Elasticsearch: Indexing
Han Yi
April 3, 2018
Concept of Near Real Time
- New index can only be searchable after a small delay (1s by default)
- Set refresh=true in indexing URL can achieve real-time searching
- Refresh is a very costly operation
- Most scenarios don't ask real-time search
- Interval can be temporarily disabled to be set to -1 for more efficient bulk indexing
PUT products/doc/_settings
{
"index": {
"refresh_interval": "30s"
}
}Beyond CRUD: Document Updating
- Entire update
- PUT products/doc/1
- Partial update
- POST products/doc/1/_update
- Scripted update (Under partial update)
- {"script": "ctx._source.qty+=1"}
- Lucene segments is immutable
- Process of update
- Soft delete old documents
- Create & Reindex new documents
- Merge segments
- Delete old segments

Beyond CRUD: Updating Performance
- Due to complicated operations behind updating, it may cause conflict when concurrency happens
- Elasticsearch uses "Version" field to resolve conflict issue
-
Use retry_on_conflict in URL can set retry times for version conflict
Operation 1
Operation 2
Get document
Soft delete
Reindex
Version 4
Timeline
Version 4
Version 4
Version 5
❌
Beyond CRUD: Concurrency
Primary and Replica Shards
- Coordinating node will forward request to any node who owns the primary shard
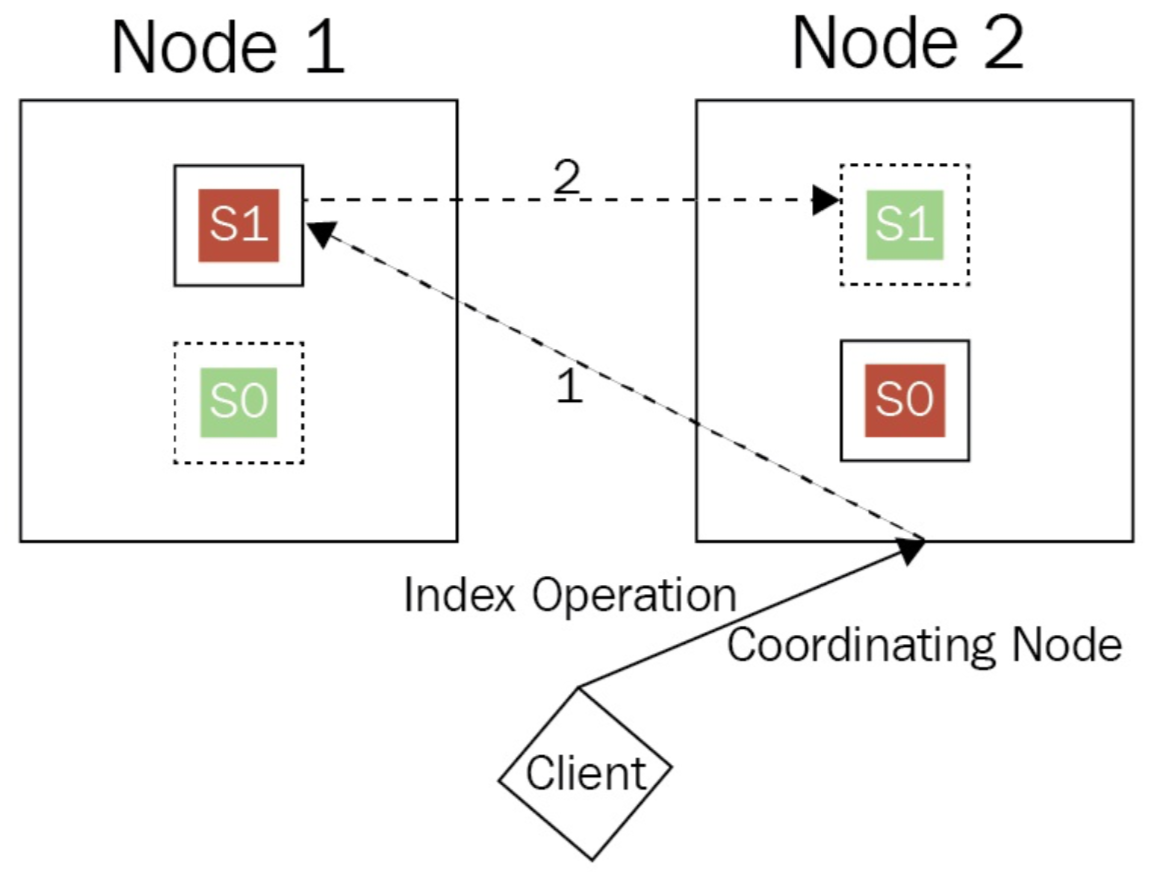
Primary and Replica Shards
- Primary preference for Query
- Use preference=_primary in URL, will only query on primary shards
- Use preference=_primary_first in URL, will first query on primary shards, then replica if primary is not available
Primary and Replica Shards
- Config for replica shards
- Number of replica shards can be changed on the fly
- Usually change it to 0 when bulk index and change back once done
PUT products/_settings
{
"index": {
"number_of_replicas": 0
}
}Translog
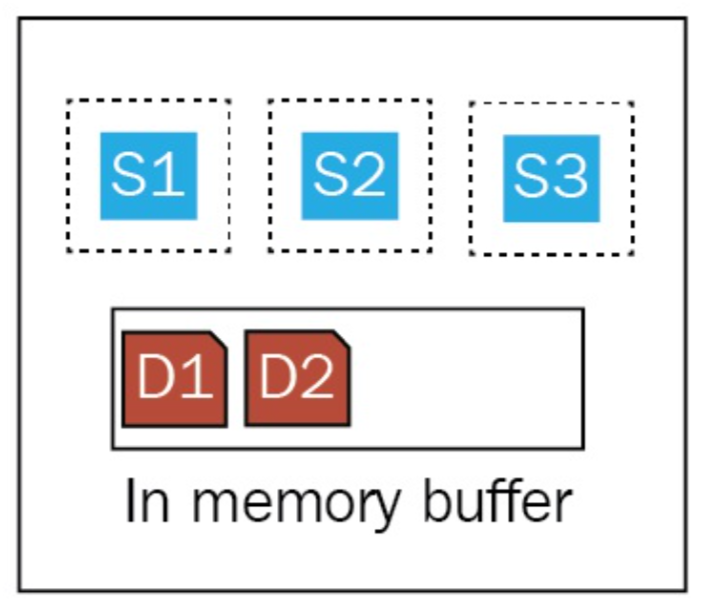
- Segment write does not write to disk directly (because of in-memory file system cache)
- Lucene commit writes segments to disk once certain conditions met
- Elasticsearch owns translog by itself
- "acknowledge" means translog created
- Existing translog will replay once system
restart due to unexpected events
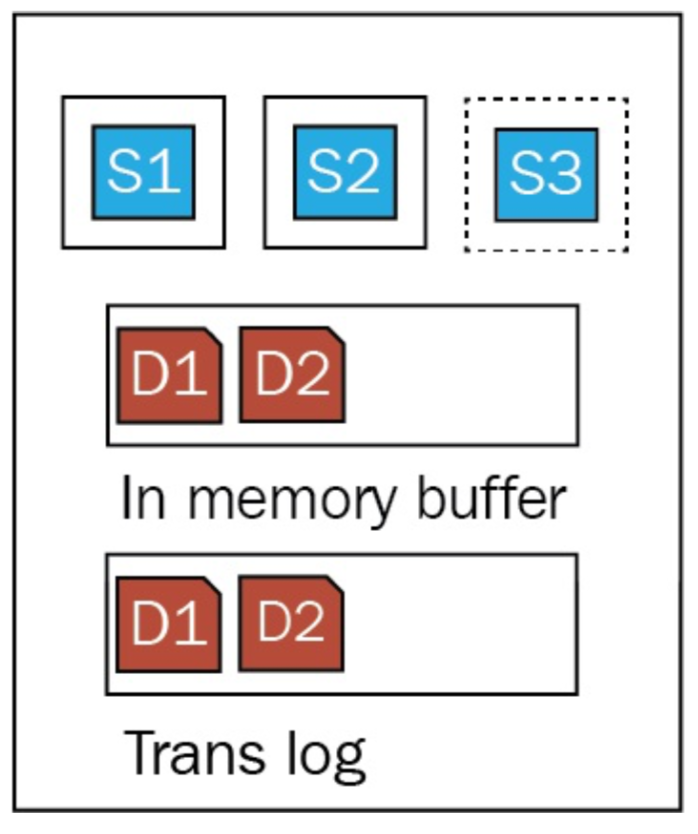
Performance of Translog
- Bulk operations may cause performance issue due to translog
- Translog can be switched between "request" or "async"
- index.translog.durability is an index setting for translog flush mode
- "request" will return response after translog is persisted
- "async" can return immediately, and the system will flush translog every index.translog.sync_interval seconds
- If you are retrieving the document using id, Elasticsearch will look at translog so there is no delay compared to full-text query
Indexing Errors
- Node/Shard errorsssssssssss
- Serialization/Mapping errors
- Thread pool rejection errors
{
"_index": "prdts",
"_type": "doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1
}