Aproximación Centrada en la Arquitectura y Basada en Ontologías para la Interoperabilidad entre Dominios de los Sistemas de Información para el cuidado de la Diabetes
PhD. Gustavo Andrés Uribe Gómez
PhD. Diego Mauricio López
PhD. Bernd Blobel


University of Regensburg

Introduction
1
El Reto de la Interoperabilidad
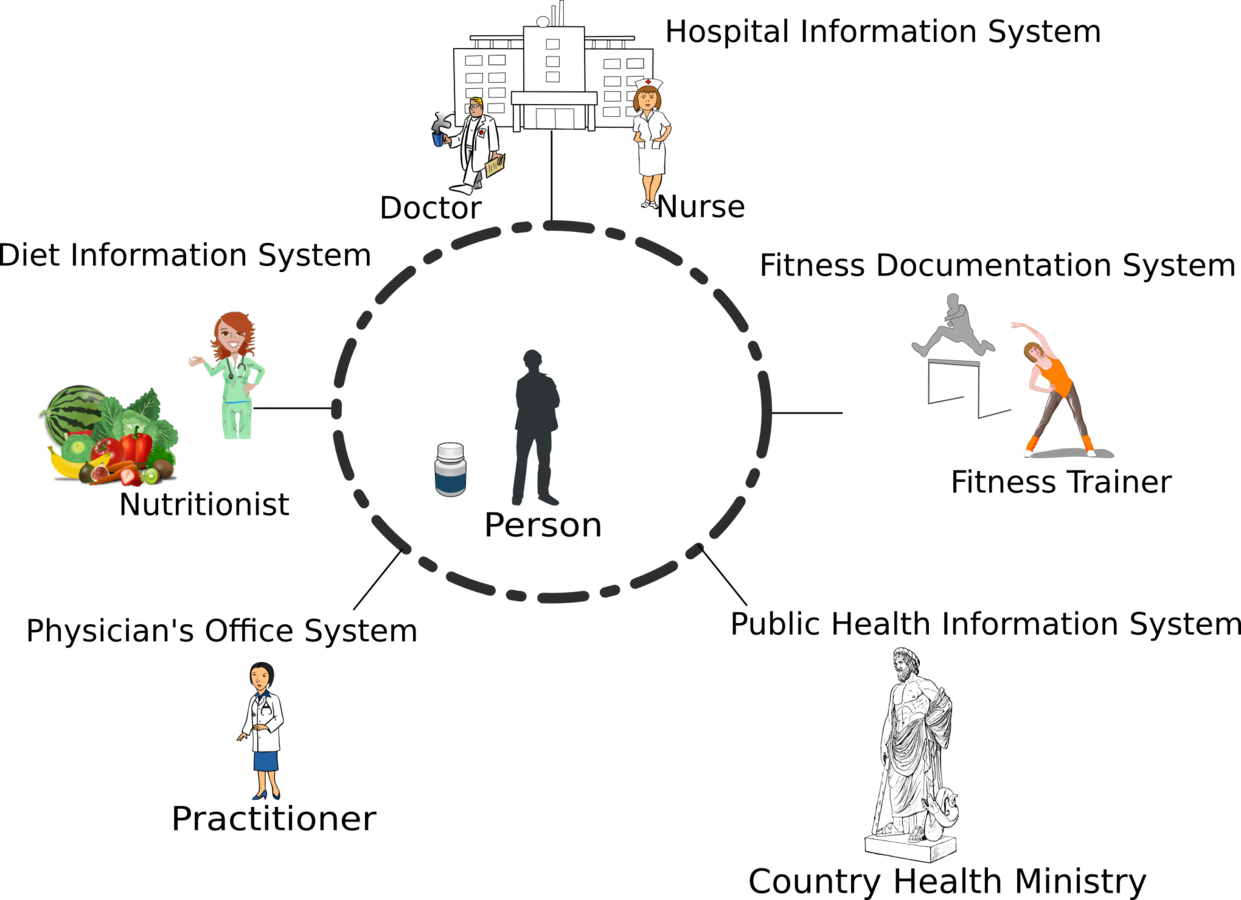
2

Trabajos Relacionados

EHR, PHR and DSS
interoperability
(Booker and Trabulsi, 2009; Fahey, 2012; Osborn et al., 2010; Quinn et al., 2011; Schnipper et al., 2012; Wake and Cunningham, 2013; Santana, 2013)
3
Trabajos Relacionados

Semantic Interoperability
(Chungoora et al., 2013; Heywood et al., 2011; Sonsilphong and Arch-int, 2013; Tessier, 2011)
3
Trabajos Relacionados

Ontology-based systems
(Tessier, 2013; Archer et al. 2011; Sonsilphong et al., 2013, Snyder et al. 2013)
3
Trabajos Relacionados

Architecture-centric approach
(Oemig F and Blobel B., 2011; Health Level 7 International, 2013; Blobel B., Goossen W, Brochhausen M., 2012; Lopez DM and Blobel B, 2009)
3
Trabajos Relacionados
No existe una propuesta que incluya todos los siguientes elementso:
- Consideración de la interoperabilidad entre dominios
- Consideración de la arquitectura del sistema
- Adherencia a politicas y guías
- Soporte a la toma de decisiones
- Manejo de conocimiento
- Formalización de conocimiento
- Capacidad de realizar inferencia
- Flexible y adaptable
- A nuevos actores
- A nuevas reglas o nuevo conocimiento
4
Metodología
7
Generic Component Model - GCM

(B.Blobel, 2012)
8
Generic Component Model - GCM

(B.Blobel, 2012)
8
Generic Component Model - GCM

(B.Blobel, 2012)
8
Generic Component Model - GCM

(B.Blobel, 2012)
RM - ODP
8
Modelado de Procesos de Negocio

Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN)
- Notación gráfica
- Permite representar elementos independientes a la computación
- Estandarizado
9
Lenguajes Formales para Describir Reglas y Políticas
SPARQL Inference Notation (SPIN)
- Compatible con OWL y RDF
- Estandarizado (Basado en RDF)
- Provee un entorno integrado de desarrollo

10
Arquitectura Genérica para un Sistema Adaptativo, Interoperable e Inteligente para el Cuidado de la Diabetes Mellitus Tipo 2
Uribe, G. A., B. Blobel, D. M. López, and S. Schulz. "A generic architecture for an adaptive, interoperable and intelligent type 2 diabetes mellitus care system." Studies in health technology and informatics 211 (2015): 121. Categoria Colciencias A2
12
Modelo Genérico

13
Representación del Dominio Médico


14-1
Representación del Dominio de las Políticas


14-2
Representación del Dominio de los Recursos


14-3
Representación de las Relaciones Entre Dominios


15-1
Representación del Dominio Médico en UML


15-2
Representación del Dominio de Política en UML


15-3
Representación del Dominio de Recursos en UML


Representación Ontológica


16

Descripción de los Procesos


17
Descripción de los Procesos - Nivel de Servicios


18-1
Descripción de Procesos - Nivel de Disciplinas


18-2
Descripción de Procesos - Nivel de Tareas

18-3

Especializando Arquitecturas para Casos de Uso en el Cuidado de la Diabetes Tipo 2 con un Enfoque en el Manejo de Procesos
Uribe, G. A., B. Blobel, D. M. López, and A. A. Ruiz. "Specializing architectures for the type 2 diabetes mellitus care use cases with a focus on process management." Studies in health technology and informatics 211 (2015): 132. Categoría Colciencias A2.
19
Selección del Caso de Uso

Lifestyle intervention
Pharmacological intervention
20
Dominio Médico en el GCM


21-1
Dominio de Políticas en GCM


21-2
Dominio de Recursos en GCM


21-3
Relaciones Entre Dominios


22-1
Dominio Medico en UML


22-2
Dominio de Políticas


22-3
Dominio de Recursos


Disciplinas en el Control Glucémico


23-1
Servicio de Observación Médica


23-2
Proceso de Examinación Médica


23-3
Alerta por Hiperglucemia
CONSTRUCT {
?id btl2:isPartOf ?patientLife .
?id btl2:hasCondition ?id .
?id a dm2co:Hyperglycemia .
?id a dm2co:MedicalAlert .
?id rdfs:label ?cause_type_en .
?id rdfs:label ?cause_type_es .
?this btl2:represents ?id .
}
WHERE {
?patient btl2:isBearerOf ?blood_glucose .
?patient btl2:hasLife ?patientLife .
?this btl2:represents ?blood_glucose .
?blood_glucose a dm2co:BloodGlucoseConcentration .
?this dm2co:hasValueIn_mg_dL ?value .
FILTER ((?value >= 200.0) && (?value < 300.0)) .
OPTIONAL {
?clonAlert a dm2co:MedicalAlert .
?this btl2:represents ?clonAlert .
} .
FILTER (!bound(?clonAlert)) .
BIND (STRLANG("hyperglycemia medical alert", "en") AS ?cause_type_en) .
BIND (STRLANG("alerta médica por hiperglucemia", "es") AS ?cause_type_es) .
BIND (IRI(fn:concat("http://purl.org/unicauca/dm2co#", STRUUID())) AS ?id) .
}
24-1
Política de Seguridad del Paciente
# if physical examination is planned then handwashing is planned before
CONSTRUCT {
?this btl2:hasPart _:b0 .
_:b0 a bpmn:SequenceFlow .
_:b0 btl2:hasComponentPart _:b1 .
_:b1 a bpmn:SequenceFlow_Target .
_:b1 btl2:represents ?physical_examination_plan .
_:b0 btl2:hasComponentPart _:b2 .
_:b2 a bpmn:SequenceFlow_Source .
_:b2 btl2:represents _:b3 .
_:b3 a dm2co:HandwashingPlan .
}
WHERE {
?this btl2:hasPart ?physical_examination_plan .
?physical_examination_plan a dm2co:PhysicalExaminationPlan .
}
24-2
Implementación
25
Métodos de Implementación

MDA
- Lógica hard-coded
- Semántica débil
- Transformaciones dependientes a modelos
+ Modelos independientes a la computación
+ Modelado de comportamiento
25-1
Métodos de Implementación


Web Semántica
- Dificultad para modelar el comportamiento
+ Modelos independientes de la computación
+ Capacidades de inferencia
26-2
Métodos de Implementación



Hibrido
+ Capacidades de inferencia
+ Modelos independientes a la computación
+ Modelado de comportamiento
+ Aproximación centrada en la arquitectura
26-3
Proceso de Implementación


27
Vista Empresarial


28
Vista de Información
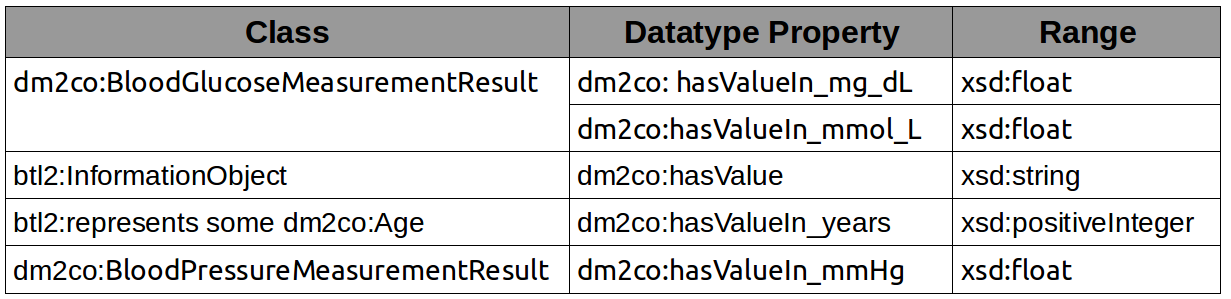

29
Vista Computacional

- Technical, Structural and Syntactical
- Semantic
- Organizational/Service
(Blobel [changed])
30
Vista Computacional


31
Vista Computacional


32
Vista de Ingeniería


33
Vista de Tecnología


34
Escenario de Prueba

35
Capturas

36
Capturas
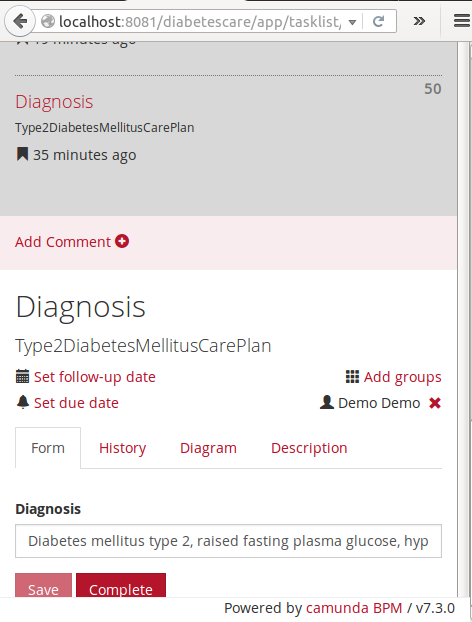
Evaluación
37
Experimento Piloto
-
Controla la ejecución de los procesos de salud acorde las políticas y guías médicas nacionales.
-
Soporta los actores en los procesos de toma de decisiones
-
Mapea la información considerando las cualidades heterogéneas de los actores.
El software provee interoperabilidad en al menos estas maneras:
38
Diseño Experimento Piloto

39
Experimento Piloto - Hipotesis
The efficiency of the system's recommendation, measured through the F-measure, is higher than 0.71 using as gold standard the suggestions provided by an internist.
The threshold of 0.71 corresponds with the F-measure average of the algorithms C4.5 and CART evaluated for the diagnosis of diabetes
D. Senthil Kumar, G. Sathyadevi, and S. Sivanesh, “Decision Support System for Medical Diagnosis Using Data Mining,” International Journal of Computer Science Issues 8, no. 3 (2011): 147–53.
40
Resultados

41
Resultados

42
Resultados

43
Resultados
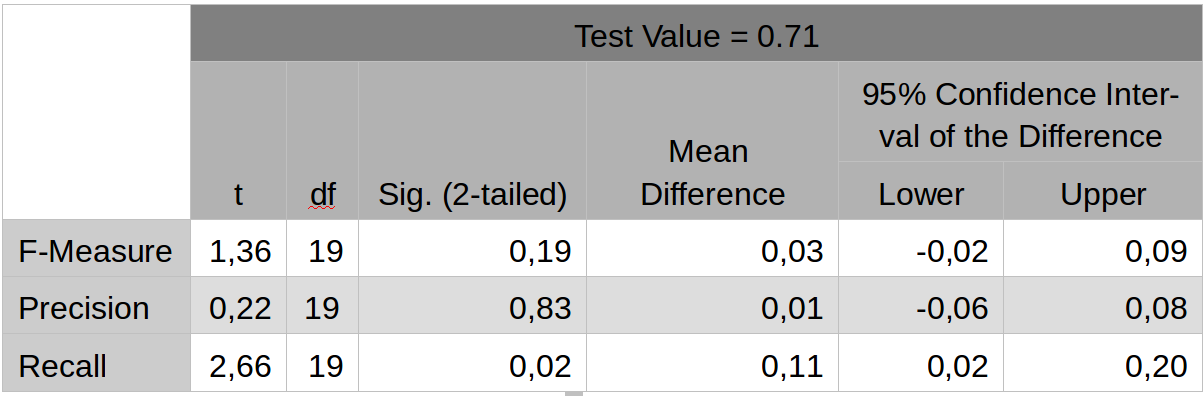
44
Resultados

45
Resultados

46
Conclusions
-
Usar el GCM facilita la constrcción de la arquitectura de un sistema
-
El uso de ontologías de nivel superior y de ontologías estandarizadas facilita la armonización entre dominios.
-
La metodología usada facilita la reusabilidad de componentes.
- La metodología permite diseñar sistemas que usan el conocimiento de expertos, para sustituirlos o asistirlos.
50
Trabajo Futuro
51
Trabajo Futuro
- Mejorar la evaluación
- Implementar el mapeo de los modelos de información
- Implementar la transformación automática de lenguajes
- Automatizar la composición de planes y el descubrimiento de servicios
- Desarrollar un framework para el método propuesto
52
¡¡Gracias!!
¿¿Preguntas??