A brief survey of recent works on microarchitectural defenses against Transient Execution attacks
Gokulan R
March 19 2020
Speculative execution attacks
- Access Phase: Victim accesses secret value, which is stored in some register (storage).
- Transmit Phase: Force victim to execute the wrong path, thereby communicating the secret into a \(\mu\)archstate, which is not reverted.
- Recover Phase: Attacker reads the secret from \(\mu\)archstate and writes to an architectural state.
Spectre v1
Meltdown
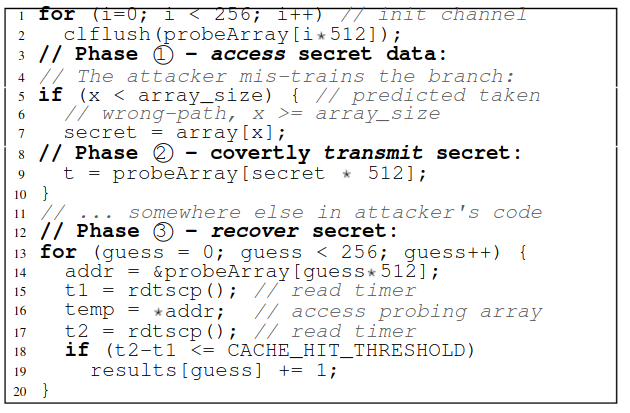

Control Steering attacks
The victim has access to hardware, however, is restricted and might be protected in software.
Eg: Spectre v1
Chosen code attacks
The attacker can generate arbitrary code and mount an attack, using which secret can be retrieved.
Eg: Meltdown
Taxonomy of attacks
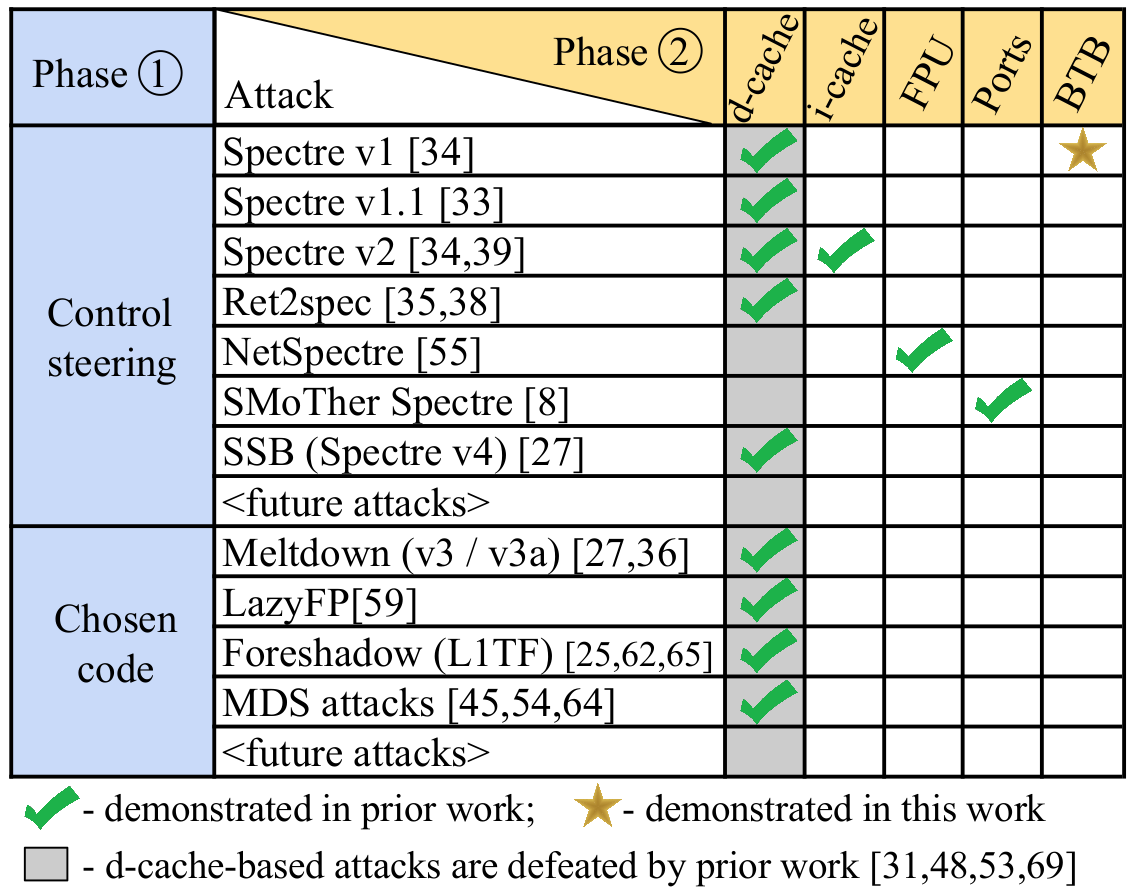
Threat Model
- Leaking memory through control steering
- Leaking GPRs through control steering
- Leaking memory through chosen code
- Leaking GPRs through chosen code -- not possible
Defenses
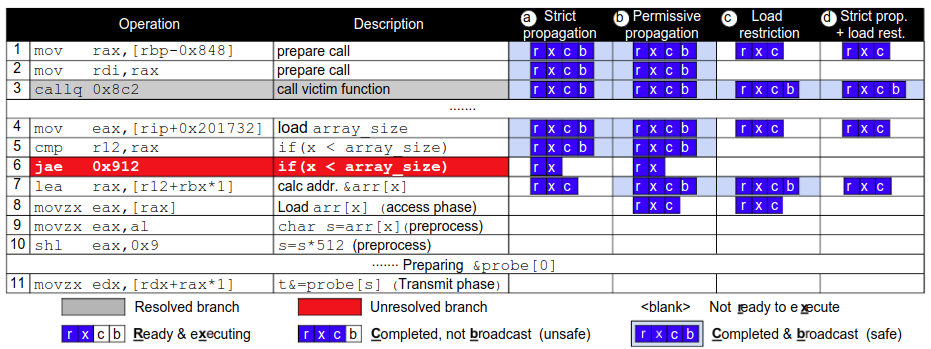
- Strict Propagation: No control or data flow from unsafe instruction
- Permissive Propagation: Only loads are unsafe, arithmetic and control instructions can still execute and broadcast.
- Load Restriction: Loads are considered safe only when they are at the head of ROB.
- Strict Propagation + Load Restriction: Prevents all transient execution attacks
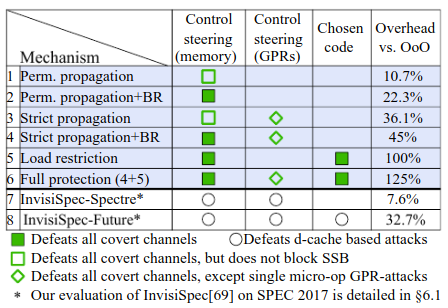
Summary
| Defense | Attacks defeated |
|---|---|
| Strict Propagation | Control Steering |
| Load Restriction | Chosen code |
| Strict Propagation + Load Restriction | Control Steering + Chosen code |
isolating speculative DATA
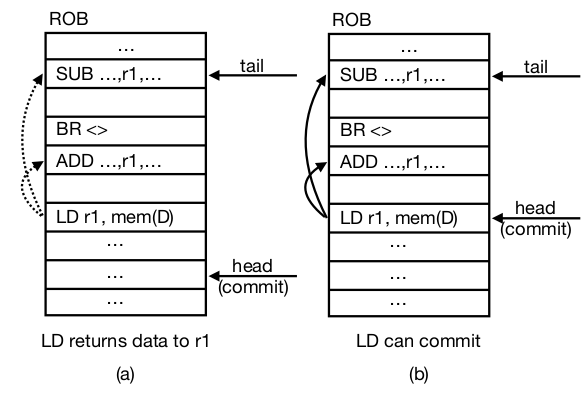
Baseline Naive Approach
isolating speculative DATA
Performance Enhanced Approach
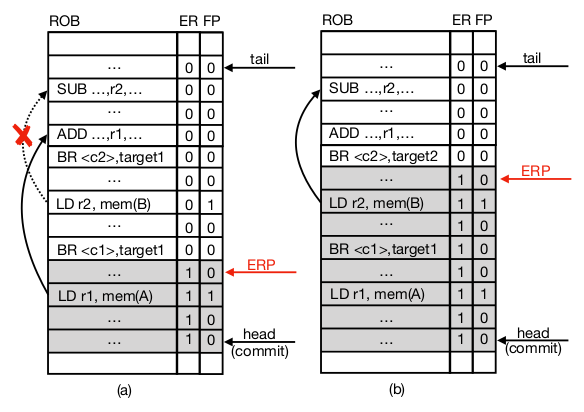
Early Resolution Pointer
Most recent in-flight instruction in the ROB which satisfies all of the following conditions
- All older branches have been resolved
- All address resolutions for older loads and stores completed and TLB translations performed
- No branch misprediction or memory access exception raised by any previous instruction
Performance
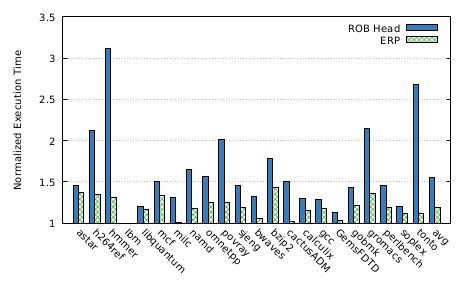
- More performance impact for benchmarks which have low miss rate
- Greater the ROB head -> ERP distance, lesser the performance penalty.
- Overall performance impact
- 55% overhead using naive approach
- 18% overhead using ERP
thank you
Speculative Taint Tracking (STT)
Goal
- Blocking leakage through all covert channels
- Disabling protection as soon as instructions become non-speculative.
Scope of the paper
Protecting leakage of data in which both the access and transmit phase are transiently executed
classification of covert channels
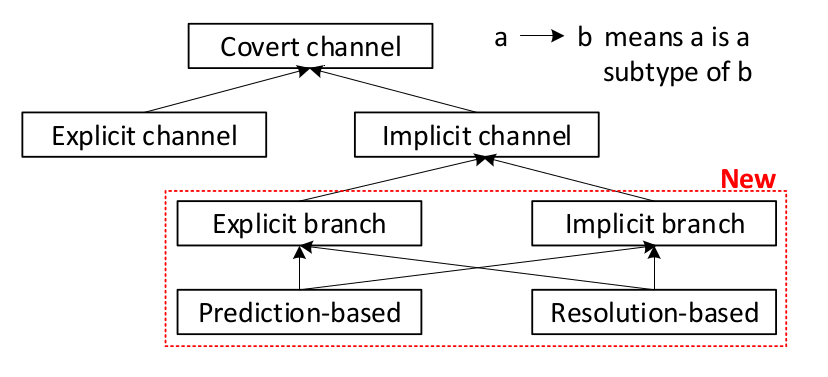
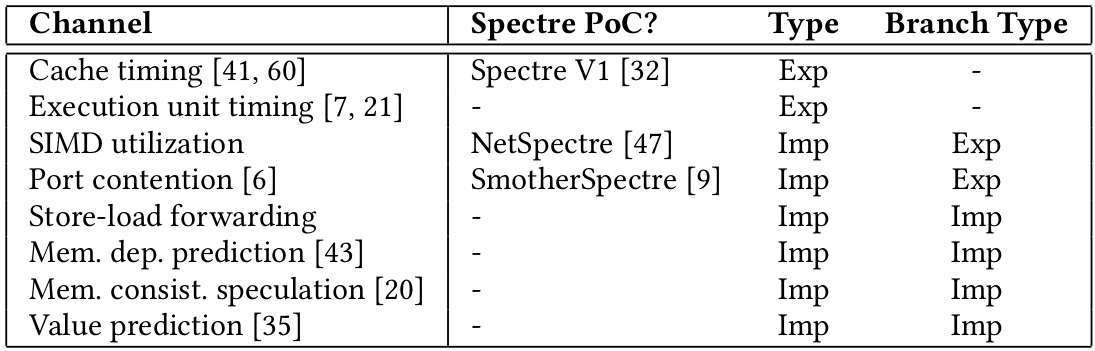
Explicit channel: Secret passed to an instruction, which performs a data-dependent change in the microarchitecture.
Implicit channel: Data indirectly influences instruction execution, changes in resource usage reveal data
Prediction vs resolution based leakage
Prediction based leakage: Instructions fetched after branch prediction but before resolution leak data. Used when predictor is mistrained previously.
Resolution based leakage: Branch resolution can also leak information, even if the predictor is not mistrained.


implicit branch

if (secret == rZ)
rY = rX;
else
rY <- (rZ)Store-Load forwarding covert channel
Speculative taint tracking
- What instructions can leak data? Access instructions. Instructions which can potentially read secret data.
- When can data be untainted? Once an instruction reaches visibility point, once an instruction is safe.
- Who can leak secrets? Transmit instructions. Instructions which can modify the microarchitecture in a data-dependent manner. Form explicit covert channels.
Tainting
- Output register of unsafe instruction is tainted.
- Once instruction becomes safe, the output register is untainted.
- Each instruction is executed only if all operands are untainted.
- Tainting and untaining are propagated along the instruction chain.
Speculative taint tracking
Blocking Explicit Channel
Delays execution of an instruction if any of its input operand is tainted.