Recursion
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
What is recursion
Recursion in computer science is a method where the solution to a problem depends on solutions to smaller instances of the same problem (as opposed to iteration).
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
How to solve a problem
- Divide into small problems.
- Solve small problems.
- Use the result of small problems to solve the original problem.
- If the small problems are the same as original one, just scale is different. Then this is called recursion.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Recursion Properties
- Base case
- simple scenario that does not need recursion to produce an answer.
- Recursion
- a set of rules that reduce all other case toward the base case.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Mathematical Induction
- To prove a given statement
- Base case, to prove the given statement for the first natural number.
- Inductive step, to prove that the given statement for any one natural number implies the given statement for the next natural number.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
- Fibonacci Number
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Base Case: F(0) = 0;
F(1) = 1;
Recursion Rule: F(n) = F(n - 1) + F(n - 2)
Text
// Fibonacci calculation
int Fibonacci (int n) {
//Base Case
if(n == 0) return 0;
if(n == 1) return 1;
//recursion rule
return Fibonacci(n - 1) + Fibonacci(n - 2);
}
f(5)
= f(4) + f(3)
= f(3) + f(2) f(2) + {f(1) = 1}
= f(2) + {f(1) = 1} {f(1)=1} + {f(0)=0} {f(1)=1} + {f(0)=0}
={f(1)=1} + {f(0)=0} Time Complexity
1 2 4 6 8 ... O(2^(n-1))
last layer nodes?
!!!binary search or tree problem BigO
More recursion problems
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Greatest Common Divisor
- How to calculate gcd(111, 259)
- gcd(111, 259) = gcd(111, 259%111) = gcd(111, 37) = gcd(37, 0) = 37
- gcd(x, y), x > y
- y = 0, x
- y != 0, gcd(y, x%y)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Binary Search
- Given sorted array and a target number, find whether the number is in the array.
- Check if the mid one is target, if yes, then found.
- If the mid one is smaller, then try to find the target in the right.
- If the mid one is bigger, then try to find the target in the left.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Towers of Hanoi
- There are three pegs which can hold stacks of disks of different diameters. A larger disk may never be stacked on top of a smaller. Starting with n disks on one peg, they must be moved to another peg one at a time. How to do that?

Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Towers of Hanoi
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Towers of Hanoi
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Towers of Hanoi
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Towers of Hanoi
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Towers of Hanoi
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Towers of Hanoi
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Towers of Hanoi
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Towers of Hanoi
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Towers of Hanoi
-
How to move n disks from A to C
- Move the first disk from A to B
- Move the other (n-1) disk from A to C
- Move the first disk from B to C
1
2
3
4
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Towers of Hanoi
-
How to move n disks from A to C
- Move the first (n-1) disk from A to B
- Move the nth disk from A to C
- Move the other (n-1) disk from B to C
1
2
3
4
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Recursive Definition
- Natural number
- A natural number is either 0 or n+1, where n is a natural number
- Linked List Node
ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
}
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
What's recursion?
Just some special problem solving strategy
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Code problem with recursion
- Base case
- recursion rules
- Represent the problem with coding function.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
How to solve a problem
- Divide into small problems.
- Solve small problems.
- Use the result of small problems to solve the original problem.
- If the small problems are the same as original one, just scale is different. Then this is called recursion.
function solveProblem() {
divide into small problems;
...
...
solveProblem();
}
Most programming languages support recursion by allowing functions to call itself within the program text.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
function tellStory() {
mountain();
temple();
oldMonk();
tellStory();
}
从前有个山,
山里有个庙,
庙里有个老和尚,
老和尚在给小和尚讲故事,
从前有个山...
讲故事
Old Monk Tells Story
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
function factorial(int n) {
int m = factorial(n-1);
return m*n;
}
Factorial of n
- calculate factorial of (n-1),mark the result as m.
- the factorial of n would be m*n
Factorial of n
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
function factorial(int n) {
if (n==1) return 1;
int m = factorial(n-1);
return m*n;
}
Factorial of n
- If n is 1, the factorial is 1.
- calculate factorial of (n-1),mark the result as m.
- the factorial of n would be m*n
Factorial of n
function factorial(int n) {
if (n==1) return 1;
return m * factorial(n-1);
}
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
function fibo(int n) {
if (n == 1) return 1;
if (n == 2) return 1;
return fibo(n-1) + fibo(n-2);
}
nth fibonacci number
- If n is 1, then the number is 1.
- If n is 2, then the number is 1.
The nth Fibonacci Number
1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, ...
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Code problem with recursion
- Base case
- recursion rules
-
Represent the problem with coding function.
-
Define the essential parameters
- Parameters that define the problem.
- Define the return value
-
Define the essential parameters
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Climb Building
- 1 stair left, one way.
- 2 stairs left, two ways.
- n stairs left,
- climb one stair first, climb the (n-1) later.
- climb two stairs first, climb the (n-2) later.
There is a building with n stairs, one person can climb 1 or 2 stairs at one time, then how many different ways there are for this person to climb to the top.
public static int climb(int n) {
if (n <= 2) return n;
return climb(n-1) + climb(n-2);
}
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Code problem with recursion
- Base case
- recursion rules
-
Represent the problem with coding function.
-
Define the essential parameters
- Parameters that define the problem.
- Parameters that store the temporary result or state.
- Define the return value
-
Define the essential parameters
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Climb Building
There is a building with n stairs, one person can climb 1 or 2 stairs at one time. Print all the possible ways to climb to the top.
public static void climb(int n, String preWay) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println(preWay + " 1");
return;
}
if (n == 2) {
System.out.println(preWay + " 2");
System.out.println(preWay + " 1 1");
return;
}
String preWay1 = preWay + " 1";
climb(n-1, preWay1);
String preWay2 = preWay + " 2";
climb(n-2, preWay2);
}
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Towers of Hanoi
- Move the first (n-1) disk from A to B
- Move the nth disk from A to C
- Move the other (n-1) disk from B to C
How many steps we need to move all n disks from A to C.
public static int hanoi(int n) {
if (n == 1) return 1;
return hanoi(n-1) + 1 + hanoi(n-1);
}
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Towers of Hanoi
- Move the first (n-1) disk from A to B
- Move the nth disk from A to C
- Move the other (n-1) disk from B to C
How many steps we need to move all n disks from A to C.
public static int hanoi(int n) {
if (n == 1) return 1;
return 2 * hanoi(n-1) + 1;
}
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Towers of Hanoi
- Move the first (n-1) disk from A to B
- Move the nth disk from A to C
- Move the other (n-1) disk from B to C
Print all the steps that is needed to move all n disks from A to C.
public static void hanoi(int n, char source, char spare, char target) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println("Move " + source + " to " + target);
return;
}
hanoi(n-1, source, target, spare);
System.out.println("Move " + source + " to " + target);
hanoi(n-1, spare, source, target);
}
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Towers of Hanoi
- Move the first (n-1) disk from A to B
- Move the nth disk from A to C
- Move the other (n-1) disk from B to C
Print all the steps that is needed to move all n disks from A to C.
public static void hanoi(int n, char source, char spare, char target) {
if (n > 0) {
hanoi(n-1, source, target, spare);
System.out.println("Move " + source + " to " + target);
hanoi(n-1, spare, source, target);
}
}
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Sum of Linked List
- If the list is empty, sum is zero.
- Calculate the sum of linked list from head.next.
- The final sum would be head.val and partial sum.
Calculate the sum of all nodes in a linked list.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Sum of Linked List
- If the list is empty, sum is zero.
- Calculate the sum of linked list from head.next.
- The final sum would be head.val and partial sum.
Calculate the sum of all nodes in a linked list.
public static int sum(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return 0;
return head.val + sum(head.next);
}
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Remove Linked List Elements
- If the head is null, nothing needs to be done.
- Remove elements in linked list from head.next, store as newHead.
- If value of head node is val, then remove head.
- Otherwise link the newHead to head.
Remove all elements from a linked list of integers that have value val.
public static ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) return null;
ListNode newHead = removeElements(head.next, val);
if (head.val == val) {
return newHead;
} else {
head.next = newHead;
return head;
}
}
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Problem
sub-problem-1
sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-sub-problem
base-problem
Problem
sub-problem-1
base-problem
sub-problem-2
sub-problem-3
sub-sub-problem-2
sub-sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-problem-1
...
...
...
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Problem
sub-problem-1
sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-sub-problem
base-problem
Problem
sub-problem-1
base-problem
sub-problem-2
sub-problem-3
sub-sub-problem-2
sub-sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-problem-1
...
...
...
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Problem
sub-problem-1
sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-sub-problem
base-problem
Problem
sub-problem-1
base-problem
sub-problem-2
sub-problem-3
sub-sub-problem-2
sub-sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-problem-1
...
...
...
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Problem
sub-problem-1
sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-sub-problem
base-problem
Problem
sub-problem-1
base-problem
sub-problem-2
sub-problem-3
sub-sub-problem-2
sub-sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-problem-1
...
...
...
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Problem
sub-problem-1
sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-sub-problem
base-problem
Problem
sub-problem-1
base-problem
sub-problem-2
sub-problem-3
sub-sub-problem-2
sub-sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-problem-1
...
...
...
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Problem
sub-problem-1
sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-sub-problem
base-problem
Problem
sub-problem-1
sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-sub-problem
base-problem
Problem
sub-problem-1
base-problem
sub-problem-2
sub-problem-3
sub-sub-problem-2
sub-sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-problem-1
...
...
...
Backtracking
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
14
0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
14, 8
0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
14, 8, 7
0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
14, 7, 5
0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
14, 5, 3
0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
14, 5, 3, 8
0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
8, 7
0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
8, 7, 5
0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
Given an item, just two options:
- pick it, the problem become (s-w[i], w - w[i])
- not pick it, the problem become (s, w - w[i])
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
public static boolean knapsack(int s, int[] weights, int index) {
if (s == 0) {
return true;
}
if (s < 0 || index >= weights.length) {
return false;
}
return knapsack(s - weights[index], weights, index+1) ||
knapsack(s, weights, index+1);
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
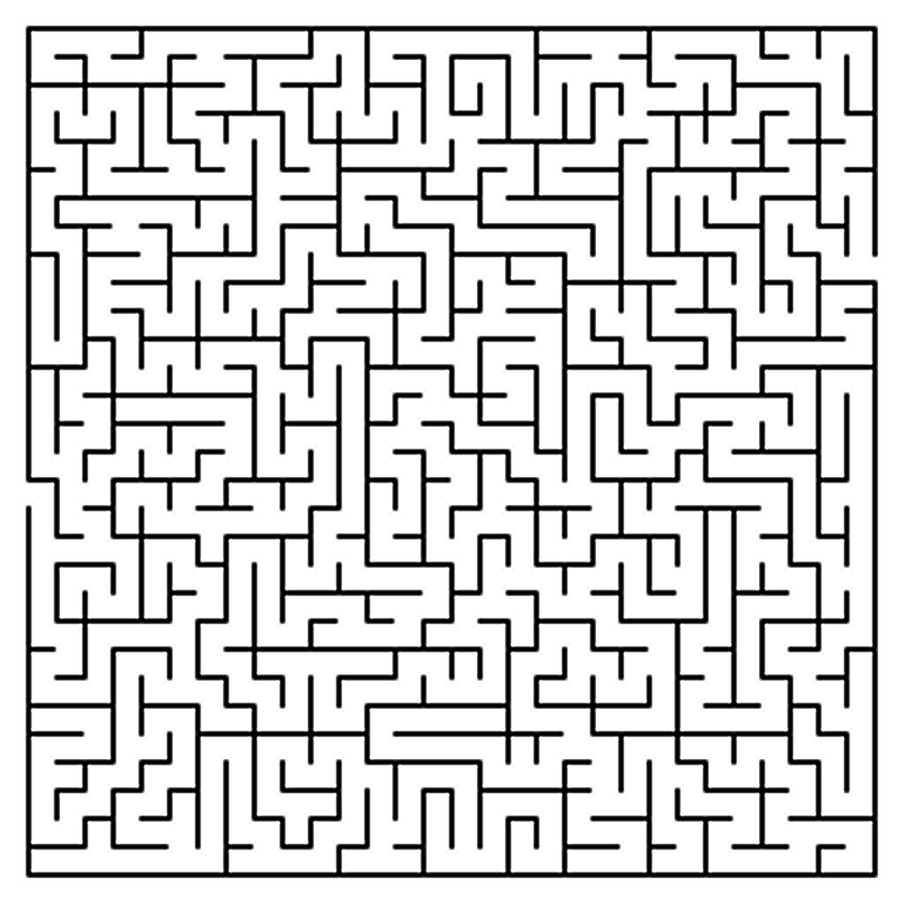
Maze
Given a maze and a start point and a target point, return whether the target can be reached.
Example Input:
Start Point: (0, 0); Target Point (5, 5);
Maze: char[][] = {
{'.', 'X', '.', '.', '.', 'X'},
{'.', '.', '.', 'X', '.', 'X'},
{'X', 'X', '.', 'X', '.', '.'},
{'.', 'X', 'X', 'X', '.', 'X'},
{'.', '.', '.', '.', '.', 'X'},
{'.', '.', '.', '.', '.', '.'}
}
Example Output: True
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Maze
Given a maze and a start point and a target point, return whether the target can be reached.
Example Input:
Start Point: (0, 0); Target Point (5, 5);
Maze: char[][] = {
{'.', 'X', '.', '.', '.', 'X'},
{'.', '.', '.', 'X', '.', 'X'},
{'X', 'X', '.', 'X', '.', '.'},
{'.', 'X', 'X', 'X', '.', 'X'},
{'.', '.', '.', '.', '.', 'X'},
{'.', '.', '.', '.', '.', '.'}
}
Example Output: True
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Maze
Given a maze and a start point and a target point, return whether the target can be reached.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
- Out of Bound
- Wall
Maze
Given a maze and a start point and a target point, return whether the target can be reached.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
- Out of Bound
- Wall
-
Visited
- (1, 2) -> (2, 2) -> (1, 2) -> (2, 2) -> ...
Maze
Given a maze and a start point and a target point, return whether the target can be reached.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Maze
Given a maze and a start point and a target point, return whether the target can be reached.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public static boolean solveMaze(char[][] maze,
int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY,
boolean[][] visited) {
if (startX < 0 || startX >= maze.length ||
startY < 0 || startY >= maze[0].length ||
maze[startX][startY] == 'X' || visited[startX][startY]) {
return false;
}
if (startX == targetX && startY == targetY) {
return true;
}
visited[startX][startY] = true;
if (solveMaze(maze, startX + 1, startY, targetX, targetY, visited) ||
solveMaze(maze, startX, startY + 1, targetX, targetY, visited) ||
solveMaze(maze, startX - 1, startY, targetX, targetY, visited) ||
solveMaze(maze, startX, startY - 1, targetX, targetY, visited)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}Maze
Given a maze and a start point and a target point, return whether the target can be reached.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public static boolean solveMaze(char[][] maze,
int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY) {
if (startX < 0 || startX >= maze.length ||
startY < 0 || startY >= maze[0].length ||
maze[startX][startY] == 'X') {
return false;
}
if (startX == targetX && startY == targetY) {
return true;
}
maze[startX][startY] = 'X';
if (solveMaze(maze, startX + 1, startY, targetX, targetY) ||
solveMaze(maze, startX, startY + 1, targetX, targetY) ||
solveMaze(maze, startX - 1, startY, targetX, targetY) ||
solveMaze(maze, startX, startY - 1, targetX, targetY)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}Maze
Given a maze and a start point and a target point, return whether the target can be reached.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public static boolean solveMaze(char[][] maze,
int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY) {
if (startX < 0 || startX >= maze.length ||
startY < 0 || startY >= maze[0].length ||
maze[startX][startY] == 'X') {
return false;
}
if (startX == targetX && startY == targetY) {
return true;
}
maze[startX][startY] = 'X';
int[] dx = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if (solveMaze(maze, startX + dx[i], startY + dy[i], targetX, targetY)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}Maze
Given a maze and a start point and a target point, return whether the target can be reached.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public static boolean solveMaze(char[][] maze,
int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY) {
if (startX == targetX && startY == targetY) {
return true;
}
maze[startX][startY] = 'X';
int[] dx = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newX = startX + dx[i], newY = startY + dy[i];
if (newX < 0 || newX >= maze.length || newY < 0 || newY >= maze.length ||
maze[newX][newY] == 'X') {
continue;
}
if (solveMaze(maze, newX, newY, targetX, targetY)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}Maze
Given a maze and a start point and a target point, return whether the target can be reached.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public static boolean solveMaze(char[][] maze,
int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY,
String path) {
if (startX < 0 || startX >= maze.length ||
startY < 0 || startY >= maze[0].length ||
maze[startX][startY] == 'X') {
return false;
}
if (startX == targetX && startY == targetY) {
System.out.println(path);
return true;
}
maze[startX][startY] = 'X';
int[] dx = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
char[] direction = {'D', 'R', 'U', 'L'};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
String newPath = path + direction[i] + " ";
if (solveMaze(maze, startX+dx[i], startY+dy[i], targetX, targetY, newPath)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}Maze
Given a maze and a start point and a target point, print out the path to reach the target.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public static boolean solveMaze(char[][] maze,
int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY,
ArrayList<Character> path) {
if (startX < 0 || startX >= maze.length ||
startY < 0 || startY >= maze[0].length ||
maze[startX][startY] == 'X') {
return false;
}
if (startX == targetX && startY == targetY) {
return true;
}
maze[startX][startY] = 'X';
int[] dx = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
char[] direction = {'D', 'R', 'U', 'L'};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
path.add(direction[i]);
if (solveMaze(maze, startX+dx[i], startY+dy[i], targetX, targetY, path)) {
return true;
}
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
return false;
}Maze
Given a maze and a start point and a target point, return the path to reach the target.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
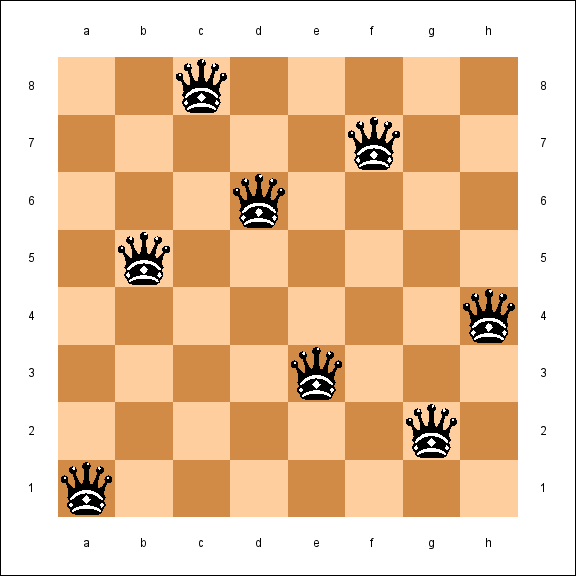
..Q.....
.....Q..
...Q....
.Q......
.......Q
....Q...
......Q.
Q.......
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
| Q | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | X | ||||
| X | X | X | X | ||||
| X | X | X | X | X | |||
| X | X | X | X | X | X | Q | X |
| X | X | X | X | ||||
| X | X | X | |||||
| X | X | X | X |
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
| X | Q | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | |||||
| X | X | ||||||
| X | X | ||||||
| X | X | ||||||
| X | X | ||||||
| X | X | ||||||
| X |
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
| X | Q | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | Q | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | ||||
| X | X | X | X | ||||
| X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| X | X | X | |||||
| X | X | X | |||||
| X | X |
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
| X | Q | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | Q | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | Q | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | |||
| X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| X | X | X | X | X | |||
| X | X | X | X | X | |||
| X | X | X | X |
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
| X | Q | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | Q | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | Q | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Q |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| X | X | X | X | X |
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
| X | Q | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | Q | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | Q | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Q |
| X | X | Q | X | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| X | X | X | X | X | X |
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
| X | Q | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | Q | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | Q | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Q |
| X | X | Q | X | X | X | X | X |
| Q | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| X | X | X | X | X | X |
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
| X | Q | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | Q | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | Q | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Q |
| X | X | Q | X | X | X | X | X |
| Q | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | Q | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
| X | Q | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | Q | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | Q | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Q |
| X | X | Q | X | X | X | X | X |
| Q | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | Q | X |
| X | X | X | X | Q | X | X | X |
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
void putQueens(char[][] board, int row,
List<List<String>> results) {
if (row == board.length) {
saveResult(board, results);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < board[0].length; col++) {
if (isLegal(board, row, col)) {
board[row][col] = 'Q';
putQueens(board, row+1, results);
board[row][col] = '.';
}
}
return;
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
void saveResult(char[][] board,
List<List<String>> results) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
result.add(new String(board[i]));
}
results.add(result);
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
boolean isLegal(char[][] board, int row, int col) {
for (int i = row-1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (board[i][col] == 'Q')
return false;
int tempCol = col - row + i;
if (tempCol >= 0 &&
tempCol < board.length &&
board[i][tempCol] == 'Q')
return false;
tempCol = col + row - i;
if (tempCol >= 0 &&
tempCol < board.length &&
board[i][tempCol] == 'Q')
return false;
}
return true;
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<List<String>> results = new ArrayList<>();
char[][] board = new char[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
board[i][j] = '.';
}
}
putQueens(board, 0, results);
return results;
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<List<String>> results = new ArrayList<>();
char[][] board = new char[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
board[i][j] = '.';
}
}
putQueens(board, 0, results);
return results;
}
void putQueens(char[][] board, int row, List<List<String>> results) {
if (row == board.length) {
saveResult(board, results);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < board[0].length; col++) {
if (isLegal(board, row, col)) {
board[row][col] = 'Q';
putQueens(board, row+1, results);
board[row][col] = '.';
}
}
return;
}
void saveResult(char[][] board, List<List<String>> results) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
result.add(new String(board[i]));
}
results.add(result);
}
boolean isLegal(char[][] board, int row, int col) {
for (int i = row-1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (board[i][col] == 'Q')
return false;
int tempCol = col - row + i;
if (tempCol >= 0 && tempCol < board.length && board[i][tempCol] == 'Q')
return false;
tempCol = col + row - i;
if (tempCol >= 0 && tempCol < board.length && board[i][tempCol] == 'Q')
return false;
}
return true;
}Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
-
We don't need a char[][] to store the board
- int[] will be enough
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<List<String>> results = new ArrayList<>();
int[] board = new int[n];
putQueens(board, 0, results);
return results;
}
void putQueens(int[] board, int row, List<List<String>> results) {
if (row == board.length) {
saveResult(board, results);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < board.length; col++) {
if (isLegal(board, row, col)) {
board[row] = col;
putQueens(board, row+1, results);
}
}
return;
}
boolean isLegal(int[] board, int row, int col) {
for (int i = row-1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (board[i] == col || Math.abs(board[i] - col) == Math.abs(row - i)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void saveResult(int[] board, List<List<String>> results) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
StringBuilder oneLine = new StringBuilder();
for (int j = 0; j < board.length; j++) {
if (j == board[i]) {
oneLine.append('Q');
} else {
oneLine.append('.');
}
}
result.add(oneLine.toString());
}
results.add(result);
}Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
public int totalNQueens(int n) {
int upper = (1 << n) -1;
int[] count = {0};
queen(0, 0, 0, upper, count);
return count[0];
}
public void queen(int row, int ld, int rd, int upper, int[] count) {
if (row != upper) {
int pos = upper & (~(row | ld | rd));
while (pos != 0) {
int p = pos & (-pos);
pos -= p;
queen(row+p, (ld+p) << 1, (rd+p) >> 1, upper, count);
}
} else {
count[0]++;
}
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Backtracking Summary
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
- Backtrack = try, iterate, traverse, etc.
- Keep trying (in the search space) until
- Solution is found
- No more meaningful methods to try (no more search space)
- Level-N problem -> M * Level-(N-1) subproblem
- Keep states the same when entering subproblem except shared fields.
Knapsack
Given a set of candidate numbers (C) and a target number (T), find all unique combinations in C where the candidate numbers sums to T.
All candidate numbers are unique.
The same repeated number may be chosen from C unlimited number of times.
Note:
- All numbers (including target) will be positive integers.
- Elements in a combination (a1, a2, … , ak) must be in non-descending order. (ie, a1 ≤ a2 ≤ … ≤ ak).
- The solution set must not contain duplicate combinations.
Example Input: [7], [2, 3, 6, 7]
Example Output: [[2, 2, 3], [7]]
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Knapsack
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Define the problem as (C, i, T), then given a number
- Pick => (C, i, T-C[i])
- Not Pick => (C, i+1, T-C[i])
Given a set of candidate numbers (C) and a target number (T), find all unique combinations in C where the candidate numbers sums to T.
All candidate numbers are unique.
The same repeated number may be chosen from C unlimited number of times.
Knapsack
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> knapsack(int[] candidates,
int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
ArrayList<Integer> cur = new ArrayList<Integer>();
knapsack(candidates, 0, target, results, cur);
return results;
}
public static void knapsack(int[] candidates, int index, int target,
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> results,
ArrayList<Integer> cur) {
if (target < 0 || (target != 0 && index == candidates.length)) {
return;
}
if (target == 0) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(cur));
return;
}
cur.add(candidates[index]);
knapsack(candidates, index, target-candidates[index], results, cur);
cur.remove(cur.size()-1);
knapsack(candidates, index+1, target, results, cur);
}Given a set of candidate numbers (C) and a target number (T), find all unique combinations in C where the candidate numbers sums to T.
Knapsack
Given a set of candidate numbers (C) and a target number (T), find all unique combinations in C where the candidate numbers sums to T.
All candidate numbers are unique.
The same repeated number may be chosen from C unlimited number of times.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Iterate all numbers to decide whether to pick the current number.
<=>
Which one of the numbers should I pick as the smallest one in the current set.
Knapsack
Given a set of candidate numbers (C) and a target number (T), find all unique combinations in C where the candidate numbers sums to T.
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> knapsack(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
ArrayList<Integer> cur = new ArrayList<Integer>();
knapsack(candidates, 0, target, results, cur);
return results;
}
public void knapsack(int[] candidates, int index, int target,
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> results,
ArrayList<Integer> cur) {
if (target < 0) {
return;
}
if (target == 0) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(cur));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++) {
cur.add(candidates[i]);
knapsack(candidates, i, target-candidates[i], results, cur);
cur.remove(cur.size()-1);
}
return;
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Knapsack II
Given a collection of candidate numbers (C) and a target number (T), find all unique combinations in C where the candidate numbers sums to T.
Candidate numbers may contain duplicate.
Each number in C may only be used once in the combination.
public List<List<Integer>> knapsack(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList<Integer>();
knapsack(candidates, 0, target, results, cur);
return results;
}
public void knapsack(int[] candidates, int index, int target,
List<List<Integer>> results, List<Integer> cur) {
if (target < 0) return;
if (target == 0) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(cur));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++) {
cur.add(candidates[i]);
knapsack(candidates, i+1, target-candidates[i], results, cur);
cur.remove(cur.size()-1);
while (i < candidates.length-1 && candidates[i] == candidates[i+1]) i++;
}
return;
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
0-1 Knapsack II
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Try to put items into the pack as many as possible, return the largest weight we can get in the knapsack.
public static int knapsack(int s, int[] weights, int index) {
if (s == 0 || index == weights.length) {
return 0;
}
if (weights[index] > s) {
return knapsack(s, weights, index+1);
}
return Math.max(knapsack(s, weights, index+1),
weights[index] + knapsack(s-weights[index], weights, index+1));
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Generate Parenthesis
Given n pairs of parentheses, write a function to generate all combinations of well-formed parentheses.
For example:
Given n = 3,
return ["((()))", "(()())", "(())()", "()(())", "()()()" ]
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Generate Parenthesis
Given n pairs of parentheses, write a function to generate all combinations of well-formed parentheses.
For example:
Given n = 3,
return ["((()))", "(()())", "(())()", "()(())", "()()()" ]
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
- n parenthesis => n left + n right => 2*n positions.
- Each time, one left or right should be chosen.
- We can always pick left.
- If there are more right remained, we can put right.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Generate Parenthesis
Given n pairs of parentheses, write a function to generate all combinations of well-formed parentheses.
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public ArrayList<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
ArrayList<String> results = new ArrayList<>();
generateParenthesis(results, "", n, n);
return results;
}
public void generateParenthesis(ArrayList<String> results, String prefix,
int left, int right) {
if (left == 0 && right == 0) {
results.add(prefix);
return;
}
if (left > 0) {
generateParenthesis(results, prefix+"(", left-1, right);
}
if (left < right) {
generateParenthesis(results, prefix+")", left, right-1);
}
}Permutation (Leetcode 46)
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible permutations.
For example,
[1,2,3] have the following permutations:
[1,2,3], [1,3,2], [2,1,3], [2,3,1], [3,1,2], and [3,2,1].
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
// Implement this method.
}
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible permutations.
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> permute(int[] num) {
ArrayList<Integer> numList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Arrays.sort(num);
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++)
numList.add(num[i]);
return permute(new ArrayList<Integer>(), numList);
}
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> permute(ArrayList<Integer> cur,
ArrayList<Integer> num) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> results =
new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if (num.size() == 0) {
results.add(cur);
return results;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.size(); i++) {
ArrayList<Integer> newCur = new ArrayList<Integer>(cur);
newCur.add(num.get(i));
ArrayList<Integer> newNum = new ArrayList<Integer>(num);
newNum.remove(i);
results.addAll(permute(newCur, newNum));
}
return results;
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Permutation (Leetcode 46)
Permutation (Leetcode 46)
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible permutations.
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] num) {
Arrays.sort(num);
return permute(new ArrayList<Integer>(), num);
}
public List<List<Integer>> permute(ArrayList<Integer> cur, int[] num) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if (cur.size() == num.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(cur));
return results;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
if (cur.contains(num[i])) {
continue;
}
cur.add(num[i]);
results.addAll(permute(cur, num));
cur.remove(cur.size() - 1);
}
return results;
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Permutation (Leetcode 46)
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible permutations.
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] num) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
Arrays.sort(num);
permute(results, new ArrayList<Integer>(), num);
return results;
}
public void permute(List<List<Integer>> results,
ArrayList<Integer> cur, int[] num) {
if (cur.size() == num.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(cur));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
if (cur.contains(num[i])) {
continue;
}
cur.add(num[i]);
permute(results, cur, num);
cur.remove(cur.size() - 1);
}
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Permutation (Leetcode 46)
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible permutations.
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] num) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
Arrays.sort(num);
permute(results, num, 0);
return results;
}
public void permute(List<List<Integer>> results, int[] num, int index) {
if (index == num.length) {
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
result.add(num[i]);
}
results.add(result);
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < num.length; i++) {
swap(num, index, i);
permute(results, num, index + 1);
swap(num, index, i);
}
}
public void swap(int[] num, int i, int j) {
int temp = num[i];
num[i] = num[j];
num[j] = temp;
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Permutation II (Leetcode 47)
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible permutations.
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] num) {
ArrayList<Integer> numList = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(num);
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++)
numList.add(num[i]);
return permute(new ArrayList<Integer>(), numList);
}
public List<List<Integer>> permute(
ArrayList<Integer> cur, ArrayList<Integer> num) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
if (num.size() == 0) {
results.add(cur);
return results;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.size(); i++) {
if (i > 0 && num.get(i) == num.get(i-1))
continue;
ArrayList<Integer> newCur = new ArrayList<>(cur);
newCur.add(num.get(i));
ArrayList<Integer> newNum = new ArrayList<>(num);
newNum.remove(i);
results.addAll(permute(newCur, newNum));
}
return results;
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Permutation II (Leetcode 47)
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible permutations.
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] num) {
Arrays.sort(num);
boolean[] visited = new boolean[num.length];
for (int i = 0; i < visited.length; i++) {
visited[i] = false;
}
return permute(new ArrayList<Integer>(), num, visited);
}
public List<List<Integer>> permute(ArrayList<Integer> cur, int[] num, boolean[] visited) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
if (cur.size() == num.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(cur));
return results;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
if (visited[i] || (i > 0 && num[i] == num[i-1] && !visited[i-1])) {
continue;
}
visited[i] = true;
cur.add(num[i]);
results.addAll(permute(cur, num, visited));
cur.remove(cur.size() - 1);
visited[i] = false;
}
return results;
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Combination
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible combinations.
For example,
[2, 6, 8] have the following permutations:
[], [2], [6], [8], [2, 6], [2, 8], [6, 8], [2, 6, 8].
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int[] nums) {
// Implement this method.
}
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Combination
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible combinations.
public static List<List<Integer>> combine(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
combination(results, nums, 0, new ArrayList<Integer>());
return results;
}
public static void combination(List<List<Integer>> results,
int[] nums, int index, ArrayList<Integer> items) {
if (index == nums.length) {
results.add(items);
return;
}
ArrayList<Integer> newItems1 = new ArrayList<Integer>(items);
combination(results, nums, index+1, newItems1);
ArrayList<Integer> newItems2 = new ArrayList<Integer>(items);
newItems2.add(nums[index]);
combination(results, nums, index+1, newItems2);
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Combination
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible combinations.
public static List<List<Integer>> combine(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
combination(results, nums, 0, new ArrayList<Integer>());
return results;
}
public static void combination(List<List<Integer>> results,
int[] nums, int index, ArrayList<Integer> items) {
if (index == nums.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(items));
return;
}
combination(results, nums, index+1, items);
items.add(nums[index]);
combination(results, nums, index+1, items);
items.remove(items.size()-1);
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Combination
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible combinations.
public static List<List<Integer>> combine(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
combination(results, nums, 0, new ArrayList<Integer>());
return results;
}
public static void combination(List<List<Integer>> results,
int[] nums, int index,
ArrayList<Integer> items) {
if (index == nums.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(items));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < nums.length; i++) {
items.add(nums[i]);
combination(results, nums, i+1, items);
items.remove(items.size()-1);
}
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
The empty set is missing.
-There will be at least one element in the "items"
Combination
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible combinations.
public static List<List<Integer>> combine(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
combination(results, nums, 0, new ArrayList<Integer>());
return results;
}
public static void combination(List<List<Integer>> results,
int[] nums, int index,
ArrayList<Integer> items) {
if (index == nums.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(items));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i <= nums.length; i++) {
if (i == nums.length) {
combination(results, nums, i, items);
return;
}
items.add(nums[i]);
combination(results, nums, i+1, items);
items.remove(items.size()-1);
}
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
This adds an empty set.
Combination
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible combinations.
public static List<List<Integer>> combine(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
combination(results, nums, 0, new ArrayList<Integer>());
return results;
}
public static void combination(List<List<Integer>> results,
int[] nums, int index,
ArrayList<Integer> items) {
if (index == nums.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(items));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < nums.length; i++) {
items.add(nums[i]);
combination(results, nums, i+1, items);
items.remove(items.size()-1);
}
combination(results, nums, nums.length, items);
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
This is the same as 89.4
Summary
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Recursion
subproblem
-> problem
subproblem-1 ||
subproblem-2 ||
subproblem-N
-> problem
subproblem-1 &&
subproblem-2 &&
subproblem-N
-> problem
Factorial,
Sum of LinkedList,
Remove Linked List Element, etc.
Maze,
Sudoku,
Most DFS problems, etc.
Knapsack
Permutations,
Combinations,
Eight Queen,
kSum, etc.
Recursion & Two Pointers
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Quicksort an array
- Pick one number from the array and do "partition sort"
- The left part will always be smaller than pivot
- The right part will always be larger than pivot
- Quicksort the left part
- Quicksort the right part
Recursion & Two Pointers
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Quicksort an array
| 5 | 7 | 3 | 2 | 6 |
|---|
Recursion & Two Pointers
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Quicksort an array
| 7 | 3 | 2 | 6 |
|---|
pivot = 5
Recursion & Two Pointers
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Quicksort an array
| 7 | 3 | 2 | 6 |
|---|
pivot = 5
Recursion & Two Pointers
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Quicksort an array
| 2 | 7 | 3 | 6 |
|---|
pivot = 5
Recursion & Two Pointers
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Quicksort an array
| 2 | 7 | 3 | 6 |
|---|
pivot = 5
Recursion & Two Pointers
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Quicksort an array
| 2 | 3 | 7 | 6 |
|---|
pivot = 5
Recursion & Two Pointers
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Quicksort an array
| 2 | 3 | 7 | 6 |
|---|
pivot = 5
Recursion & Two Pointers
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Quicksort an array
| 2 | 3 | 7 | 6 |
|---|
pivot = 5
Recursion & Two Pointers
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Quicksort an array
| 2 | 3 | 7 | 6 |
|---|
pivot = 5
Recursion & Two Pointers
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Quicksort an array
| 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 6 |
|---|
pivot = 5
Recursion & Two Pointers
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Quicksort an array
Recursion & Two Pointers
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Quicksort an array
public static void quicksort(int[] nums, int begin, int end) {
if (begin >= end) {
return;
}
int pivotPostion = partition(nums, begin, end);
quicksort(nums, begin, pivotPostion - 1);
quicksort(nums, pivotPostion + 1, end);
}
public static int partition(int[] nums, int begin, int end) {
int pivot = nums[begin];
while (begin < end) {
while (begin < end && nums[end] >= pivot) {
end--;
}
nums[begin] = nums[end];
while (begin < end && nums[begin] <= pivot) {
begin++;
}
nums[end] = nums[begin];
}
nums[begin] = pivot;
return begin;
}Recursion & LinkedList
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Reverse a linked list
- Reverse head.next, mark as newHead
- newTail.next = head
- return newHead;
Recursion & LinkedList
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Reverse a linked list
- Reverse head.next, mark as newHead
- newTail.next = head
- return newHead;
1
2
3
4
Recursion & LinkedList
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Reverse a linked list
- Reverse head.next, mark as newHead
- newTail.next = head
- return newHead;
1
2
3
4
1
4
3
2
Recursion & LinkedList
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Reverse a linked list
- Reverse head.next, mark as newHead
- newTail.next = head
- return newHead;
1
2
3
4
1
4
3
2
1
4
3
2
Recursion & LinkedList
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Reverse a linked list
- Reverse head.next, mark as newHead
- newTail.next = head
- return newHead;
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Summary
- Recursion is a strategy.
- Always try to split a problem into sub-problems and solve the sub-problem first.
- If the solution is the same, then you can call the same method.
Homework
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Try to put items into the pack as many as possible, print out all the items that can get the largest weight. Each item can only get picked once.
public int[] knapsack(int s, int[] weights) {
// Please implement this method.
}
vector<int> knapsack(int s, vector<int> weights {
// Please implement this method.
}
0-1 Knapsack (Required)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Homework (Required)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Homework (Optional)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/