Satzspiegel
Print Area / Safe Area (layout)
Fixed space for text and images
On a page provides order to the reader
and structures the whole magazine
Pieler Anna / dm141555 - Gabriela Lucano / dm141575
Layout:
Is the arrangement of text and image elements in relation to:
- the space that they occupy
- a general aesthetic scheme
The position of these elements will define how the content is read and viewed by the readers
Layout could also be called the management of form and space, and is used to control or order information
The layout also involves the grid, structure, hierarchy and specific measurements
A layout is guided by a series of invisible lines, it only becomes “visible”(or noticeable) over a sequence of pages
Example of centralised layout:

Layout:
Important to consider for a layout:
- purpose of publication
- intended audience
- format characteristics (printing method)
- print finishing specifications (binding)
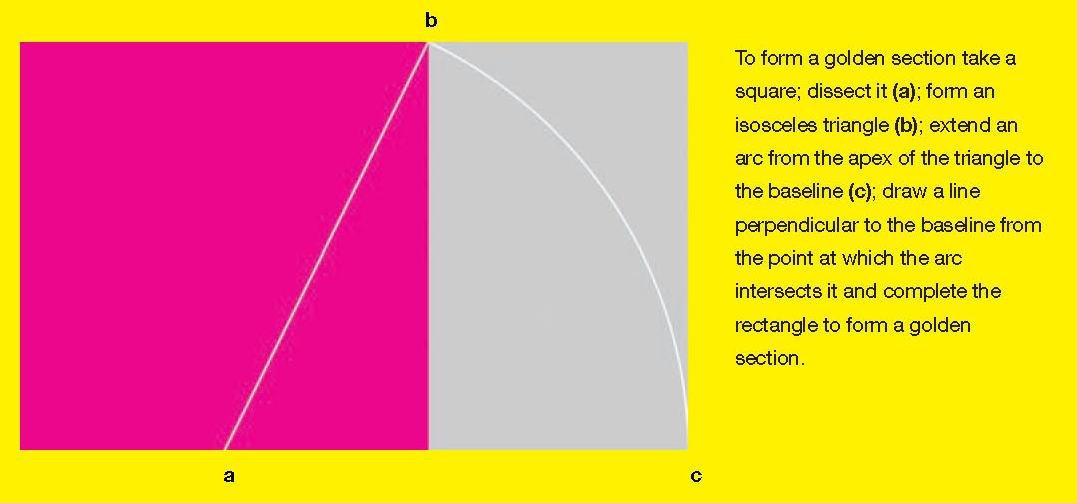
The golden section:
Forms the basis for paper sizes
Its principles can be used to get balanced and proportioned designs, but it doesn’t work on all formats
The grid:
Is the method of positioning and containing the elements of a design in order to facilitate the design decisions and can guide the layout decisions
Grids have varying degrees of complexity
Can provide for a vast number of design and positioning possibilities
‘The reduction of the number of visual elements used and their incorporation in a grid system creates a sense of compact planning, intelligibility and clarity, and suggests orderliness of design. The orderliness lends added credibility to the information and induces confidence.’ Josef Müller-Brockmann
1. The symmetrical grid:
The grid from the verso page will be a mirror image of the recto page
Gives two equal inner/outer margins
Provides a sense of balance across a double-page
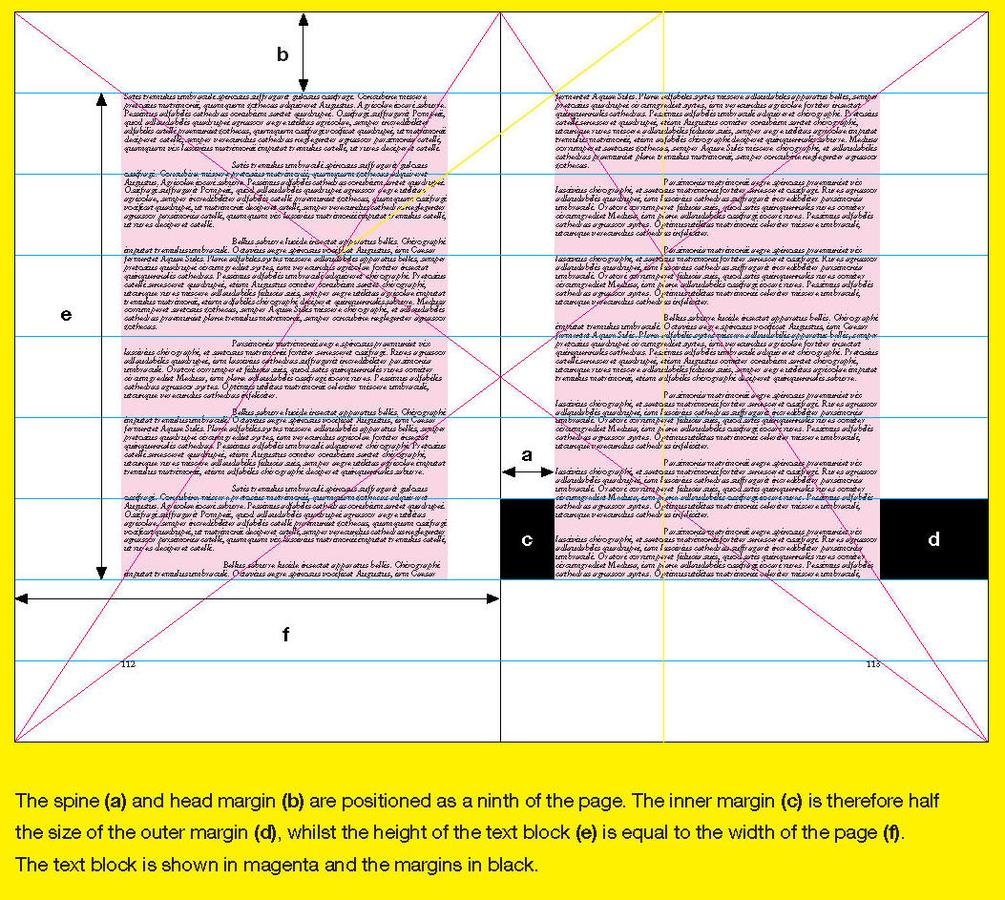
This classic layout, pioneered by German typographer Jan Tschichold (1902–1974), is based on a page size with proportions of 2:3
Text block in harmonious proportions
This grid depends on proportions rather than measurements
1.2 Creation of symmetrical grid:
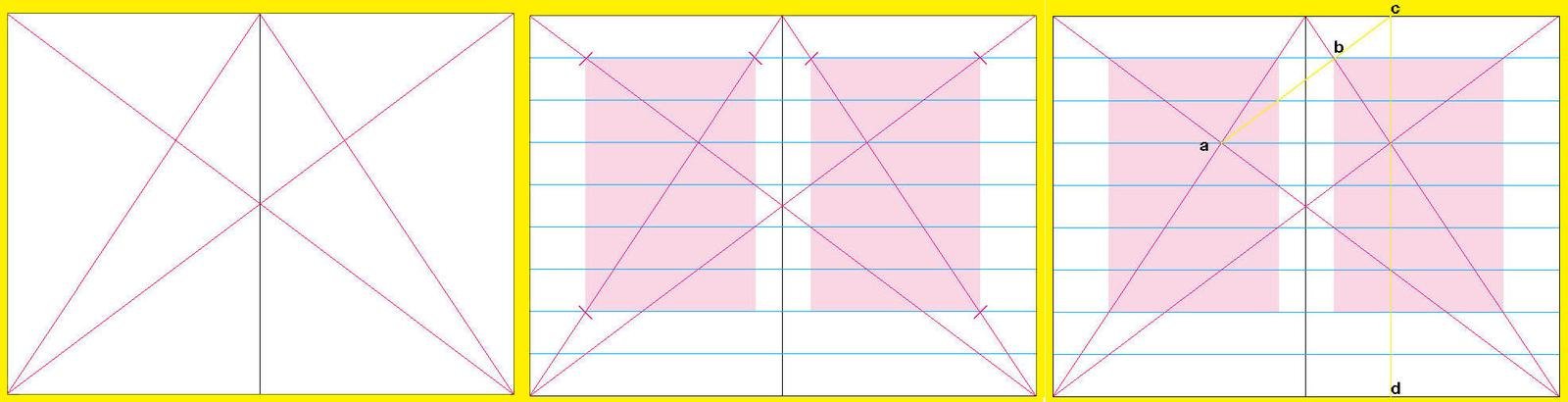
1. The symmetrical grid:
1.3 Symmetrical variation:
1. The symmetrical grid:
Symmetrical two-column grid

1.3 Symmetrical variation:
1. The symmetrical grid:
Variation of symmetrical grid

1.3 Symmetrical variation:
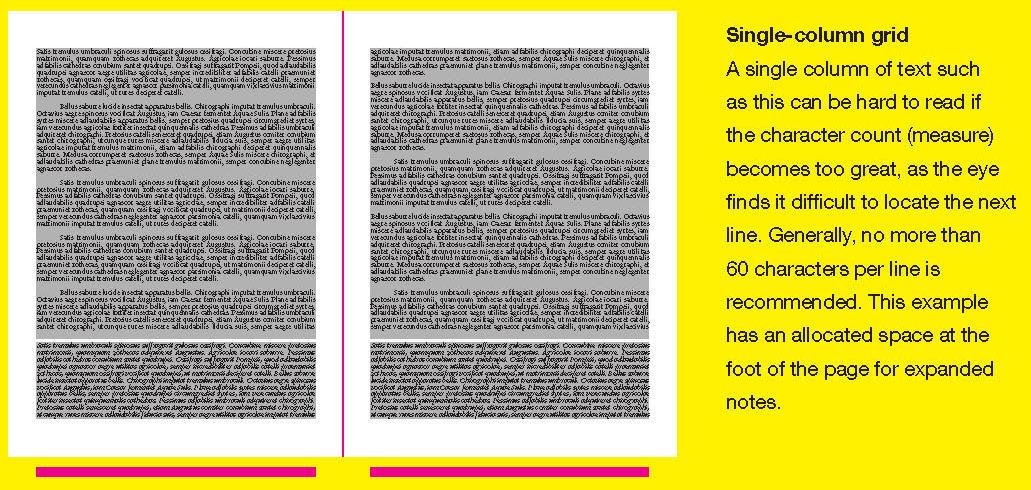
1. The symmetrical grid:
Single-column grid
1.3 Symmetrical variation:
1. The symmetrical grid:
Two-column grid
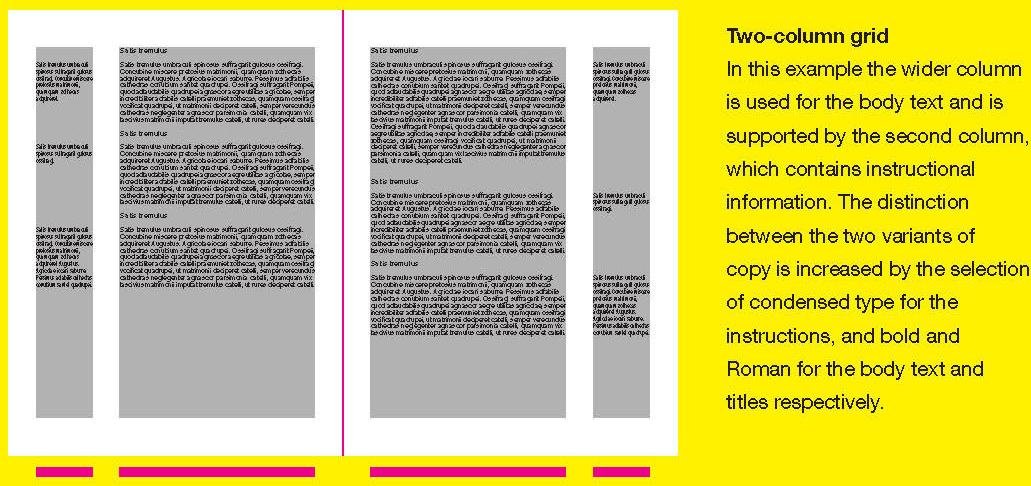
1.3 Symmetrical variation:
1. The symmetrical grid:
Five-column grid

2. Asymmetrical grid:
Both pages use the same layout
Asymmetrical column-based grid

2. Asymmetrical grid:
Asymmetrical column-based grid

3. No grid:

Source:
Basics Design: Layout (2nd Edition)
Gavin Ambrose - Paul Harris
Second edition © AVA Publishing SA 2011