ethanol vs ethene
by georgia jarmolkiewicz
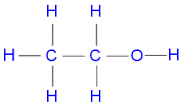
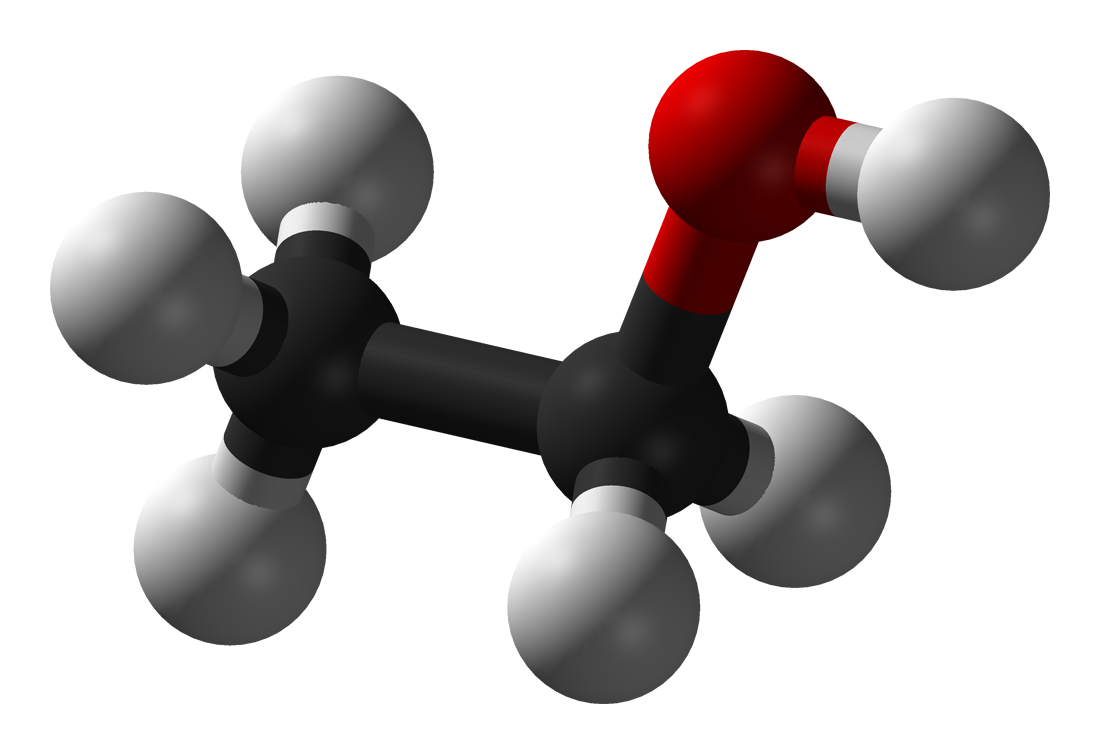
ethanol
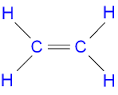
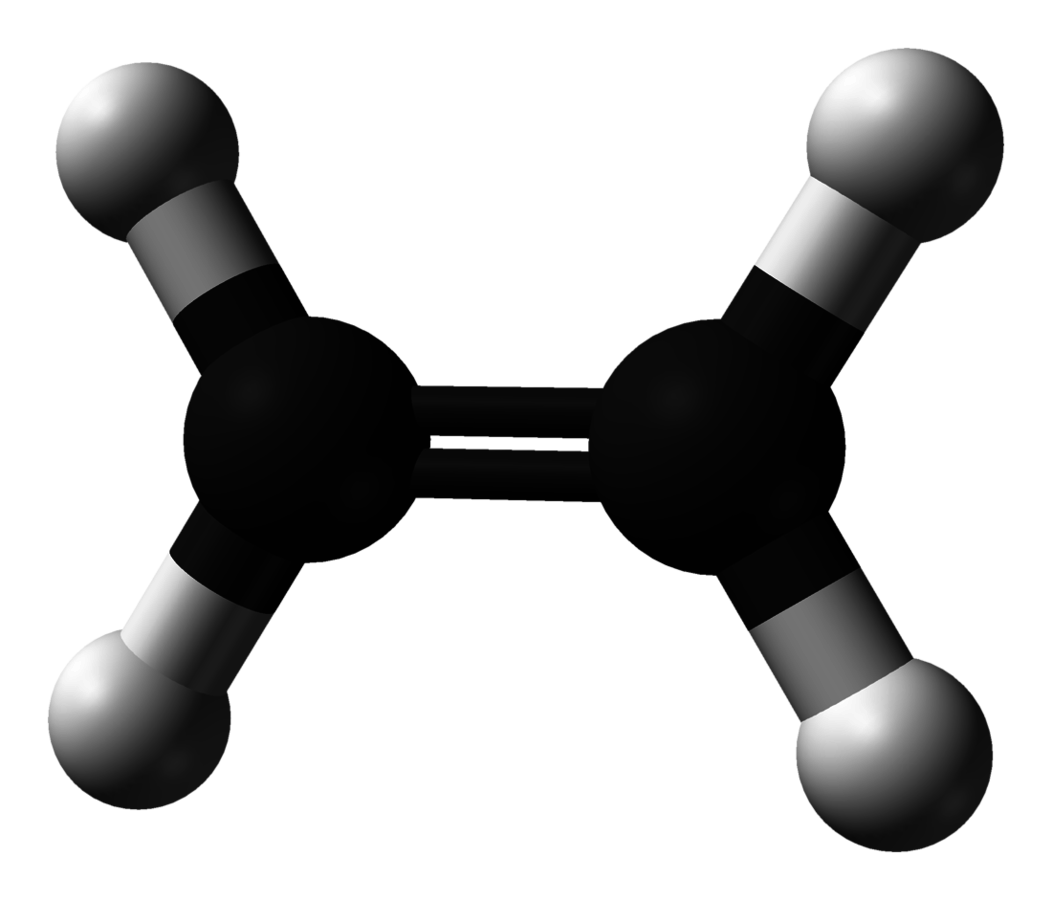
ethene
- colourless gas at room temperature and pressure
- Melting point -169oC
- Boiling point -104oC
- slightly sweet smell
- flammable
- non-polar molecule
- soluble in non-polar solvents & insoluble in polar solvents like water
- reactive: the active site is the double bond
Used in:
Socially
surfactants and detergents
Economically
- polythene production
- polystyrene
- making ethanol
- glass welding
Environmentally
- hastening fruit ripening
- colourless gas at room temperature and pressure
- Melting point -169oC
- Boiling point -104oC
- slightly sweet smell
- flammable
- non-polar molecule
- soluble in non-polar solvents & insoluble in polar solvents like water
- reactive: the active site is the double bond
Used in:
Socially
- drinking alcohol (vodka/rum)
- antitussive agent (pill form)
- dissolving many water-insoluble medications
- cough syrup
- central nervous system depressant, used as a psychoactive drug
- used recreationally for this purpose
- used in glues and paints
Economically
- engine fuel and fuel additive
- rocket fuel
- household heating
- used in glues and paints
Environmentally
- hand wipes and sanitizers
- often abused in its couch syrup, paint, alcohol, or pure drug form for recreation purposes
C2H6O (alkane)
C2H4 (alkene)
ETHANOL






some of Ethanol's uses: antibacterial materials, paint, rocket fuel, cough syrup, and alcohol
ETHENE
some of Ethene's uses: detergents, polystyrene, ethanol, glass welding




bibiography
-
https://ethanol.org/
-
www.ausetute.com.au/ethene.html
-
www.essentialchemicalindustry.org/chemicals/ethene.html
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/ethanol