Stock
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock I
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock I
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i.
If you were only permitted to complete at most one transaction (ie, buy one and sell one share of the stock), design an algorithm to find the maximum profit.
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock I
Example 1:
Input: [7, 1, 5, 3, 6, 4] Output: 5 max. difference = 6-1 = 5 (not 7-1 = 6, as selling price needs to be larger than buying price)
Example 2:
Input: [7, 6, 4, 3, 1] Output: 0 In this case, no transaction is done, i.e. max profit = 0.
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock I
solution 1:
dp[i] means MaxProfit in [0,1,2...i]
dp[i + 1] = max{dp[i], prices[i] - minprice }
// minprice is the lowest price in [0,1,2 ...i]
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int minPrice = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int maxProfit = 0;
for(int p:prices) {
minPrice = Math.min(minPrice, p);
maxProfit = Math.max(p - minPrice, maxProfit);
}
return maxProfit;
}Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock I
solution 2:
make a difference array:
prices[1] - prices[0], prices[2] - prices[0].....
prices[n-1] - prices[n-2]
=> Maximum subarray
Maximum subarray
Find the contiguous subarray within an array (containing at least one number) which has the largest sum.
For example, given the array [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4],
the contiguous subarray [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum = 6.
maxSubArray(A, i) = maxSubArray(A,i-1)>0?maxSubArray(A,i-1):0 + A[i];
Maximum subarray
Find the contiguous subarray within an array (containing at least one number) which has the largest sum.
For example, given the array [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4],
the contiguous subarray [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum = 6.
public int maxSubArray(int[] A) {
int n = A.length;
int[] dp = new int[n];//dp[i] means the maximum subarray ending with A[i];
dp[0] = A[0];
int max = dp[0];
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
dp[i] = A[i] + (dp[i - 1] > 0 ? dp[i - 1] : 0);
max = Math.max(max, dp[i]);
}
return max;
}Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
You may complete as many transactions as you like (ie, buy one and sell one share of the stock multiple times).
However, you may not engage in multiple transactions at the same time (ie, you must sell the stock before you buy again).
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
Solution 1:
Find all increasing range , buy at lowest price and sell at highest price.
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int> &prices) {
int n = prices.size();
if(n <= 1)return 0;
int i = 0;
int res = 0;
while(i < n - 1)
{
int buy, sell;
//递减区间
while(i+1 < n && prices[i+1] < prices[i])i++;
buy = i++;
//递增区间
while(i < n && prices[i] >= prices[i-1])i++;
sell = i-1;
res += prices[sell] - prices[buy];
}
return res;
}
};Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
solution 2:
make a difference array:
prices[1] - prices[0], prices[2] - prices[0].....
prices[n-1] - prices[n-2]
=> Sum all positive element.
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int n = (int)prices.size();
int res = 0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
if(prices[i]>prices[i-1]){
res +=(prices[i]-prices[i-1]);
}
}
return res;
}
int maxProfit1(vector<int>& prices) {
int n = (int)prices.size();
int res =0;
for(int i =1;i<n;i++)
{
res += (prices[i]-prices[i-1]>0?prices[i]-prices[i-1]:0);
}
return res;
}
};Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
Design an algorithm to find the maximum profit. You may complete at most two transactions.
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
solution 1: divide array into two part, find the maxProfit in each part.
*two traversal
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int n = (int) prices.size();
if(n==0) return 0;
vector<int> prev(n,0);
vector<int> post(n,0);
//prev traversal
int minprice = prices[0];
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
minprice = min(prices[i],minprice);
prev[i] = max(prices[i]-minprice,prev[i-1]);
}
//post traversal
int maxprice = prices[n-1];
for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--){
maxprice = max(prices[i],maxprice);
post[i] = max(maxprice-prices[i],post[i+1]);
}
int res = 0;
for(int i=0; i<n;i++){
res = max(res,prev[i]+post[i]);
}
return res;
}
};Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
solution 2:
use four variables represent your profit after executing corresponding transaction
sell2, hold2, sell1, hold1
*one traversal
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
public class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int hold1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE, hold2 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int sell1 = 0, sell2 = 0;
for(int i:prices){
// The maximum if we've just sold 2nd stock so far.
sell2 = Math.max(sell2, hold2+i);
// The maximum if we've just buy 2nd stock so far.
hold2 = Math.max(hold2, release1-i);
// The maximum if we've just sold 1nd stock so far.
sell1 = Math.max(sell1, hold1+i);
// The maximum if we've just buy 1st stock so far.
hold1 = Math.max(hold1, -i);
}
return sell2;
}
}Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV
Design an algorithm to find the maximum profit. You may complete at most k transactions.
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV
solution:
use 2k variables represent your profit after executing corresponding transaction
sellk, holdk, .......sell2, hold2, sell1, hold1
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV
A simple case: == maxProfit2
2k > n // n is length of prices array
do as many operations as you can.
// Simple case.
if (k >= length / 2) {
int profit = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
profit += Math.max(prices[i] - prices[i - 1], 0);
}
return profit;
}Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV
Fill up a 2k * n form
| sell k | hold k | .... | sell 1 | hold1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV
Fill up a 2k form
int[] hold = new int[k + 1];
int[] sell = new int[k + 1];
Arrays.fill(hold, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
for (int price: prices) {
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
sell[i] = Math.max(sell[i], hold[i] + price);
hold[i] = Math.max(hold[i], sell[i - 1] - price);
}
}
public class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int k, int[] prices) {
int length = prices.length;
if (length < 2) return 0;
// Simple case.
if (k >= length / 2) {
int profit = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
profit += Math.max(prices[i] - prices[i - 1], 0);
}
return profit;
}
// Dynamic programming.
int[] hold = new int[k + 1];
int[] sell = new int[k + 1];
Arrays.fill(hold, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
for (int price: prices) {
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
sell[i] = Math.max(sell[i], hold[i] + price);
hold[i] = Math.max(hold[i], sell[i - 1] - price);
}
}
return sell[k];
}
}Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Cooldown
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Cooldown
Design an algorithm to find the maximum profit. You may complete as many transactions as you like (ie, buy one and sell one share of the stock multiple times) with the following restrictions:
- You may not engage in multiple transactions at the same time (ie, you must sell the stock before you buy again).
- After you sell your stock, you cannot buy stock on next day. (ie, cooldown 1 day)
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Cooldown
Example:
prices = [1, 2, 3, 0, 2] maxProfit = 3 transactions = [buy, sell, cooldown, buy, sell]
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Cooldown
solution 1:
//buy[i] means maxprofit when we buy stack at time i;
//sell[i] means maxprofit when we sell stack at time i;
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Cooldown
solution 1:
//buy[i] means maxprofit when we buy stack at time i;
// buy[i] = max(sell[i-2]-prices[i],buy[i-1]+prices[i-1]-prices[i])
//sell[i] means maxprofit when we sell stack at time i;
// sell[i] = max(buy[i-1]+prices[i],sell[i-1]-prices[i-1]+prices[i])
class Solution {
public:
//buy[i] means maxprofit when we buy stack at time i;
// buy[i] = max(sell[i-2]-prices[i],buy[i-1]+prices[i-1]-prices[i])
//sell[i] means maxprofit when we sell stack at time i;
// sell[i] = max(buy[i-1]+prices[i],sell[i-1]-prices[i-1]+prices[i])
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int n = (int)prices.size();
if(n==0)return 0;
vector<int> buy(n,0);
vector<int> sell(n,0);
buy[0] = -prices[0];
sell[0] = 0;
int res = 0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
sell[i] = max(buy[i-1]+prices[i],sell[i-1]-prices[i-1]+prices[i]);
res = max(res,sell[i]);
if(i==1){
buy[i] = -prices[i];
}
else{
buy[i] = max(sell[i-2]-prices[i],buy[i-1]+prices[i-1]-prices[i]);
}
}
return res;
}
};Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Cooldown
solution 2:
//buy[i] means Max profit till index i. The series of transaction is ending with a buy;
To make a decision whether to buy at i, we either take a rest, by just using the old decision at i - 1, or sell at/before i - 2, then buy at i, We cannot sell at i - 1, then buy at i, because of cooldown.
//sell[i] means Max profit till index i. The series of transaction is ending with a sell;
To make a decision whether to sell at i, we either take a rest, by just using the old decision at i - 1, or buy at/before i - 1, then sell at i.
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Cooldown
solution 2:
//buy[i] means Max profit till index i. The series of transaction is ending with a buy;
buy[i] = Math.max(buy[i - 1], sell[i - 2] - prices[i]);
//sell[i] means Max profit till index i. The series of transaction is ending with a sell;
sell[i] = Math.max(sell[i - 1], buy[i - 1] + prices[i]);
solution 2:
//buy[i] means Max profit till index i. The series of transaction is ending with a buy;
buy[i] = Math.max(buy[i - 1], sell[i - 2] - prices[i]);
//sell[i] means Max profit till index i. The series of transaction is ending with a sell;
sell[i] = Math.max(sell[i - 1], buy[i - 1] + prices[i]);
DP solution only depending on i - 1 and i - 2 can be optimized using O(1) space.
- Let b2, b1, b0 represent buy[i - 2], buy[i - 1], buy[i]
- Let s2, s1, s0 represent sell[i - 2], sell[i - 1], sell[i]
Then arrays turn into Fibonacci like recursion:
b0 = Math.max(b1, s2 - prices[i]);
s0 = Math.max(s1, b1 + prices[i]);
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if(prices == null || prices.length <= 1) return 0;
int b0 = -prices[0], b1 = b0;
int s0 = 0, s1 = 0, s2 = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
b0 = Math.max(b1, s2 - prices[i]);
s0 = Math.max(s1, b1 + prices[i]);
b1 = b0; s2 = s1; s1 = s0;
}
return s0;
}Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Cooldown
solution 3: State machine:
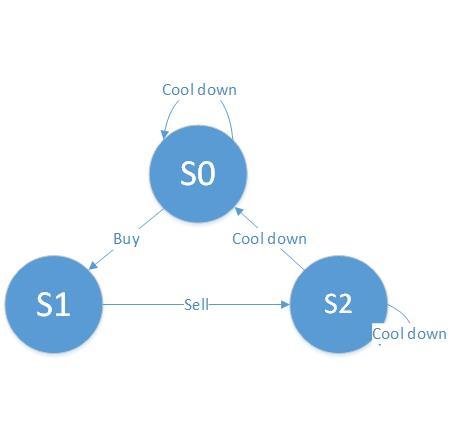
solution 3: State machine:

s0[i] = max(s0[i - 1], s2[i - 1]); // Stay at s0, or rest from s2
s1[i] = max(s1[i - 1], s0[i - 1] - prices[i]); // Stay at s1, or buy from s0
s2[i] = s1[i - 1] + prices[i]; // Only one way from s1
find the maximum of
s0[n] and s2[n]
Base case:
s0[0] = 0; // At the start, you don't have any stock if you just rest
s1[0] = -prices[0]; // After buy, you should have -prices[0] profit. Be positive!
s2[0] = INT_MIN; // Lower base case
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices){
if (prices.size() <= 1) return 0;
vector<int> s0(prices.size(), 0);
vector<int> s1(prices.size(), 0);
vector<int> s2(prices.size(), 0);
s1[0] = -prices[0];
s0[0] = 0;
s2[0] = INT_MIN;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.size(); i++) {
s0[i] = max(s0[i - 1], s2[i - 1]);
s1[i] = max(s1[i - 1], s0[i - 1] - prices[i]);
s2[i] = s1[i - 1] + prices[i];
}
return max(s0[prices.size() - 1], s2[prices.size() - 1]);
}
};int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int sold = 0; //s2
int hold = Integer.MIN_VALUE; //s1
int rest = 0; //s0
for (int i=0; i<prices.length; ++i)
{
int prvSold = sold;
sold = hold + prices[i];
hold = Math.max(hold, rest-prices[i]);
rest = Math.max(rest, prvSold);
}
return Math.max(sold, rest);
}Design a stock api
Design a stock api
class System { // assume time being used is unique
public:
int getMax() {} //O(1)
int getMin() {} //O(1)
int getRecent() {} //O(1)
void add(long time, int price) {}
void update(long time, int price) {}
void remove(long time) {}
private:
};
Design an array api
Design a array api
Get, Set, SetAll // All operation is O(1)
Get(4) -> get element at index 4
Set(index, value);
SetAll(5) -> set all element to 5
class Array{
private:
public:
Status Get(int index){}
void Set(int index, int val){}
void SetAll(int val){}
};
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Homework
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/