (Integer, String)Solution

What is the type of a parser?
What is the type of a function that parses integers?
parseInteger :: String -> BoolNo, we want to retrieve an actual Integer. This looks like a predicate.
parseInteger :: String -> IntegerNo, parsers can fail.
parseInteger :: String -> Maybe Integer -- 'Either' for a more descriptive errorClose. How do you parse two space-separated integers? Or by any number of spaces? Or a comma-separated list of integers? Or the same list inside the square brackets "[]" with any number of spaces between the elements?
parseInteger :: String -> Maybe (Integer, String)Solution
Understanding the Parser type
┌─ result type ┌── input stream ┌─ remaining stream
│ │ │
newtype Parser a = Parser { runP :: String -> Maybe (a, String) }
│ │ │
└─ selector │ └─ parsed result
│
└─ parsing may failparseInteger :: String -> Maybe (Integer, String)Instead of this...
... it is more convenient to work with a newtype wrapper
newtype allows us to have useful instances!
Some examples
parseInteger :: Parser Integer -- String -> Maybe (Integer, String)Recall the datatype
newtype Parser a = Parser { runP :: String -> Maybe (a, String) }Specialization to Integers:
runP :: Parser a -> String -> Maybe (a, String)How to use it and what behavior do we desire?
ghci> runP parseInteger "5"
Just (5, "") :: Maybe (Integer, String)
ghci> runP parseInteger "42x7"
Just (42, "x7") :: Maybe (Integer, String)
ghci> runP parseInteger "abc"
Nothing :: Maybe (Integer, String)Such behavior allows us to combine parsers relatively easily!
The idea and the first step
The key idea of parser combinators: manually implement simple parsers, implement combinators that combine such parsers, and then build more complex parsers by combining simpler ones via parser combinators.
instance Functor Parser -- replace the parser value
instance Applicative Parser -- run parsers sequentially, one after another
instance Monad Parser -- same as above, but with monadic capabilities
instance Alternative Parser -- allows to choose a non-failing parserHaskell provides some combinators through standard typeclasses and the underlying functions, which turn out to be convenient to use. What we need are
these four instances!
Simple parsers
newtype Parser a = Parser { runP :: String -> Maybe (a, String) }-- always succeeds without processing any input
ok :: Parser ()
ok = Parser $ \s -> Just ((), s)-- fails w/o processing any input if the given parser succeeds, succeeds otherwise
isNot :: Parser a -> Parser ()
isNot parser = Parser $ \s -> case runP parser s of
Just _ -> Nothing
Nothing -> Just ((), s)-- succeeds only if the input stream is empty
eof :: Parser ()
eof = Parser $ \s -> case s of
[] -> Just ((), "")
_ -> Nothing-- processes only the first character, if present,
-- and returns it if the predicate on this character is true
satisfy :: (Char -> Bool) -> Parser Char
satisfy p = Parser $ \s -> case s of
[] -> Nothing
(x:xs) -> if p x then Just (x, xs) else NothingCombining simple parsers
-- processes a given character and returns it
char :: Char -> Parser Char
char c = satisfy (== c)-- always fails without processing any input
notOk :: Parser ()
notOk = isNot okghci> runP eof ""
Just ((),"")
ghci> runP eof "aba"
Nothing
ghci> runP (char 'a') "aba"
Just ('a',"ba")
ghci> runP (char 'x') "aba"
Nothing
-- processes any character / any digit respectively
anyChar, digit :: Parser Char
anyChar = satisfy (const True)
digit = satisfy isDigitInstances for more power
instance Functor Parser where
fmap :: (a -> b) -> Parser a -> Parser b
fmap f (Parser parser) = Parser (fmap (first f) . parser)newtype Parser a = Parser { runP :: String -> Maybe (a, String) }instance Applicative Parser where
pure :: a -> Parser a
pure a = Parser $ \s -> Just (a, s)
(<*>) :: Parser (a -> b) -> Parser a -> Parser b
Parser pf <*> Parser pa = Parser $ \s -> case pf s of
Nothing -> Nothing
Just (f, t) -> case pa t of
Nothing -> Nothing
Just (a, r) -> Just (f a, r)
-- can be written more eloquently by using Maybe as a Monadinstance Monad Parser -- exerciseinstance Alternative Parser where -- exercise
empty :: Parser a -- always fails
(<|>) :: Parser a -> Parser a -> Parser a -- runs the first parser;
-- if fails, runs the second parserSimple combinators: the core
-- datatype
newtype Parser a = Parser { runP :: String -> Maybe (a, String) }
-- simple parsers
eof, ok :: Parser ()
satisfy :: (Char -> Bool) -> Parser Char
empty :: Parser a
-- parser combinators
fmap :: (a -> b) -> Parser a -> Parser b
pure :: a -> Parser a
(<*>) :: Parser (a -> b) -> Parser a -> Parser b -- apply
(<|>) :: Parser a -> Parser a -> Parser a -- orElse
(>>=) :: Parser a -> (a -> Parser b) -> Parser b -- andThenSimple combinators: cont.
-- datatype
newtype Parser a = Parser { runP :: String -> Maybe (a, String) }
-- simple parsers
eof, ok :: Parser ()
satisfy :: (Char -> Bool) -> Parser Char
-- parser combinators
-- * Functor
fmap :: (a -> b) -> Parser a -> Parser b
(<$) :: a -> Parser b -> Parser a -- replaces the value with the first argument
-- * Applicative
pure :: a -> Parser a
(<*>) :: Parser (a -> b) -> Parser a -> Parser b
(<*) :: Parser a -> Parser b -> Parser a -- sequential comp., result of the 1st
(*>) :: Parser a -> Parser b -> Parser b -- sequential comp., result of the 2nd
-- * Alternative
empty :: Parser a
(<|>) :: Parser a -> Parser a -> Parser a -- orElse
many :: Parser a -> Parser [a] -- zero or more
some :: Parser a -> Parser [a] -- one or more (should result in a 'NonEmpty')
-- * Monad
(>>=) :: Parser a -> (a -> Parser b) -> Parser b -- andThenCombinator examples
ghci> runP (ord <$> char 'A') "A"
Just (65,"")ghci> runP ((\x y -> [x, y]) <$> char 'a' <*> char 'b') "abc"
Just ("ab","c")
ghci> runP ((\x y -> [x, y]) <$> char 'a' <*> char 'b') "xxx"
Nothingghci> runP (char 'a' <* eof) "a"
Just ('a',"")
ghci> runP (char 'a' <* eof) "ab"
Nothingghci> runP (many $ char 'a') "aaabcd"
Just ("aaa","bcd")
ghci> runP (many $ char 'a') "xxx"
Just ("","xxx")
ghci> runP (some $ char 'a') "xxx"
Nothingghci> runP (char 'a' <|> char 'b') "abc"
Just ('a',"bc")
ghci> runP (char 'a' <|> char 'b') "bca"
Just ('b',"ca")
ghci> runP (char 'a' <|> char 'b') "cab"
NothingMore complex combinators
string :: String -> Parser String -- like 'char' but for Strings
oneOf :: [String] -> Parser String -- parses the first matched stringProblem: parse a user's [y/n] answer
data Answer = Yes | NoyesP :: Parser Answer
yesP = Yes <$ oneOf ["y", "Y", "yes", "Yes", "ys"]noP :: Parser Answer
noP = No <$ oneOf ["n", "N", "no", "No"]answerP :: Parser Answer
answerP = yesP <|> noPParser combinator libraries
-- | @'ParsecT' e s m a@ is a parser with custom data component of error
-- @e@, stream type @s@, underlying monad @m@ and return type @a@.
newtype ParsecT e s m a = ParsecT
{ unParser ::
forall b.
State s e ->
(a -> State s e -> Hints (Token s) -> m b) -> -- consumed-OK
(ParseError s e -> State s e -> m b) -> -- consumed-error
(a -> State s e -> Hints (Token s) -> m b) -> -- empty-OK
(ParseError s e -> State s e -> m b) -> -- empty-error
m b
}
-- snippet taken from the Text.Megaparsec.Internal.ParsecT datatypeparsec — the first mature library, very old
attoparsec — fast, poor error messages, backtracks by default
megaparsec — excellent error messages, mature
Types in mature libraries are scary...
Testing
Testing libraries
hspec — declarative unit testing
hedgehog — property-based testing
tasty — testing framework for combining different approaches
• tasty-hspec — tasty provider for hspec
• tasty-hedgehog — tasty provider for hedgehog
It's easier to understand and write things if you're familiar with the IO monad and do-notation but bear with me...
Unit testing
HSpec library (1 / 2)
Test.Unit module
module Test.Unit
( hspecTestTree
) where
import Data.Maybe (isJust, isNothing)
import Test.Tasty (TestTree)
import Test.Tasty.Hspec (Spec, describe, it, shouldBe, shouldSatisfy, testSpec)
import Parser (char, eof, runP)
hspecTestTree :: IO TestTree
hspecTestTree = testSpec "Simple parser" spec_Parser
spec_Parser :: Spec
spec_Parser = do
describe "eof works" $ do
it "eof on an empty input" $
runP eof "" `shouldSatisfy` isJust
it "eof on a non-empty input" $
runP eof "x" `shouldSatisfy` isNothing
describe "char works" $ do
it "char parses a character" $
runP (char 'a') "abc" `shouldBe` Just ('x', "bc")HSpec library (2 / 2)
Now using our TestTree
module Main where
import Test.Tasty (defaultMain, testGroup)
import Test.Unit (hspecTestTree)
main :: IO ()
main = hspecTestTree >>= \unitTests ->
let allTests = testGroup "Parser" [unitTests]
in defaultMain allTests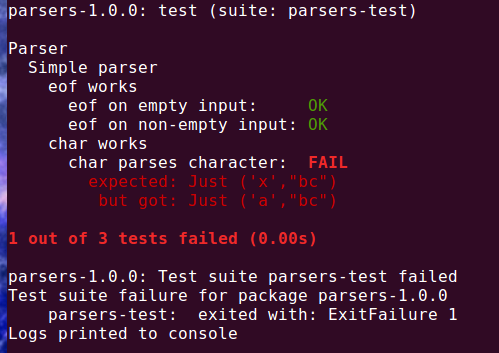
Property-based testing
Shalyto
Writing unit tests for different cases is really boring and tedious. We have a lot of functions, some of which may have corner cases, and our tests will be quite limited in terms of the size of the test set.
With property-based testing:
1. Library generates arbitrary input for your function.
2. Instead of specifying expected values you specify desired properties to which function results should satisfy.
Often it's much more difficult to write property-based tests rather than unit tests. But properties test your functions better (more cases, more reliable, more robust).
Simple example
import Hedgehog
import qualified Data.List as List
import qualified Hedgehog.Gen as Gen
import qualified Hedgehog.Range as Range
genIntList :: Gen [Int]
genIntList =
let listLength = Range.linear 0 100000
in Gen.list listLength Gen.enumBounded
prop_reverse :: Property
prop_reverse = property $
forAll genIntList >>= \xs ->
List.reverse (List.reverse xs) === xs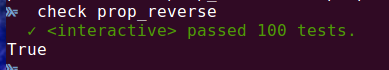
Shrinking (1 / 3)
If a test is not passed we can show the generated test case. But because this test case is generated randomly, it can be very big! It's much easier to test on smaller inputs.
Property-based libraries usually come with shrinking — a technique for automatically decreasing the size of a faulty test in order to come up with a minimal reproducible example.
Shrinking (2 / 3)
-- drops an element somewhere around the middle of the list
fauxReverse :: [a] -> [a]
fauxReverse xs =
let sx = List.reverse xs
mp = length xs `div` 2
(as, bs) = List.splitAt mp sx
in as ++ List.drop 1 bsLet's implement a bad reverse function
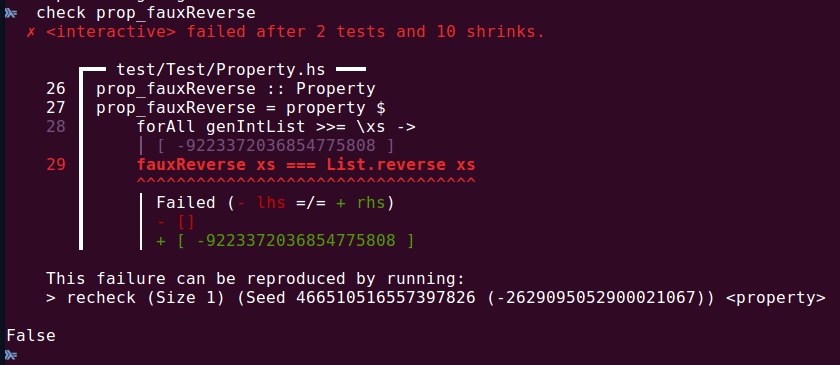
prop_fauxReverse :: Property
prop_fauxReverse = property $
forAll genIntList >>= \xs ->
fauxReverse xs === List.reverse xsShrinking (3 / 3)
And the output is...
Some standard use cases
1. Round-trip properties
read . show ≡ id
decode . encode ≡ id
deserialize . serialize ≡ id2. Type classes laws
(a <> b) <> c ≡ a <> (b <> c)
a <> mempty ≡ a
mempty <> a ≡ aThough, some laws are harder to test...
(m >>= f) >>= g ≡ m >>= (\x -> f x >>= g)You need to generate arbitrary functions and show them. Don't worry, it is possible, just not out of the box...
Testing parsers with properties
Very simple and naive test...
module Test.Property (okTestTree) where
import Hedgehog (Gen, Property, forAll, property, (===))
import Test.Tasty (TestTree)
import Test.Tasty.Hedgehog (testProperty)
import Parser (ok, runP)
import qualified Hedgehog.Gen as Gen
import qualified Hedgehog.Range as Range
okTestTree :: TestTree
okTestTree = testProperty "ok always succeeds" prop_Ok
genString :: Gen String
genString =
let listLength = Range.linear 0 100
in Gen.list listLength Gen.alpha
prop_Ok :: Property
prop_Ok = property $
forAll genString >>= \s ->
runP ok s === Just ((), s)Cont Monad
Continuation Passing Style (CPS)
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}add :: Int -> Int -> Int
add x y = x + y
addCPS :: Int -> Int -> (Int -> r) -> r
addCPS x y onDone = onDone (x + y)function addCPS(a, b, callback) {
callback(a + b);
}addCPS(1, 2, function (result) {
// use result here
});onInput :: (String -> IO ()) -> IO () -- every callback framework
onInput action = forever $ getLine >>= actionJavaScript
Haskell
«Abuse of the Continuation monad can produce code that is impossible to understand and maintain.»
Example (anonymous callbacks)
square :: Int -> Int
square x = x * x
pythagoras :: Int -> Int -> Int
pythagoras x y = (+) (square x) (square y)addCPS :: Int -> Int -> ((Int -> r) -> r)
addCPS x y = \k -> k (x + y)
squareCPS :: Int -> ((Int -> r) -> r)
squareCPS x = \k -> k (square x)pythagorasCPS :: Int -> Int -> ((Int -> r) -> r)
pythagorasCPS x y = \k -> -- k :: Int -> r
squareCPS x $ \x2 ->
squareCPS y $ \y2 ->
addCPS x2 y2 $ k -- addCPS x2 y2 :: (Int -> r) -> rghci> pythagorasCPS 3 4 id
25Cont data type
ghci> :t ($)
($) :: (a -> b) -> a -> bgchi> :t ($ 2)
($ 2) :: Num a => (a -> b) -> bghci> map ($ 2) [(3*), (2+),(1-)]
[6,4,-1]newtype Cont r a = Cont { runCont :: (a -> r) -> r }ghci> :t cont
cont :: ((a -> r) -> r) -> Cont r a
gchi> runCont (cont ($ 2)) `map` [(3*), (2+), (1-)]
[6,4,-1]
ghci> runCont (cont ($ 2)) id
2Example (plain Cont data type)
addCPS :: Int -> Int -> Cont r Int
addCPS x y = cont $ \k -> k (x + y)
squareCPS :: Int -> Cont r Int
squareCPS x = cont $ \k -> k (square x)pythagorasCPS :: Int -> Int -> Cont r Int
pythagorasCPS x y = cont $ \k ->
runCont (squareCPS x) $ \x2 ->
runCont (squareCPS y) $ \y2 ->
runCont (addCPS x2 y2) $ kghci> runCont (pythagorasCPS 3 4) id
25Cont monad
newtype Cont r a = Cont { runCont :: (a -> r) -> r }instance Monad (Cont r) where
return :: a -> Cont r a
return a =
(>>=) :: Cont r a -> (a -> Cont r b) -> Cont r b
Cont arr >>= f =instance Monad (Cont r) where
return :: a -> Cont r a
return a = Cont ($ a)
(>>=) :: Cont r a -> (a -> Cont r b) -> Cont r b
Cont arr >>= f = Cont $ \br -> arr $ \a -> runCont (f a) br
-- arr :: (a -> r) -> r
-- br :: (b -> r)
-- f :: a -> Cont r bExample (Cont monad)
addCPS :: Int -> Int -> Cont r Int
addCPS x y = return $ x + y
squareCPS :: Int -> Cont r Int
squareCPS = return . squarepythagorasCPS :: Int -> Int -> Cont r Int
pythagorasCPS x y = squareCPS x >>= \x2 ->
squareCPS y >>= \y2 ->
addCPS x2 y2