The GitLab Flow
Enhance Software Engineering Quality
by
Adopting GitLab Flow
- Basic Git Concept
- Challenges of Software Engineering in a Scale
- How GitLab Flow Solve?
- GitLab Flow Explained
- Live Demo
Enhance Software Engineering Quality by
Adopting GitLab Flow
zsh (Z Shell)
branch name
directory name
last command return
git status
Basic Git Concept
Basic Git Concept
git merge
(master)$ git merge feature-1
Basic Git Concept
git rebase
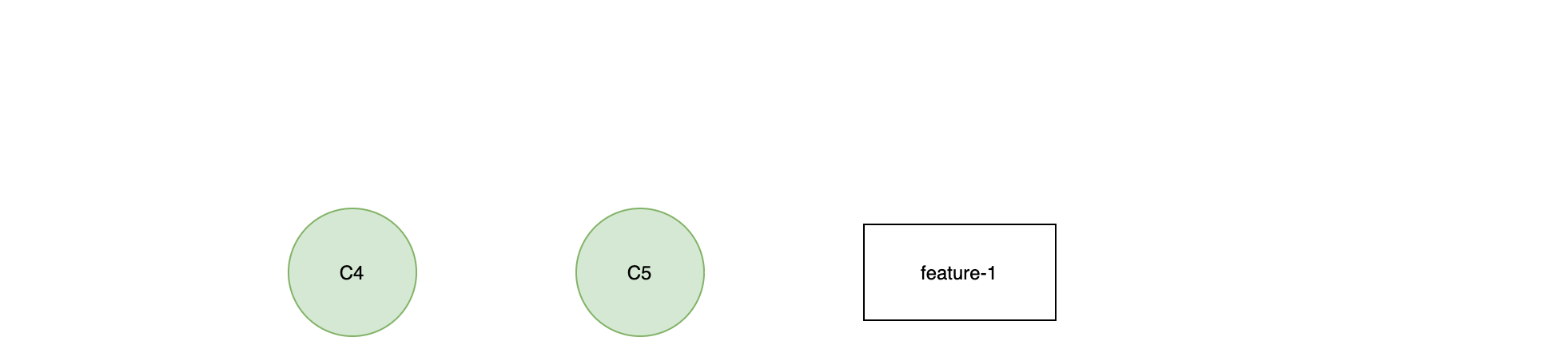
(feature-1)$ git rebase master
Basic Git Concept
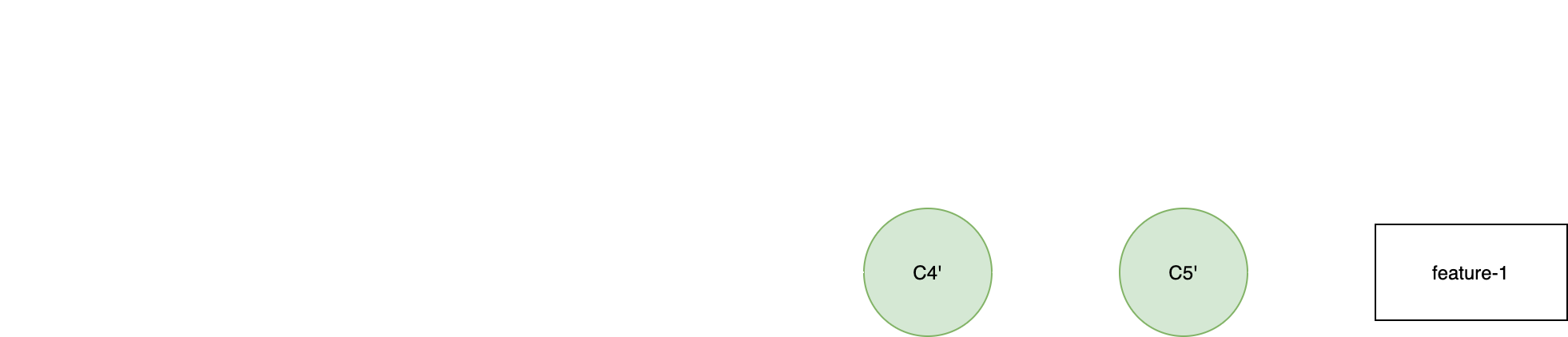
git squash
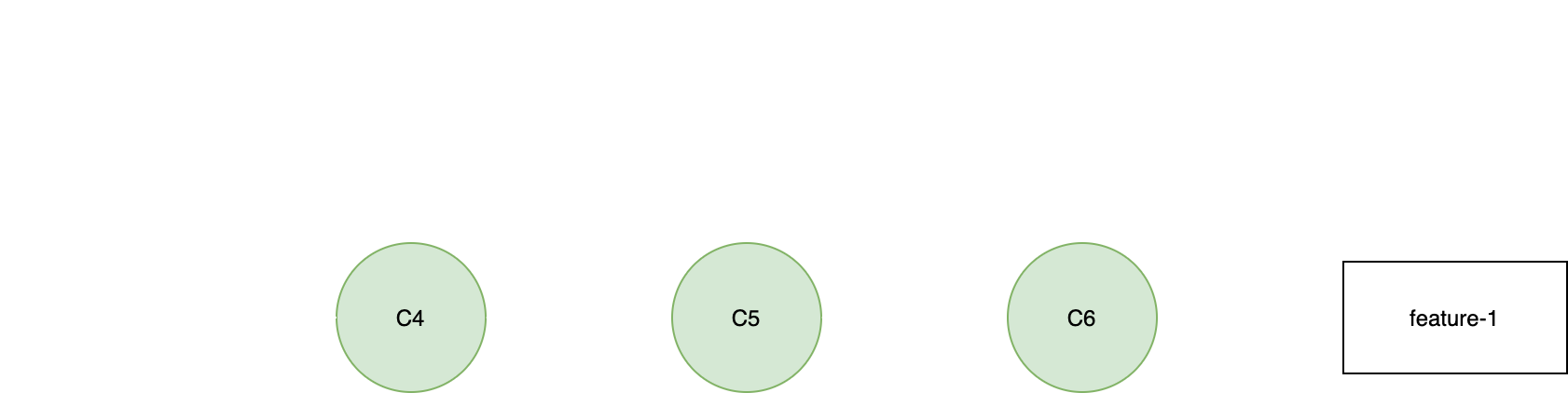
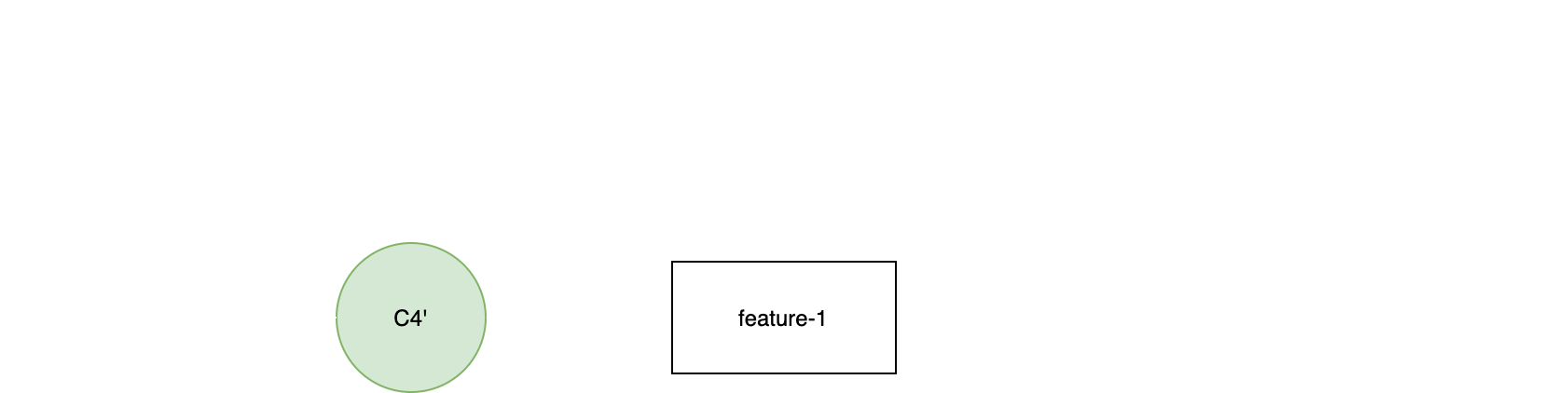
(feature-1)$ git rebase -i C1
Basic Git Concept
git cherry-pick

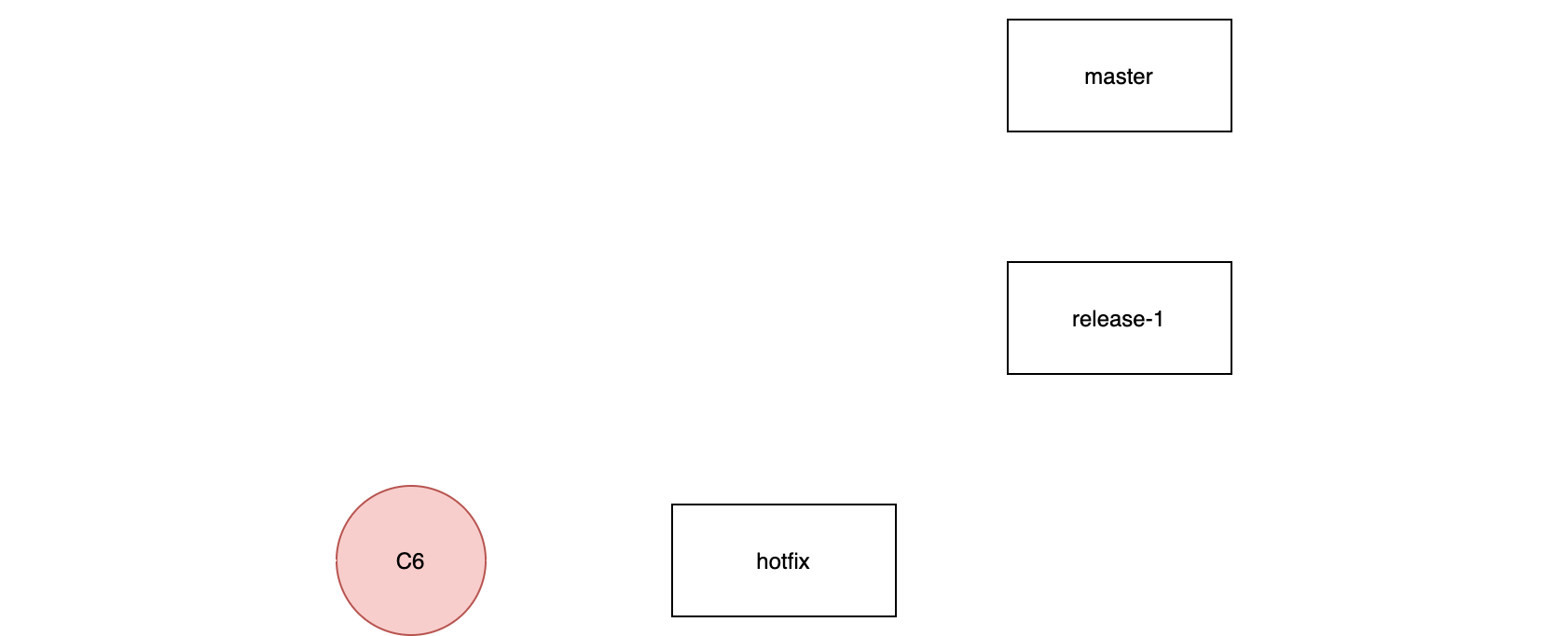
(master)$ git cherry-pick C6 (release-1)$ git cheery-pick C6
Challenges of Software Engineering in a Scale

Challenges of Software Engineering in a Scale
- Code Changes
- Release Management
- Task Reporting
- Code & Commit Quality
- Confident Level of Resolving Conflict
Challenges of Software Engineering in a Scale
Code Changes Challenges
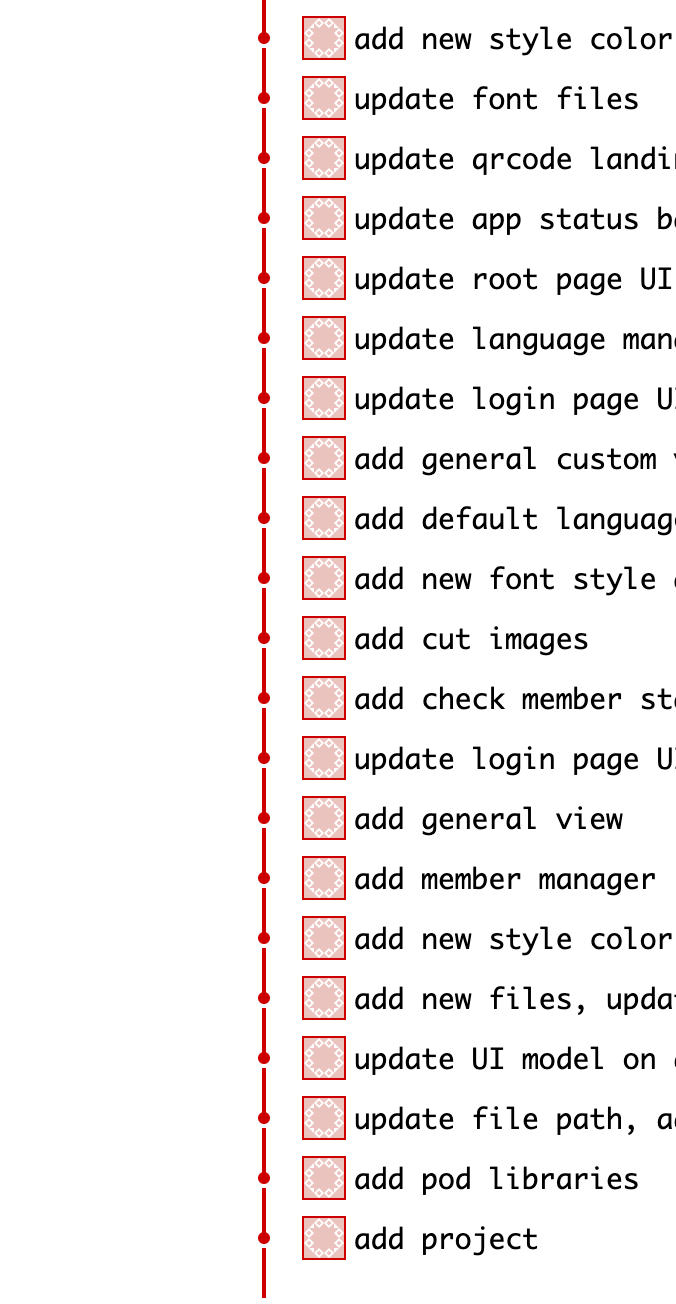
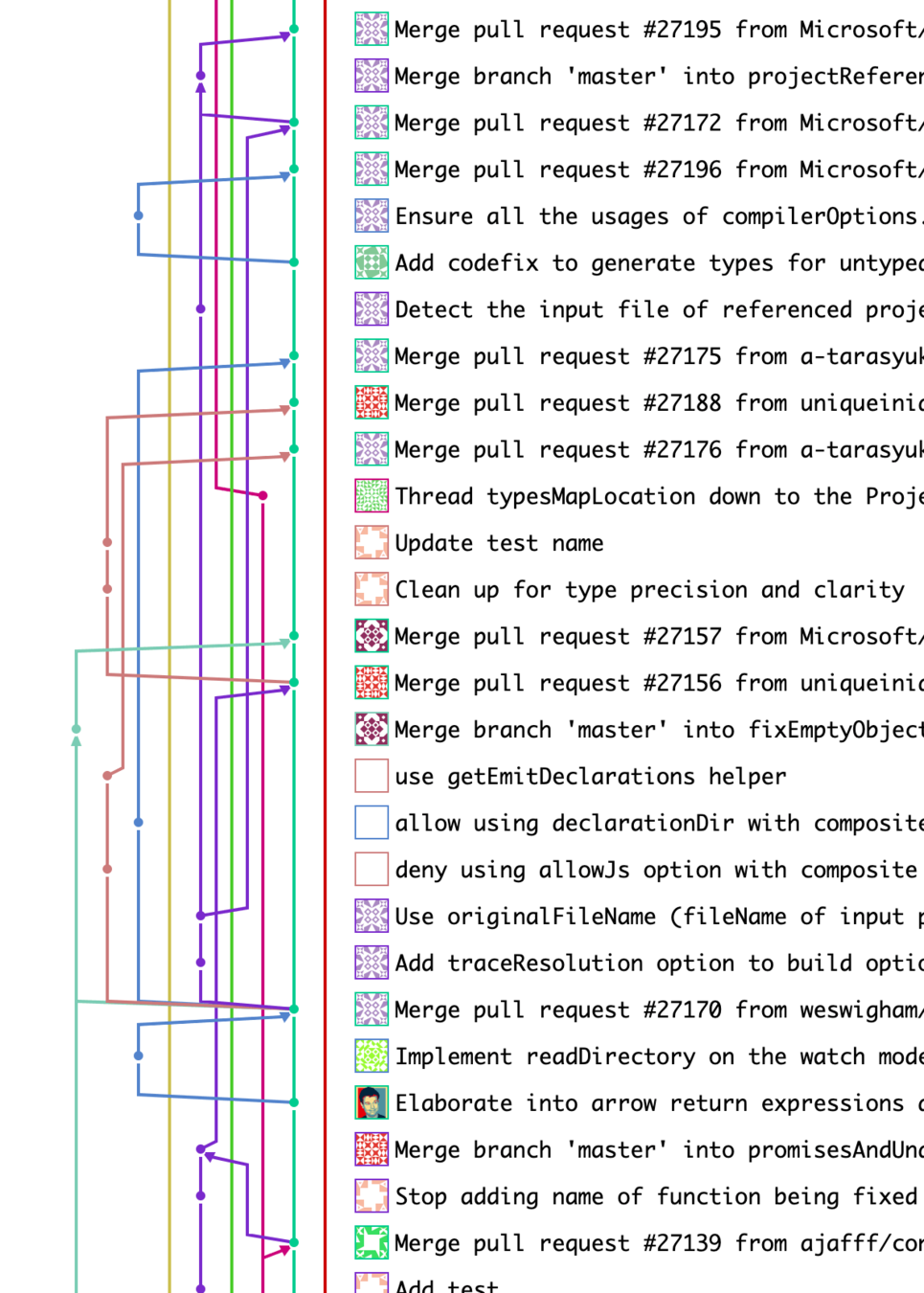
Complex Git History (Untraceable)
Inconsistent Git Commit Message
Challenges of Software Engineering in a Scale
Release Management Challenges
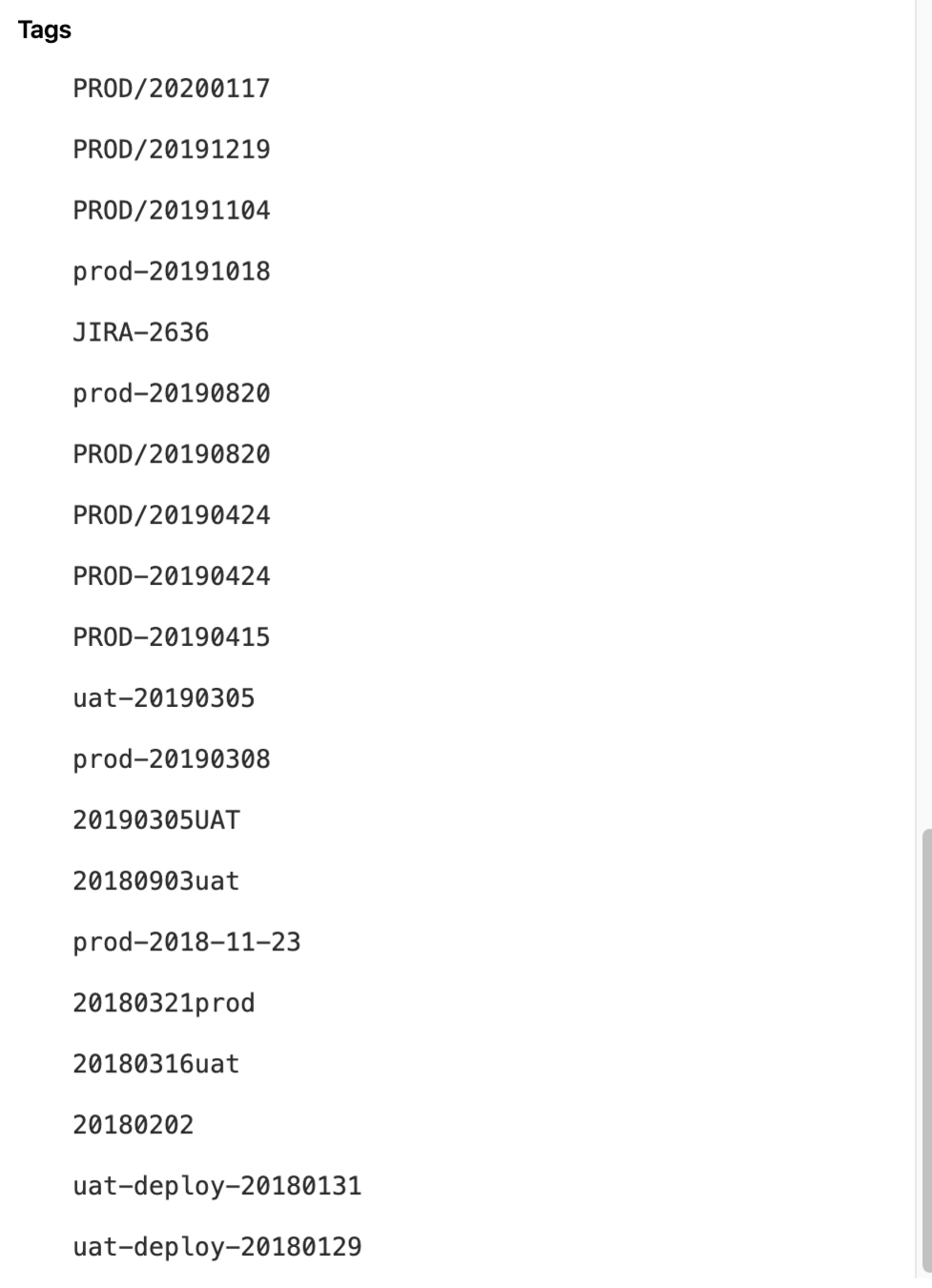
Tag Management
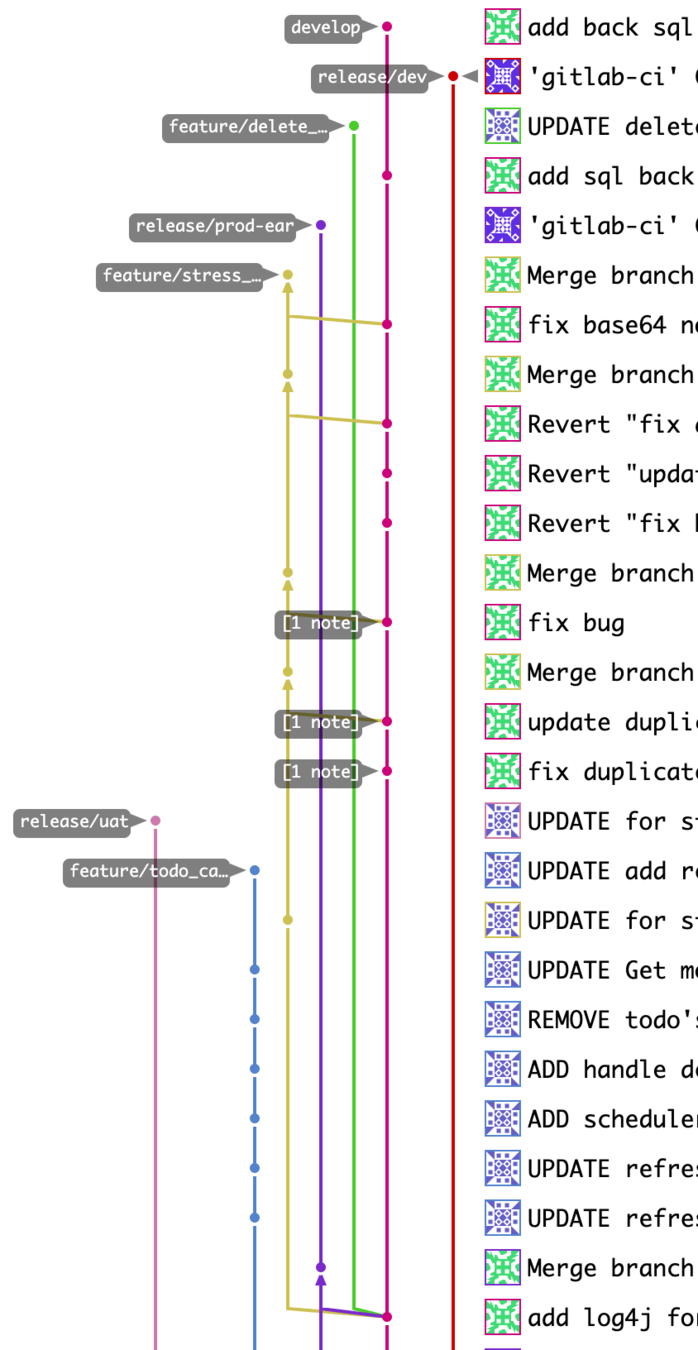
Branch Management
Inconsistent Branching
Inconsistent Tags

Challenges of Software Engineering in a Scale
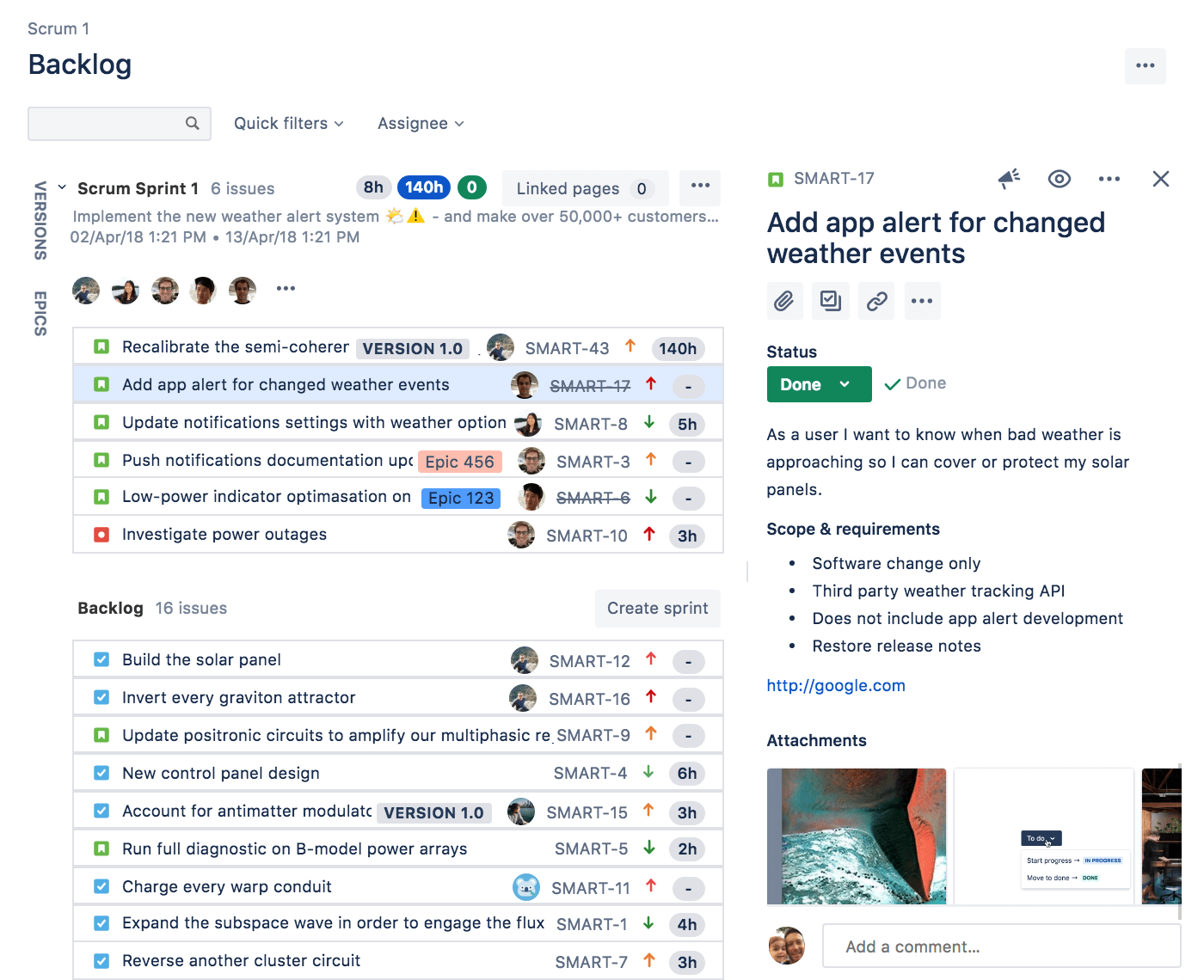
Task Reporting Challenges
git add .
git commit -m "add fancy animation"
git pull --rebase
git pushManually Synchronize Task Status

git add .
git commit -m "hotfix sql injection"
git pull --rebase
git pushMaintain Task & Commit Relationship
Report progress
Report bugfix
Challenges of Software Engineering in a Scale
Code & Commit Quality Challenges I
Unnecessary Complexity
Inconsistent Code Style
Brainless Copy and Paste

Challenges of Software Engineering in a Scale
Code & Commit Quality Challenges II
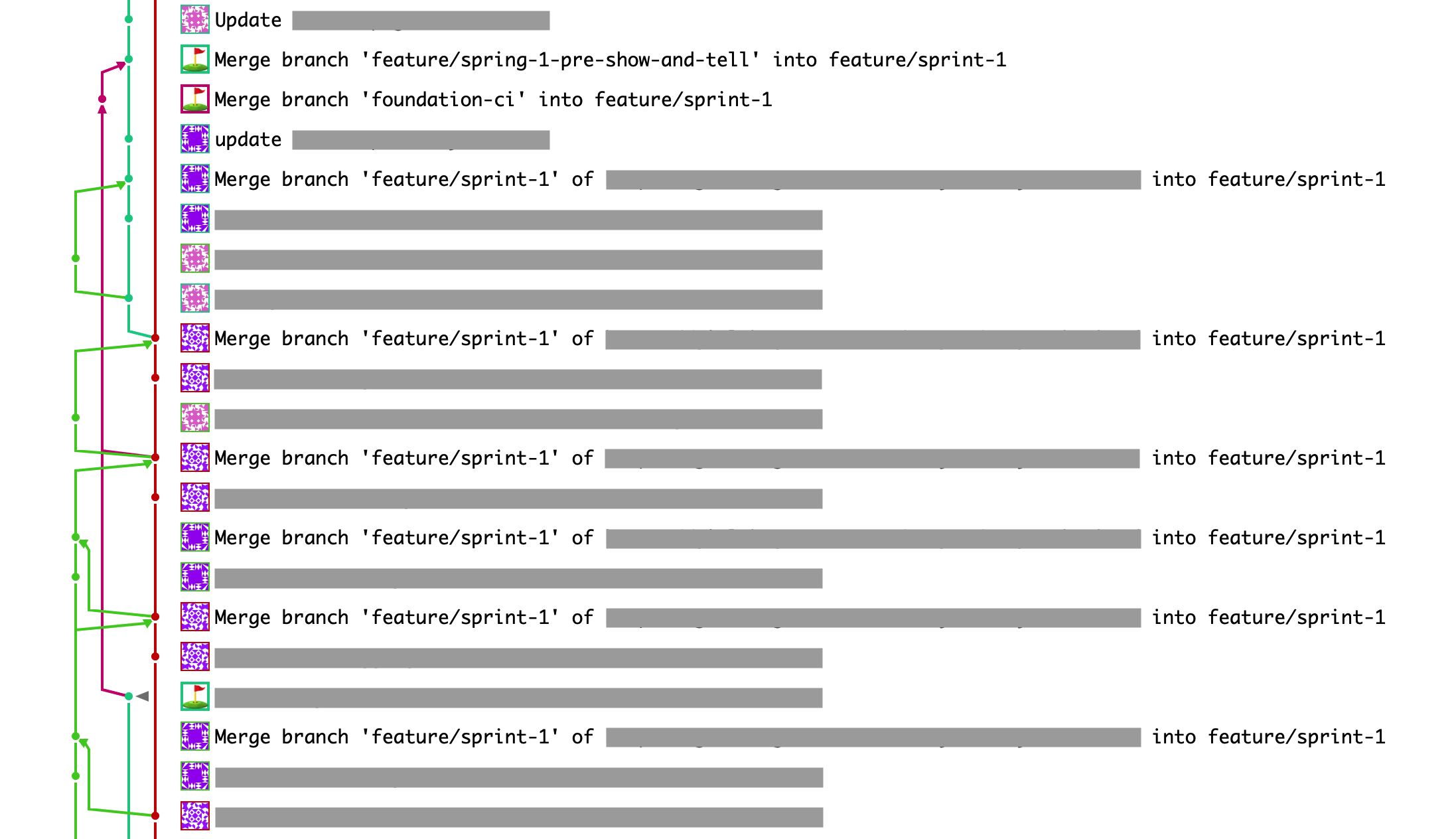
Unnecessary Merge Commit
Fragmented Commit History
Challenges of Software Engineering in a Scale
Confident Level of Resolving Conflict I
Unwanted Bad Code exist in Git History

A sunny day, CI run successfully on your branch...
but it failed on CI after merged into master
“Developer should run local test before push”
Some Integration Tests on CI might NOT available locally .
Challenges of Software Engineering in a Scale
Confident Level of Resolving Conflict II
Unwanted Bad Commit & Merge exist in Git History
“I won't directly commit to master”
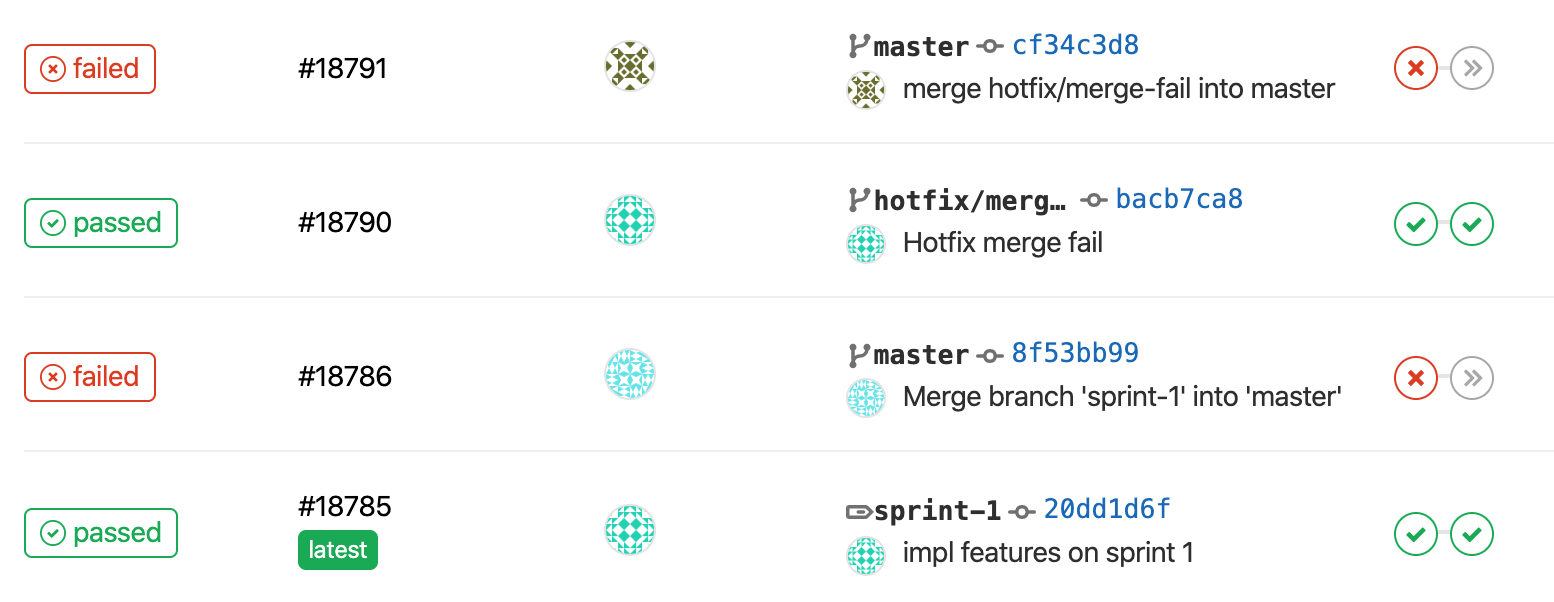
forgot to checkout master before doing the hotfix and merge, things get worse
Challenges of Software Engineering in a Scale
Consequences
Not able to Scale
High Maintenance Cost
High Turn-over overhead
Unwanted Bad Commit & Merge exist in Git History
Unnecessary Merge Commit
Fragmented Commit History
Unnecessary Complexity
Inconsistent Code Style
Brainless Copy and Paste
Manually Synchronize Task Status
Maintain Task & Commit Relationship
Inconsistent Branching
Inconsistent Tags
Complex Git History (Untraceable)
Inconsistent Git Commit Message
Sign Of Poor Software Engineering Quality
Difficult to Collaborate
Inefficient Development
Unnecessary Complex Development Procedures
How GitLab Flow Solve?
“GitLab Flow provides list of best practices”
“Combining those best practices to solve all challenges in whatever scale”
How GitLab Flow Solve?
However...
“Enforce the best practices by GitLab Project Settings”
“Rules without enforcement are merely
words on paper. ”
How GitLab Flow Solve?
- Merge ONLY via Merge Request
- Enforce Linear History
- Enforce Naming Convention
- Upstream first policy
- Stable Branches and Tag Release
- JIRA Integration
Proposed Minimal Practices
GitLab Flow Explained
Merge ONLY via Merge Request I
No Local merge & push
Who can approve merge request
GitLab Flow Explained
Merge ONLY via Merge Request II
- Senior / SA are accountable to the merge requests
- Senior / SA has also no special authority to bypass Merge Request
GitLab Flow Explained
Merge ONLY via Merge Request II
Back-Traceable Merge Request Records for performance review
Code Review Process
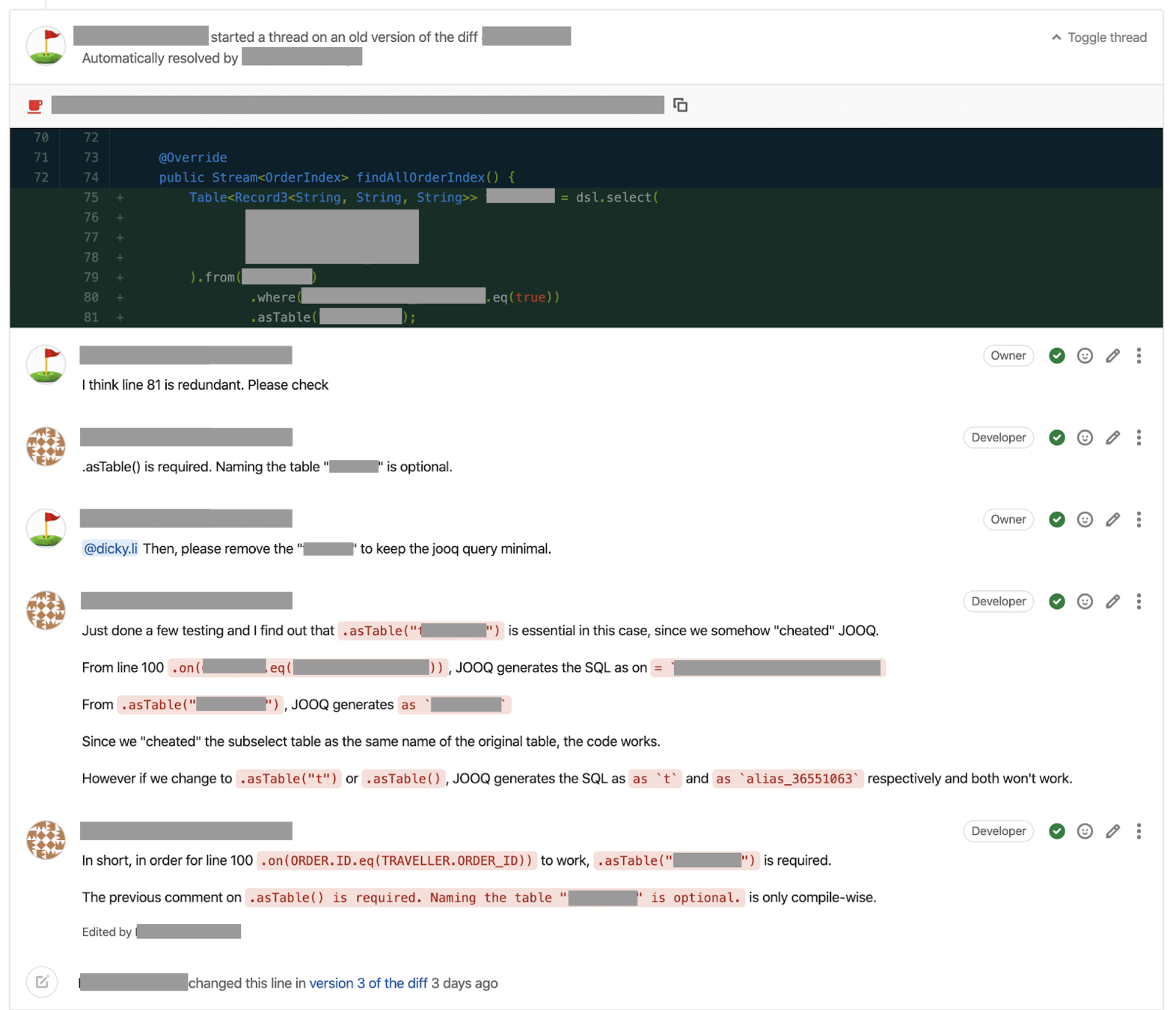
GitLab Flow Explained
Enforce Linear History I
-
Linear history (NOT create merge commit, only allow fast-forward merge)
-
Semi-linear history (create merge commit, only allow fast-forward merge)
-
Non-linear history (Free style)

Linear
Semi-Linear

Non-linear
GitLab Flow Explained
Enforce Linear History II
“Quality always comes with cost”
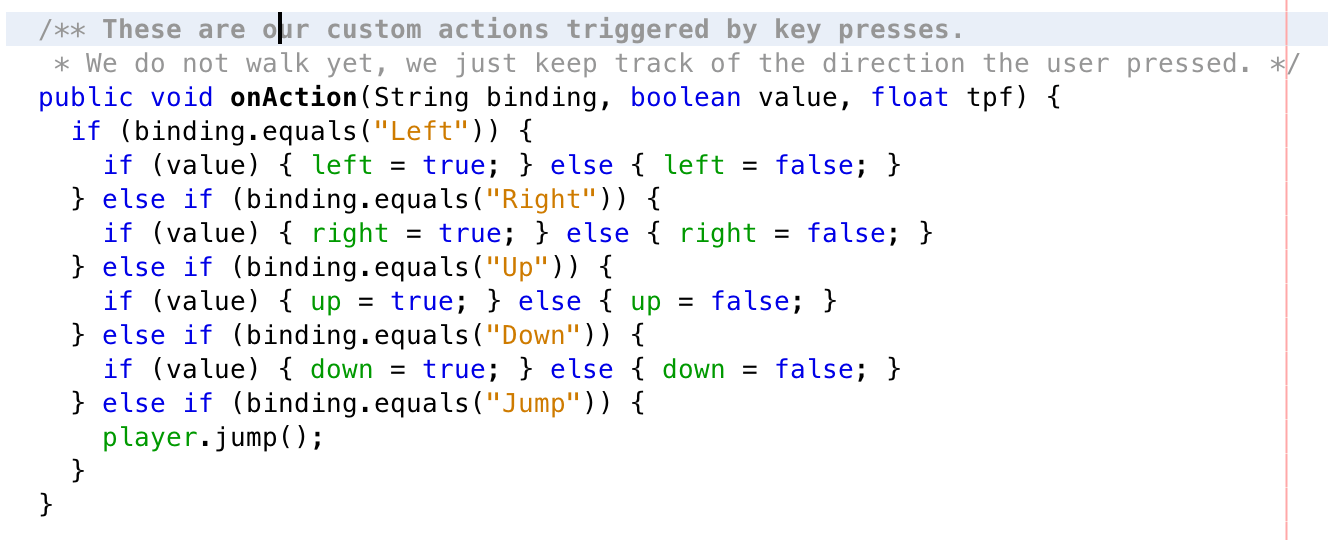
The cost of learning how to achieve fast-forward merge
# Linear. Mostly used commands to achieve fast-forward merge
git pull --rebase
git rebase origin/master
git rebase -i HEAD~2
git cherry-pick bacb7ca8
# Rewrited git history, need force push
git push --force origin some-branch
# Non linear. Mostly used commands
git merge
git pushGitLab Flow Explained
Enforce Linear History III

Settings > General > Merge Requests
GitLab Flow Explained
Enforce Naming Conventions - Branch
Feature branch
{JIRA projectKey}-{JIRA issueId}-{some descriptive wording}
Hotfix branch
{JIRA projectKey}-{JIRA issueId}-hotfix-{some descriptive wording}
Examples
ABC-345-create-registration-api
DEF-25-impl-registration-flow-ui
Examples
ABC-543-hotfix-registration-crash
DEF-478-hotfix-alert-dialog-showing-empty
GitLab Flow Explained
Enforce Naming Conventions - Release Branch & Tag
Release branch
{major}-{minor}-stable
Tag
{major}.{minior}.{patch}-{env}.{build}
Examples
1.0-stable (includes all 1.0.x fix)
1.1-stable (includes all 1.1.x fix)
Examples
1.0.0-prod
1.1.0-alpha.1
1.1.0-uat
GitLab Flow Explained
Upstream First Policy
- Create stable branches using master as a starting point, and branch as late as possible.
- Merge these bug fixes into master, and then cherry-pick them into the release branch
- All bug fixes that applied in release branch must already applied in master
Steps
GitLab Flow Explained
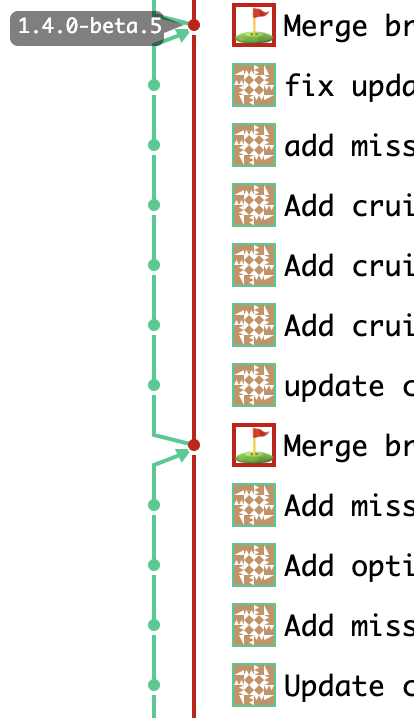
Upstream First Policy
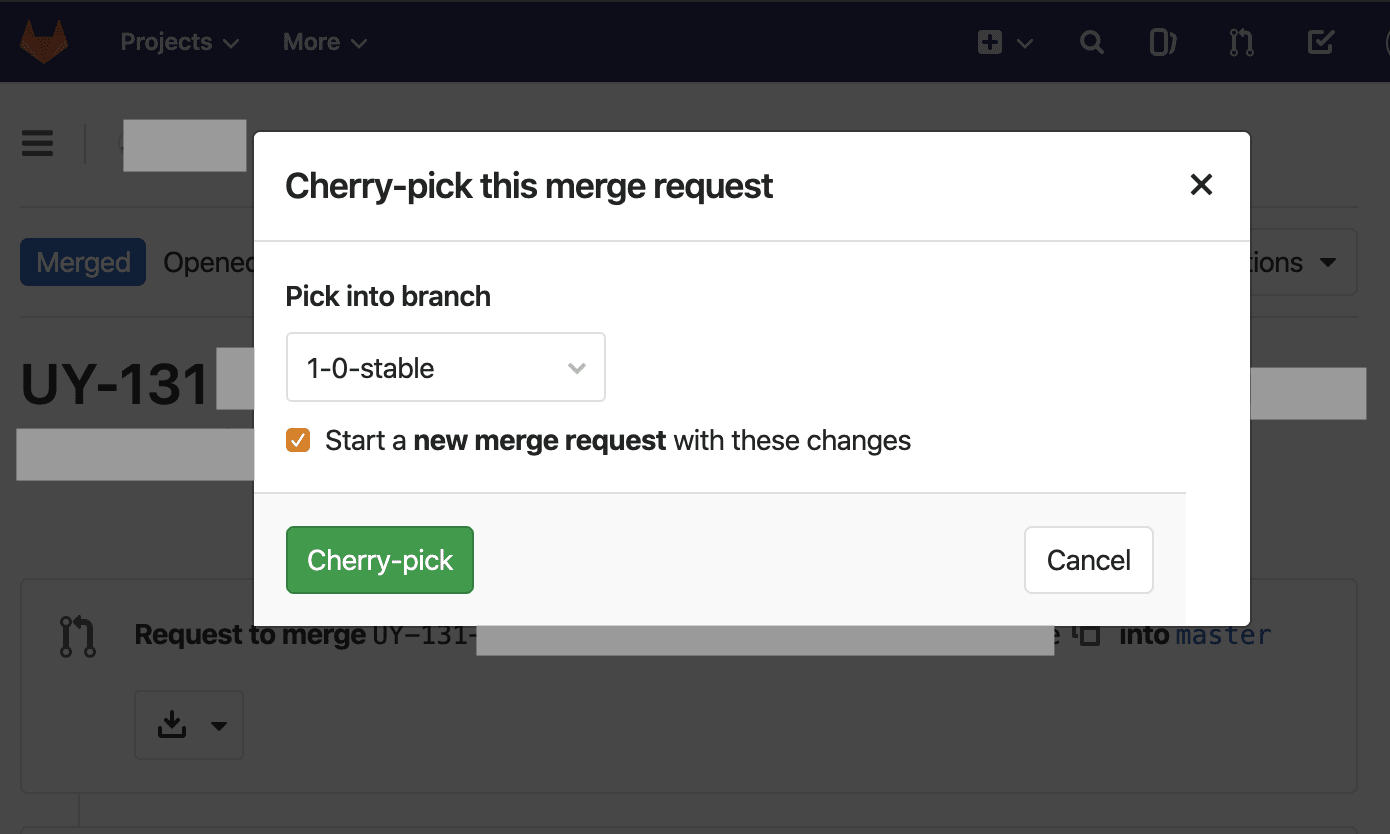
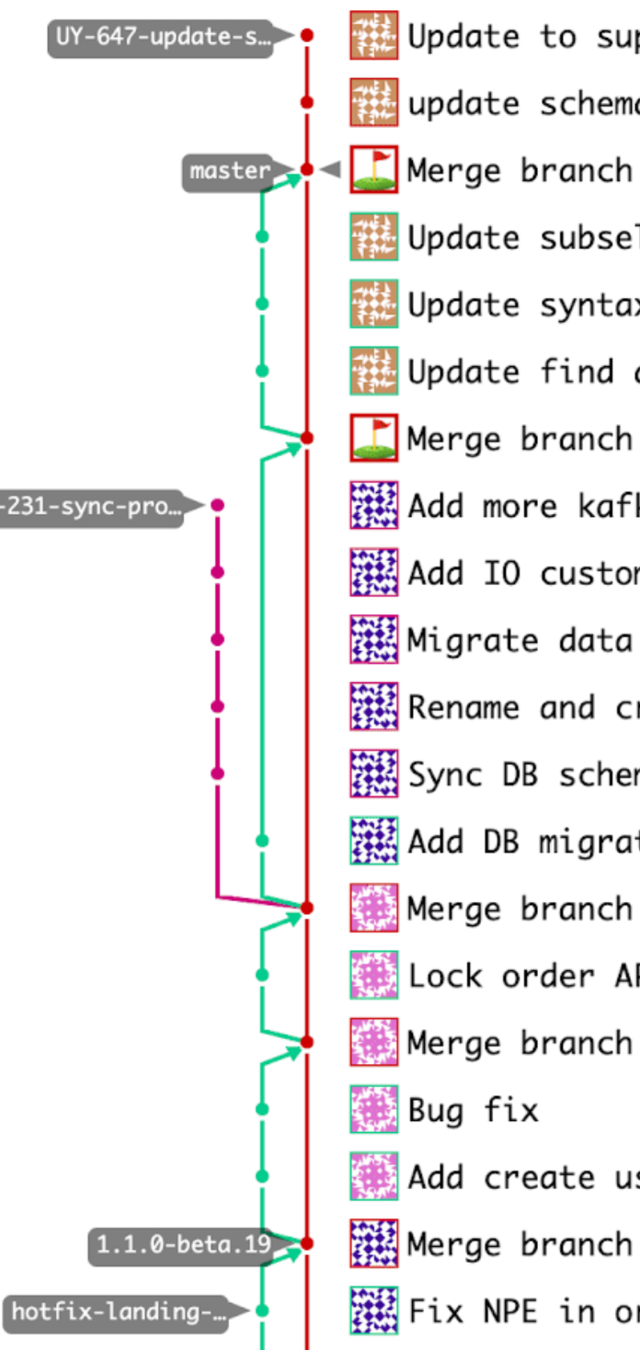
Smooth Workflow to cherry-pick to stable branches
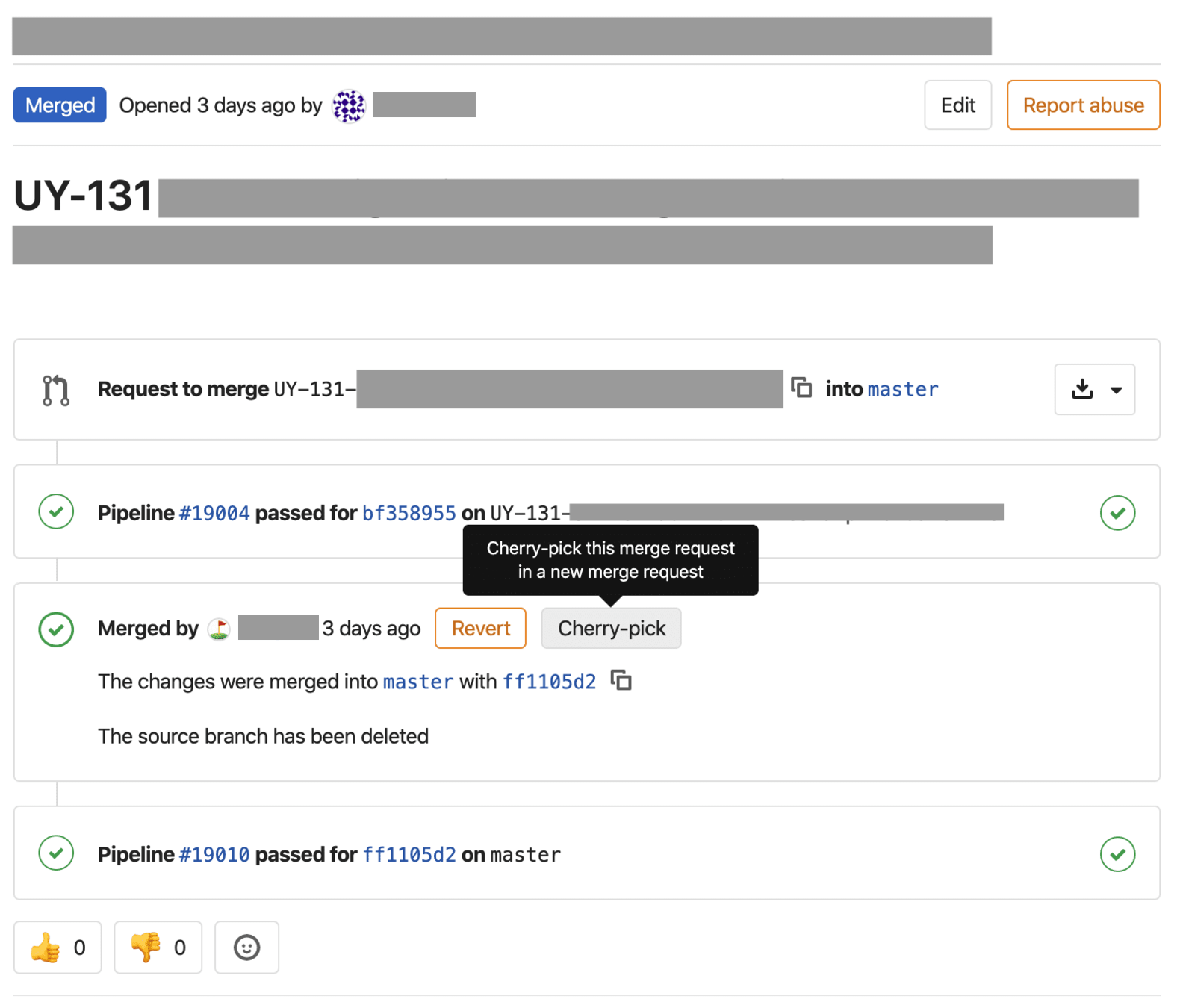
GitLab Flow Explained
Stable Branches and Tag Release I
-
Support preparation of a new production release
-
Only allow for bug fixes and preparing meta-data
-
Tag to Release NOT by branch
GitLab Flow Explained
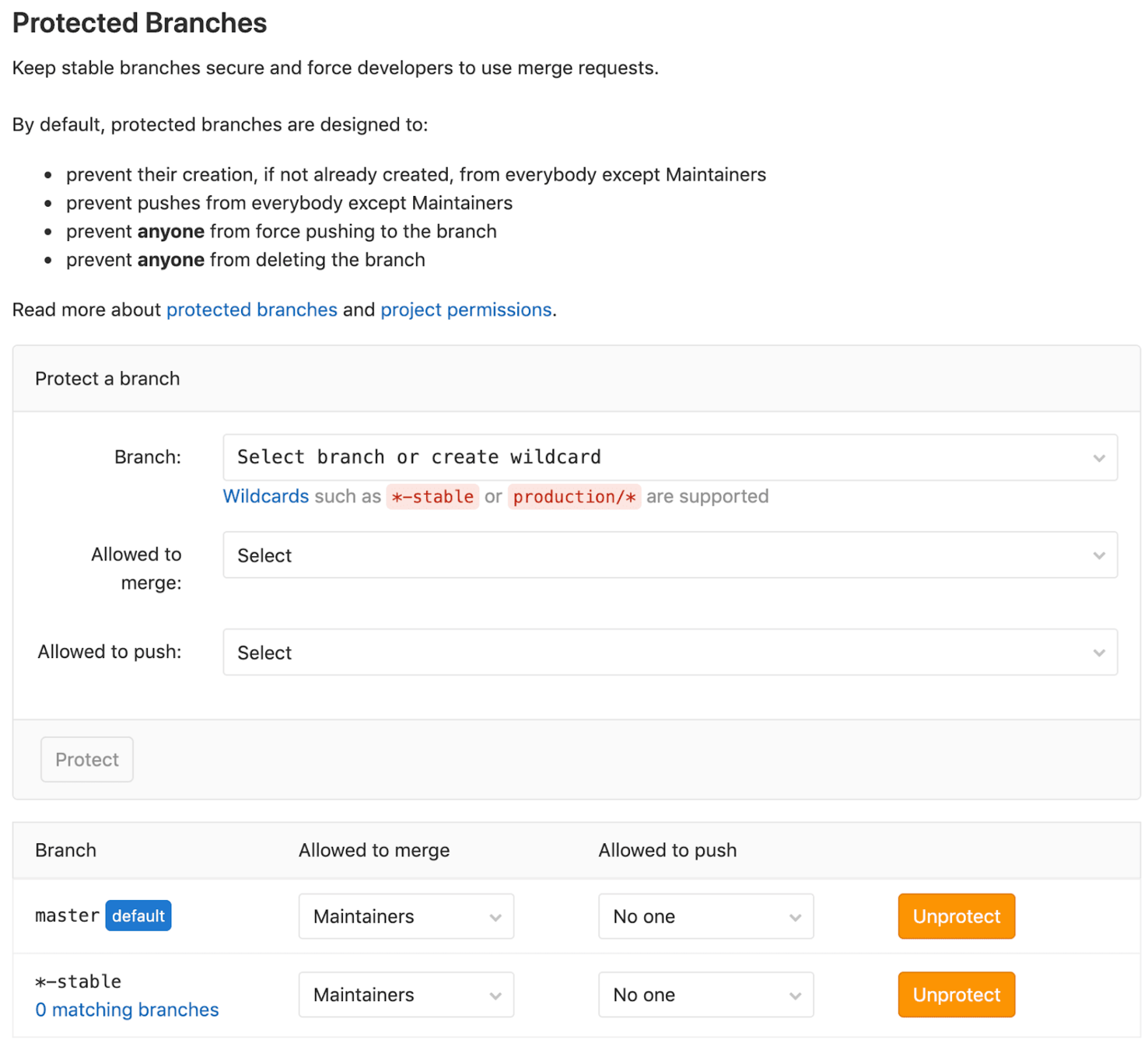
Stable Branches and Tag Release II
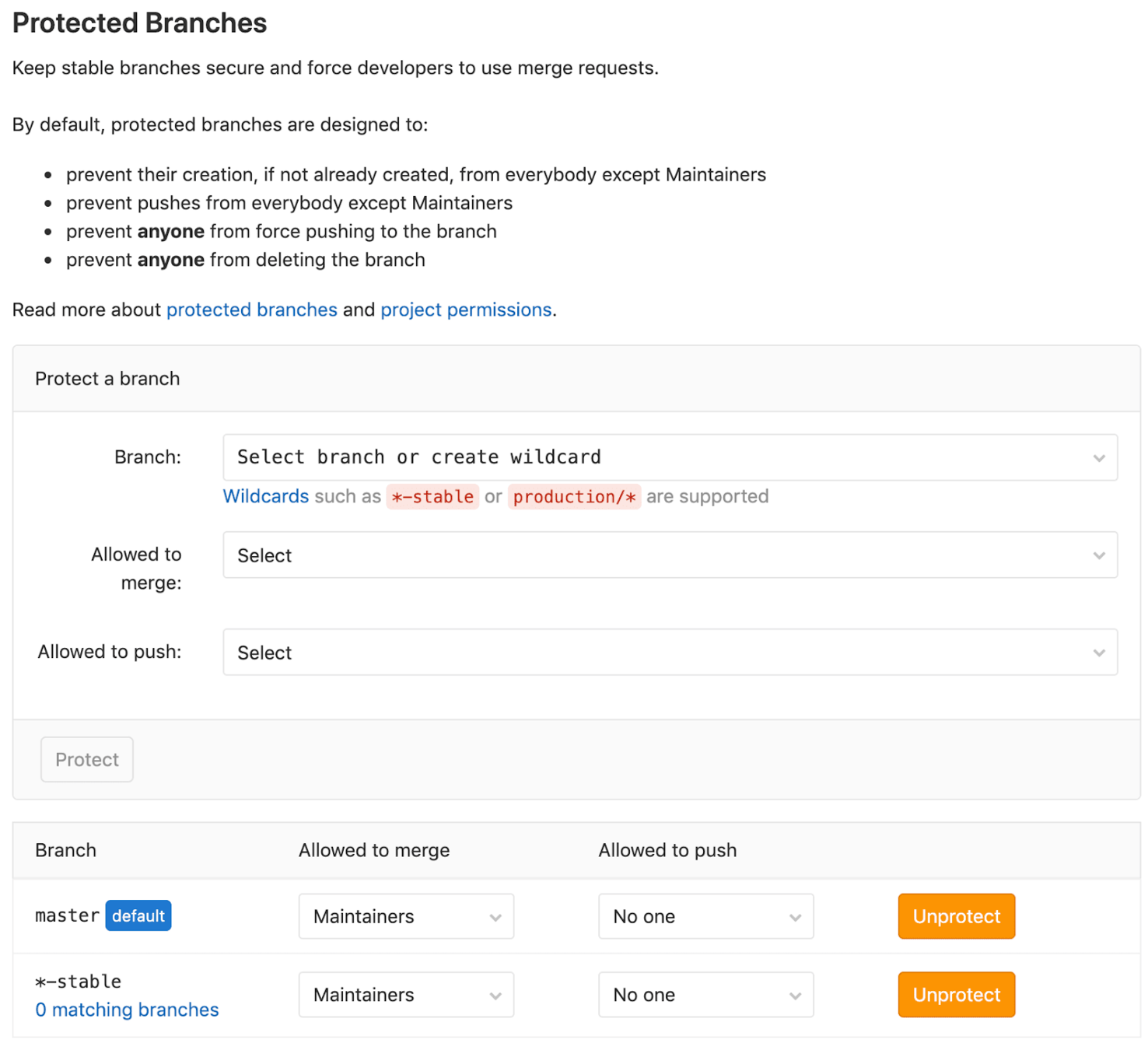
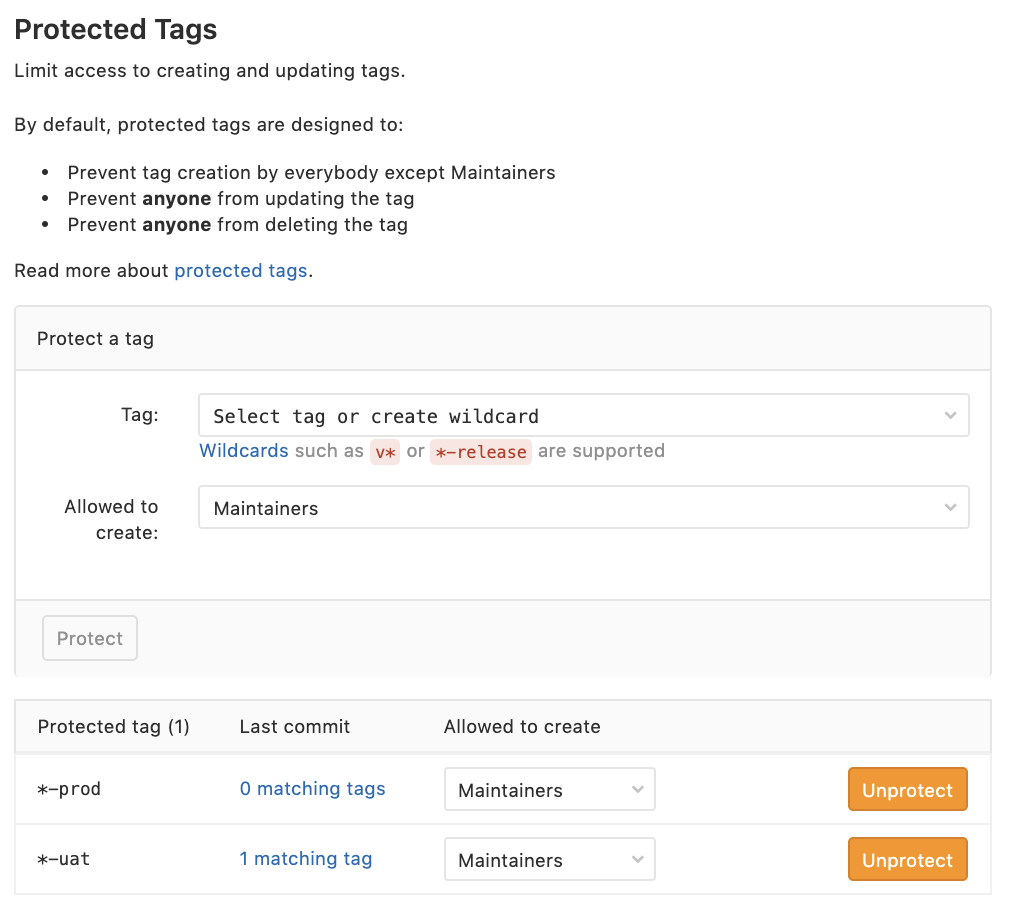
Protected the branch & tag name that ONLY Maintainers to create
GitLab Flow Explained
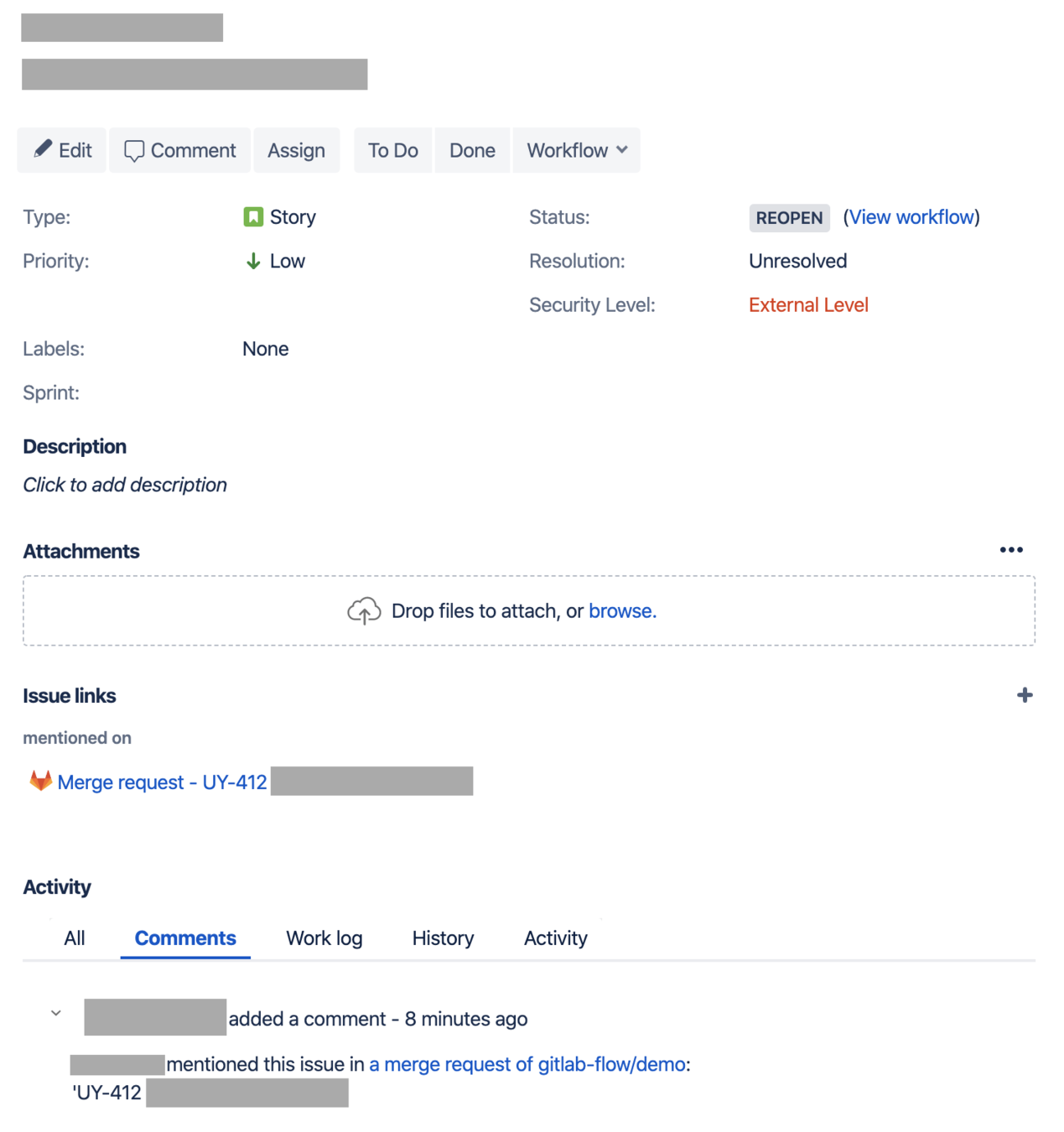
JIRA Integration
- Reduce the Task Reporting overhead
- Instant Jump between in JIRA & GitLab
GitLab
JIRA

GitLab Flow Explained
Core Concepts Recap
- master is always the latest branch, always deployable
- Split *-stable branch from master, NEVER merge back
- Enforce semi-linear git history
- Upstream first policy
- ONLY allow merge request to merge
- Tag to Release (Semantic Versioning)
- Stable Branches
- Enable GitLab - JIRA Integration