stack & queue
Stack
LIFO (last-in-first-out)
Queue
FIFO (first-in-first-out)
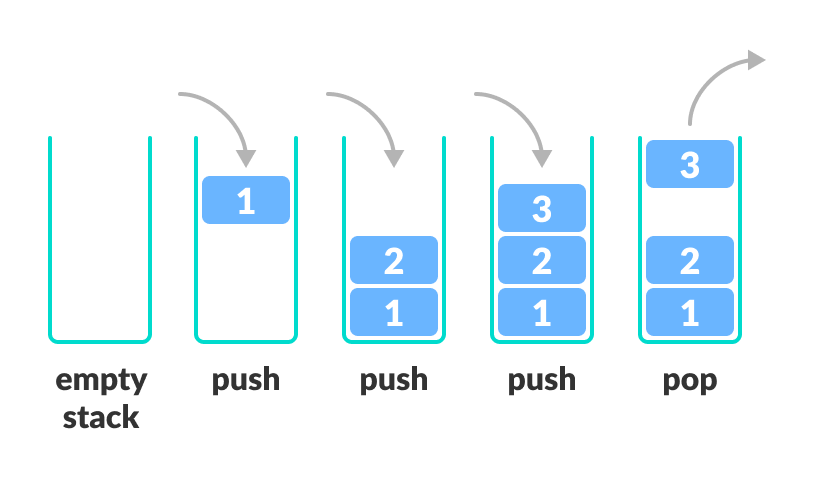
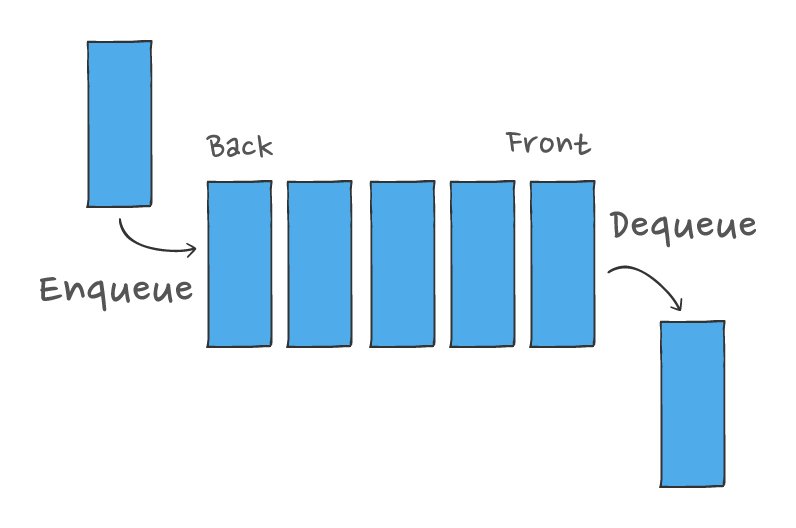
Stack
Queue
s
q
s.top()
s.push(t)
t
s.pop()
是否為空:s.empty()
q.push(t)
q.pop()
q.front()
是否為空:q.empty()
Example 1
用stack和queue輸入和輸出
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
// #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
queue<int> Q;
int n,t;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>t;
Q.push(t);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
t=Q.front();
cout<<t<<" ";
Q.pop();
}
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
// #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
stack<int> S;
int n,t;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>t;
S.push(t);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
t=S.top();
cout<<t<<" ";
S.pop();
}
return 0;
}Exercise 1
zerojudge_e447 queue練習
Exercise 1_ans
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int n,t;
queue<int> q;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>t;
if(t==1){
int p;
cin>>p;
q.push(p);
}
else if(t==2){
if(!q.empty()){
cout<<q.front()<<'\n';
}
else{
cout<<-1<<'\n';
}
}
else if(t==3){
if(!q.empty()){
q.pop();
}
}
}
return 0;
}括弧配對

想法:
用一個堆疊(Stack),每次讀入字串的一個字元。
如果是左括弧,就把它push進去Stack裡面
如果是右括弧,就把它和堆疊最上面的字元配對,如果不符則error
如果最後堆疊還有剩下括弧是error
如果都沒錯,則是平衡的
())
))
| ( |
|---|
))
| ( |
|---|
成功配對
pop
)
沒有配對
error
Answers
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int sol(){
stack<int> S;
char in[210], ch[7]="([{)]}";
while(cin>>in){
bool error=false;
int len=strlen(in);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
int sym=strchr(ch,in[i])-ch;
if(sym>=6){
return -1;
}
if(sym<3){
S.push(sym);
}
else{
if(S.empty()||sym!=S.top()+3){
error=true;
break;
}
S.pop();
}
}
if(!S.empty())
error=true;
(error)?cout<<"no\n":cout<<"yes\n";
return 0;
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
while(sol()==0);
return 0;
}
Question
- 為什麼括弧有六種卻要ch卻要宣告七格?
- 如果不先宣告len=strlen(in),而在for迴圈裡面寫i<strlen(in)會有什麼缺點?
- 想想int sym=strchr(ch, in[i])-ch 這句中的指標怎麼轉換的? (strchr用法) 提示:陣列的名字是一個?
- (error)?cout<<"no\n":cout<<"yes\n"; 是什麼意思?
- 為什麼要設一個布林型態的error,而不能在遇到錯誤的時候直接cout<<"no"然後break?
priority_queue
n.優先考慮的事
優先佇列
How to use priority_queue?
宣告
priority_queue<型態> 名字;
priority_queue<int> pq;加入元素
pq.push(x);查詢最大
pq.top()因為priority_queue會把加入的元素由大到小排序
刪除最大
pq.pop()是否為空
pq.empty();P.s. 不在APCS範圍內
Example_2

#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int n;
cin>>n;
priority_queue<LL> PQ;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int m;
cin>>m;
PQ.push(-(LL)m);
}
LL cost=0;
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
LL m=PQ.top();
PQ.pop();
m+=PQ.top();
PQ.pop();
PQ.push(m);
cost+=m;
}
cout<<-PQ.top()<<'\n'<<-cost<<'\n';
return 0;
}Ans
Greedy Algorithm
adj. 貪婪的
貪心演算法
Greedy

如果面額改成[1,7,8,15]呢?
如果測資是14元,依照貪心演算法會是8*1+1*6,需要7枚代幣。
但這可以靠7*2,2枚代幣解決,所以貪心演算法不適用於所有情況。