Virtual Chains and Proof of Burn
Friedger Müffke
Blockchain Mania #20
Hamburg, 16 April 2019
Virtual Chains vs L2 Networks

L2 networks
- Lightning Network (Bitcoin payment channels)
- Plasma, Loom Network (Ethereum side chains)
Virtual Chain
- Blockstack
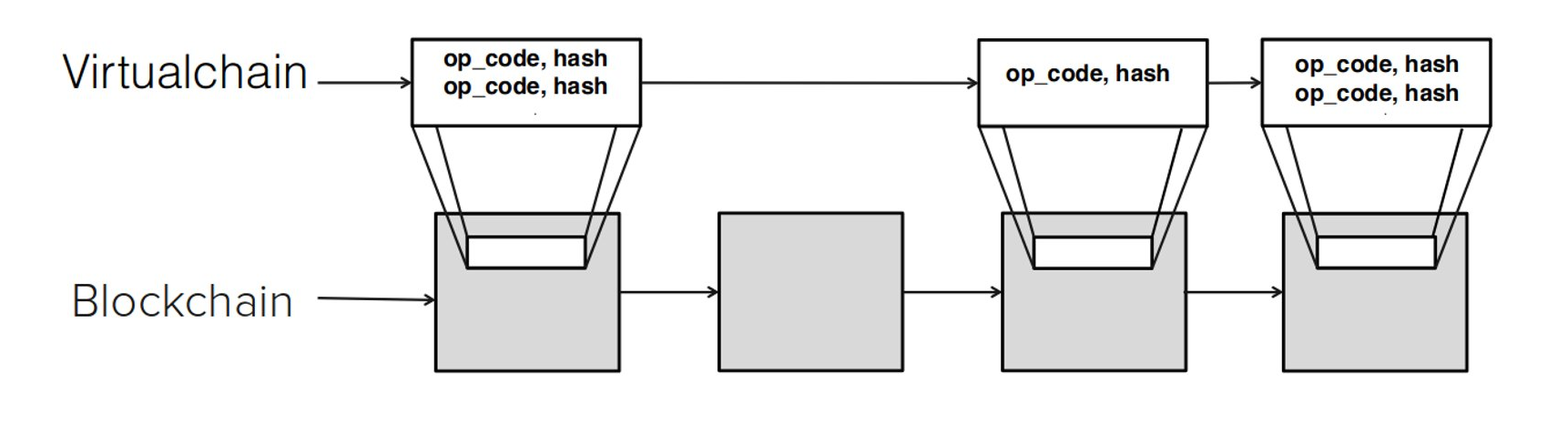
- Fork* Resistant
- Consensus Hash
Stacks Blockchain

High Validation Throughput
one block
one transaction

Low-latency block inclusion
block streaming

Open Leadership Set
proof of burn mining

Participation without mining hardware
negligible extra energy
burn existing cryptos

Fair Mining Pool
aggregation of small burns
no pool operator
hedge bets

Possibility to Migrate
(unchanged)

Proof of Burn

Assumption
- Deep forks exponentially rarer in function of length
- Deep fork unrelated to stacks transactions
- Burn chain miners do not censor all stacks transactions
- 2/3+ stack leaders candidates (by burn weight) are correct and honest
Properties
- Global knowledge of time
- Global knowledge of blocks
- Global knowledge of burns
- Mitigate block-withholding attacks
- Ancillary burns enhance chain quality
- Ancillary burning to hedge bets
Block production
- one burn chain block, at most one stacks block
- not atomic, microblocks (Bitcoin-NG)
- some transactions can be promised